Protein production in transgenic alfalfa plants
A transgenic alfalfa, transgenic technology, applied in the direction of anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, plant products, genetic engineering, etc., can solve problems such as infeasibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] To exemplify the usefulness of alfalfa in expressing proteins, including multimeric proteins such as mAbs, a high affinity mAb (C5 -1). When tested with erythrocytes weakly sensitized with blood group antibodies, the C5-1 mAb gave reactivity similar to that of commercial rabbit polyclonal reagents. Integration and expression of transgene in alfalfa
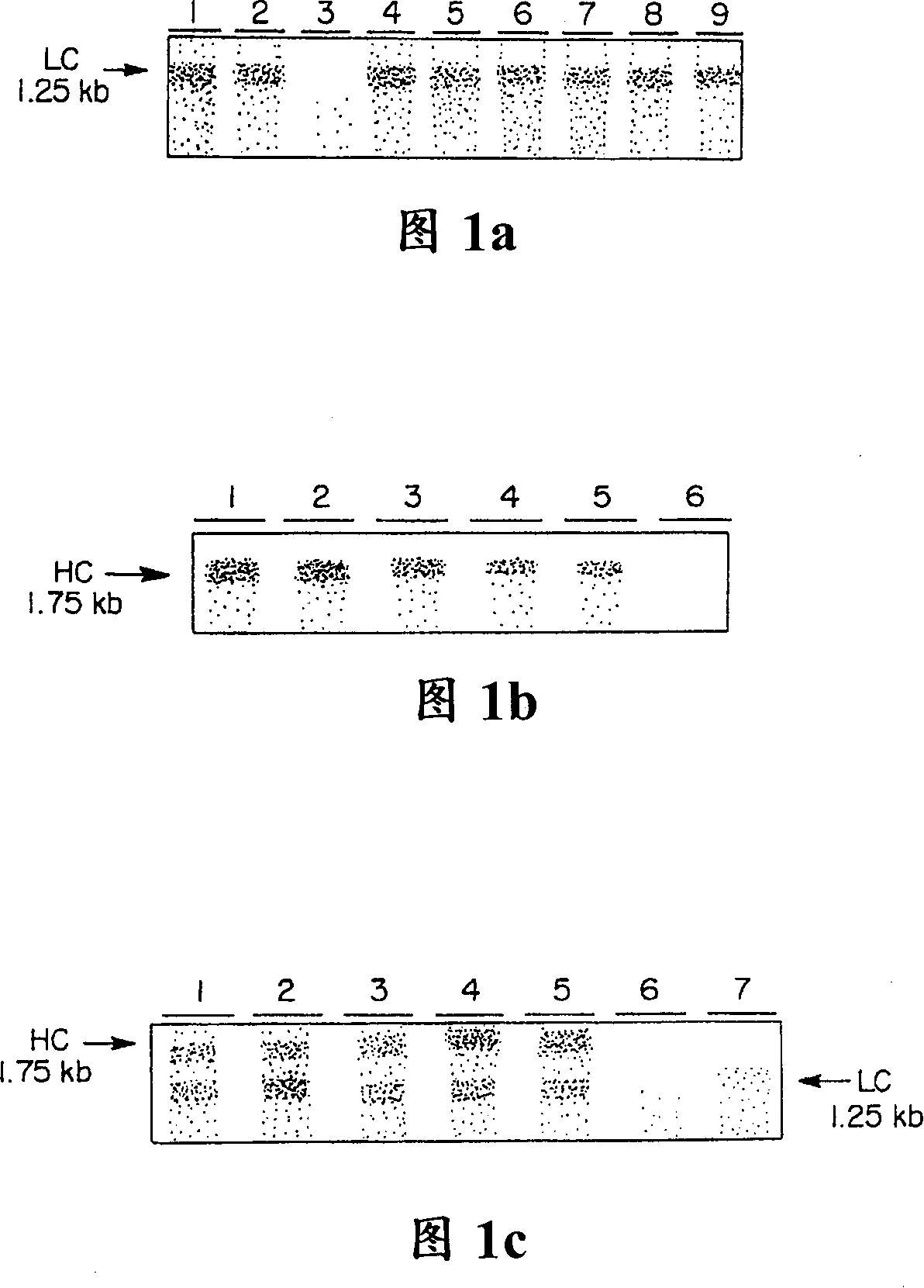
[0090] The cDNAs encoding the C5-1 light and heavy chains were transferred into alfalfa plants following the protocol of Desgagnes et al. (1995). 15 plants and 25 plants of κ chain and γ chain were obtained respectively. The mRNA levels of kappa chain and gamma chain were monitored by RNA hybridization. The probe specifically hybridized to approximately 1.25 kbp kappa chain mRNA (Fig. 1A) and 1.75 kbp gamma chain mRNA (Fig. 1B). The alfalfa-derived mRNA was approximately 250 bp longer than the murine cDNA, indicating that in both cases the polyadenylation signal of gene 7 was used. Among the 29 F1 plants analyzed, 7 we...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Example 3 Produced in alfalfa and the stability of the transgenic protein extracted therefrom
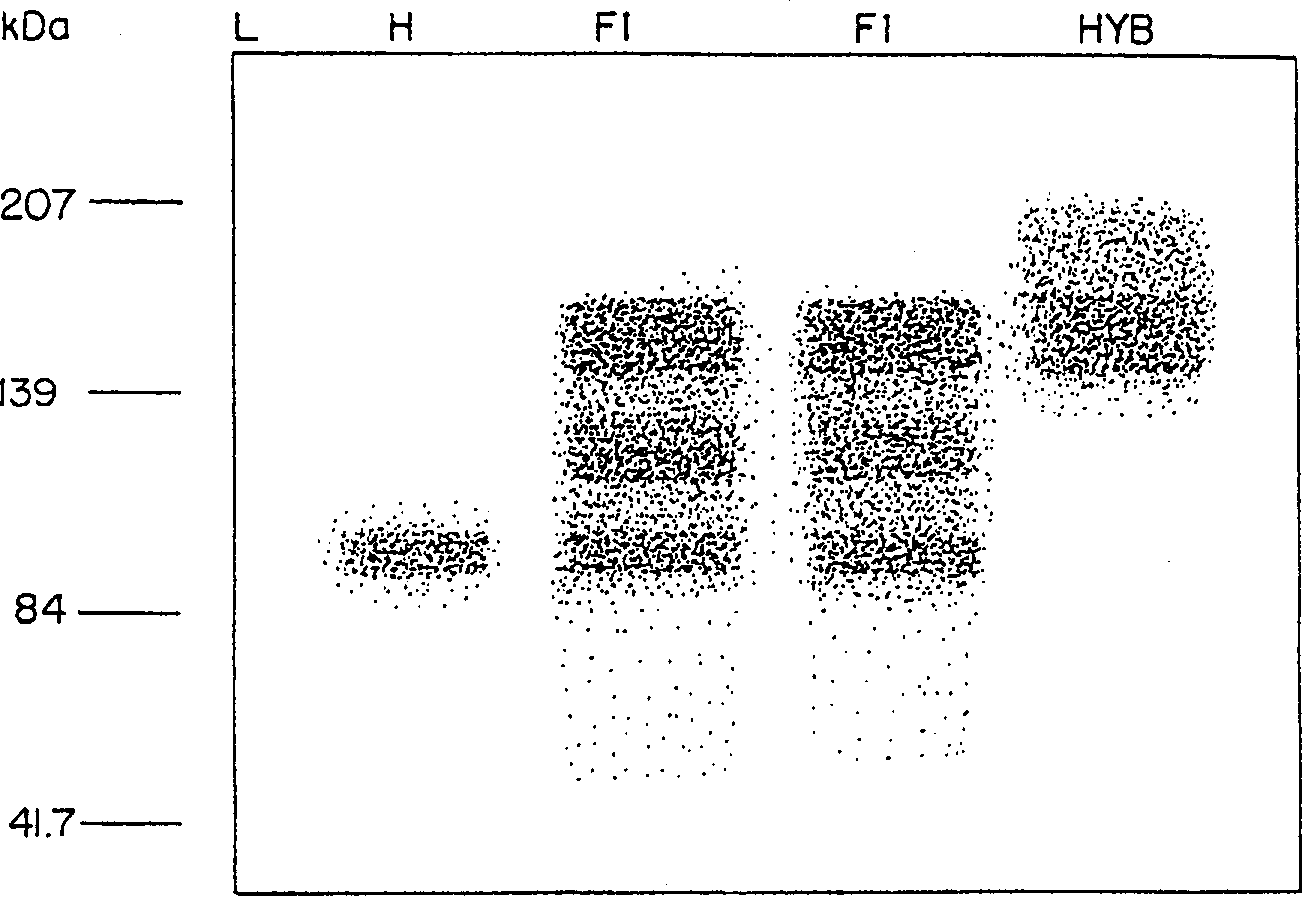
[0095]Proteolysis of recombinant IgG has been shown to occur in Nicotiana tabacum and Arabidopsis thaliana (Hiatt et al., 1989; Ma et al. 1994). Although non-truncated IgG is synthesized in plants with a signal peptide that facilitates targeting to the inert extracellular matrix (De Wilde et al. 1996), it has been observed that IgG can be degraded by endogenous proteases upon extraction ( Hiatt et al. (1989), During et al. (1990), Ma et al. (1995), Ma and Hein (1995), Schouten (1996)). Since the present invention concerns the preparation of monomeric or multimeric proteins such as mAb C5-1 in alfalfa, the stability of such preparations was examined. 1) Protein stability in alfalfa extract compared to tobacco extract
[0096] To establish whether the protein was stable in crude extracts of alfalfa tissue, plant-derived or hybridoma-derived C5-1 were co-extracted in water in ...
Embodiment 5
[0111] The large-scale purification of embodiment 5 plant C5-1
[0112] 300 g of plant material were homogenized in 1.2 L of extraction buffer, pH 9.0, containing 50 mM borate and 4M NaCl. The homogenate was clarified by filtration on cheesecloth. The homogenate was then directly loaded by upflow onto an expanded bed of Streamline rProtein A matrix (Pharmacia). Samples were loaded at 4°C at a rate of 7ml / min. The column was washed with 250 ml extraction buffer and eluted with 50 mM sodium citrate, 50 mM sodium phosphate and 300 mM NaCl pH 3.0. The fraction (1.5 ml) was recovered and immediately neutralized with 100 µl of 1.5M Tris pH 8.8.
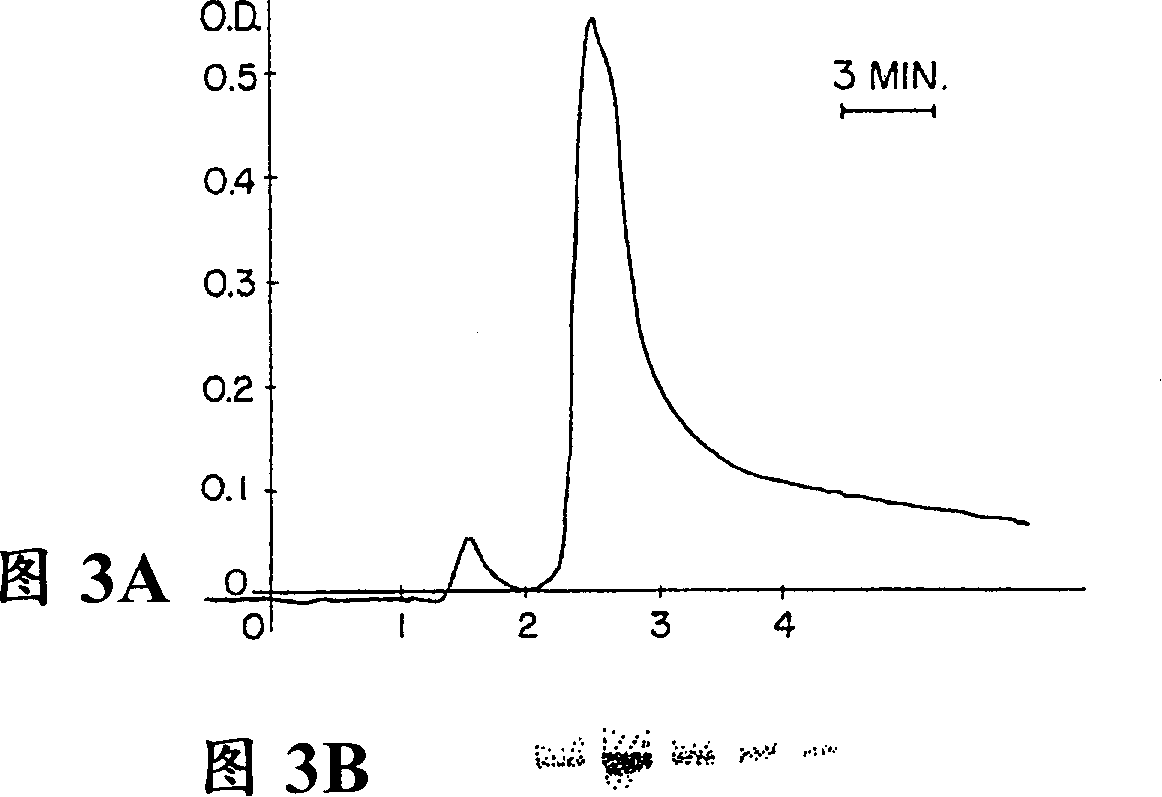
[0113] Selective expanded bed adsorption (STREAMLINE TM r Protein A), allowing the loading of partially clarified colloidal material-containing plant extracts at high flow rates. Using this technique, plant C5-1 was purified from non-clarified plant crude extracts, and the purified plant C5-1 was visualized as a single peptide by Coom...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com