Mammalian-derived peptides for the treatment of microbial infection
A mammalian, antimicrobial technique for use in the field of treating microbial infections in mammals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
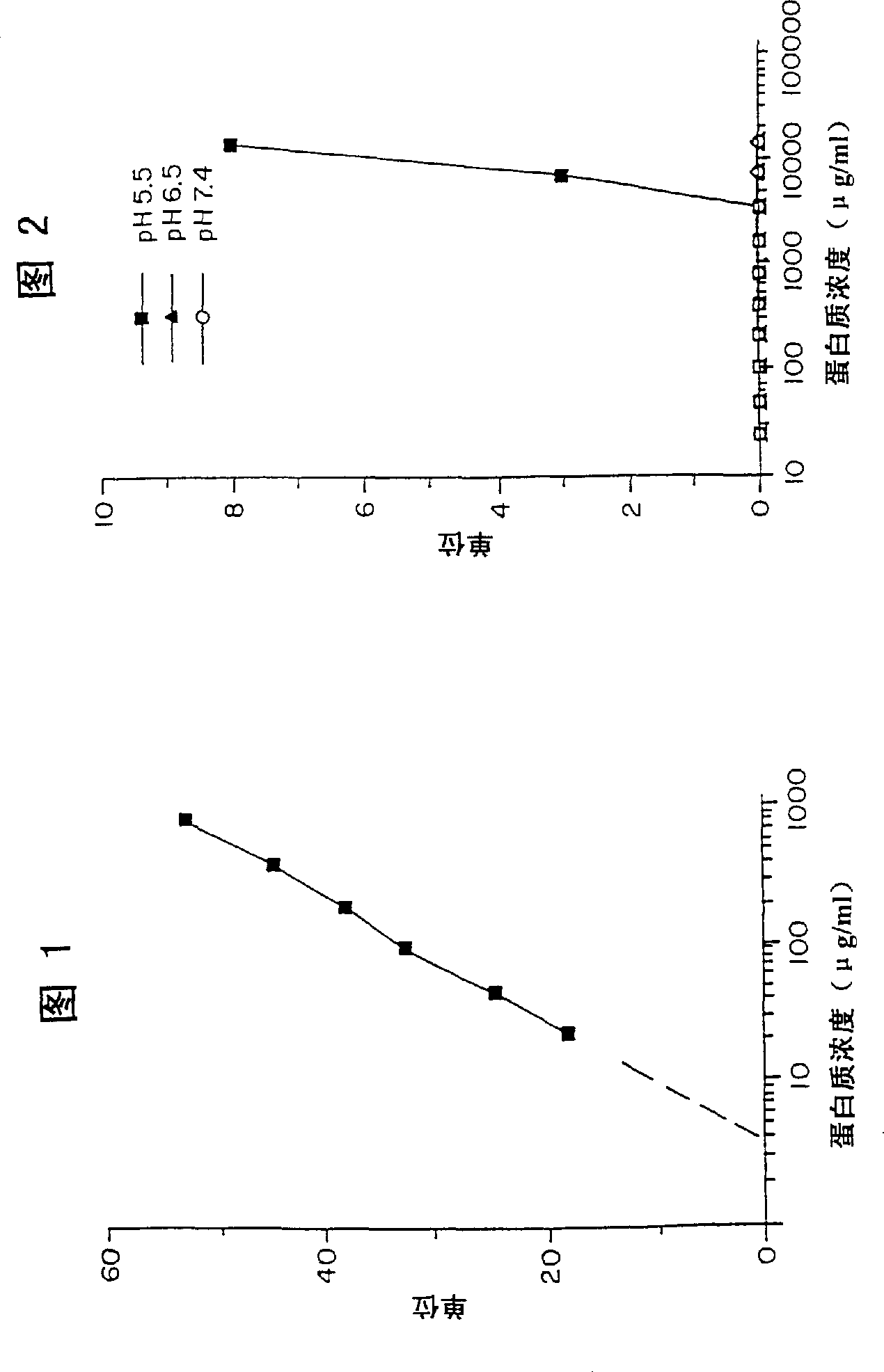
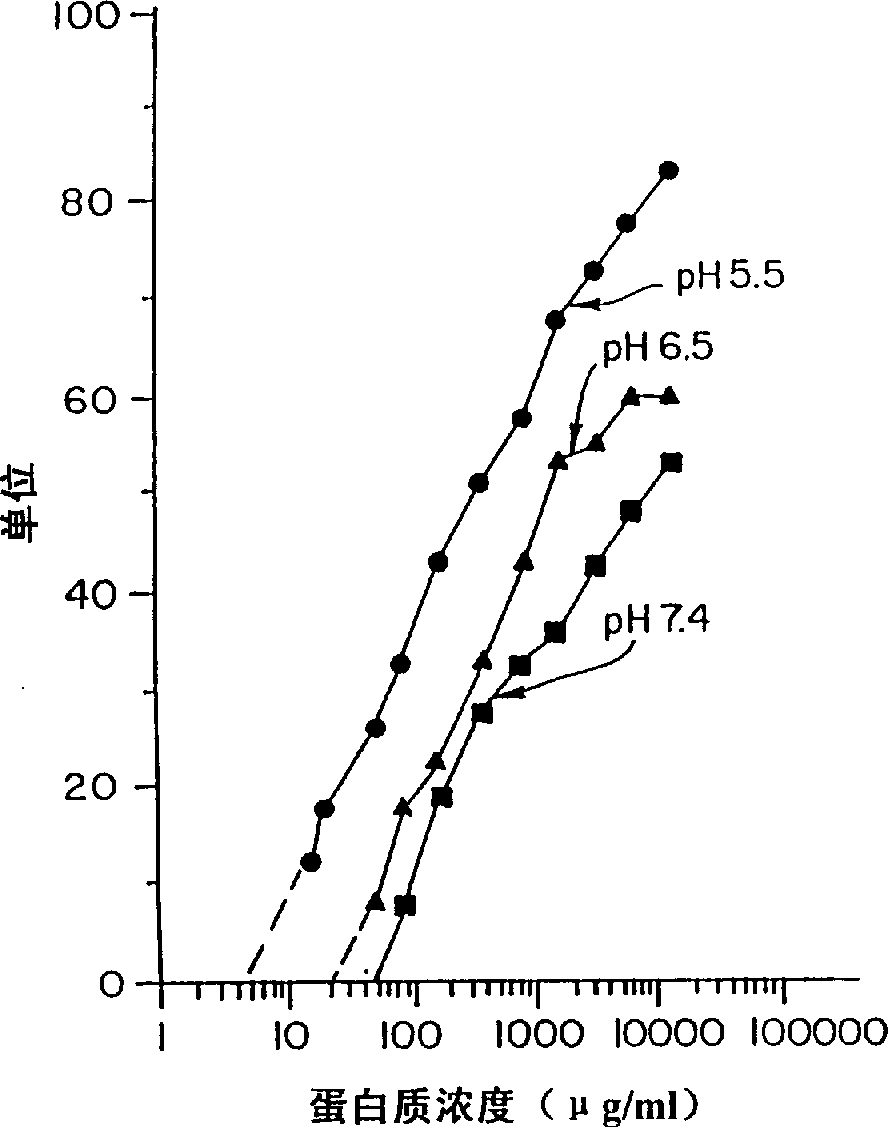
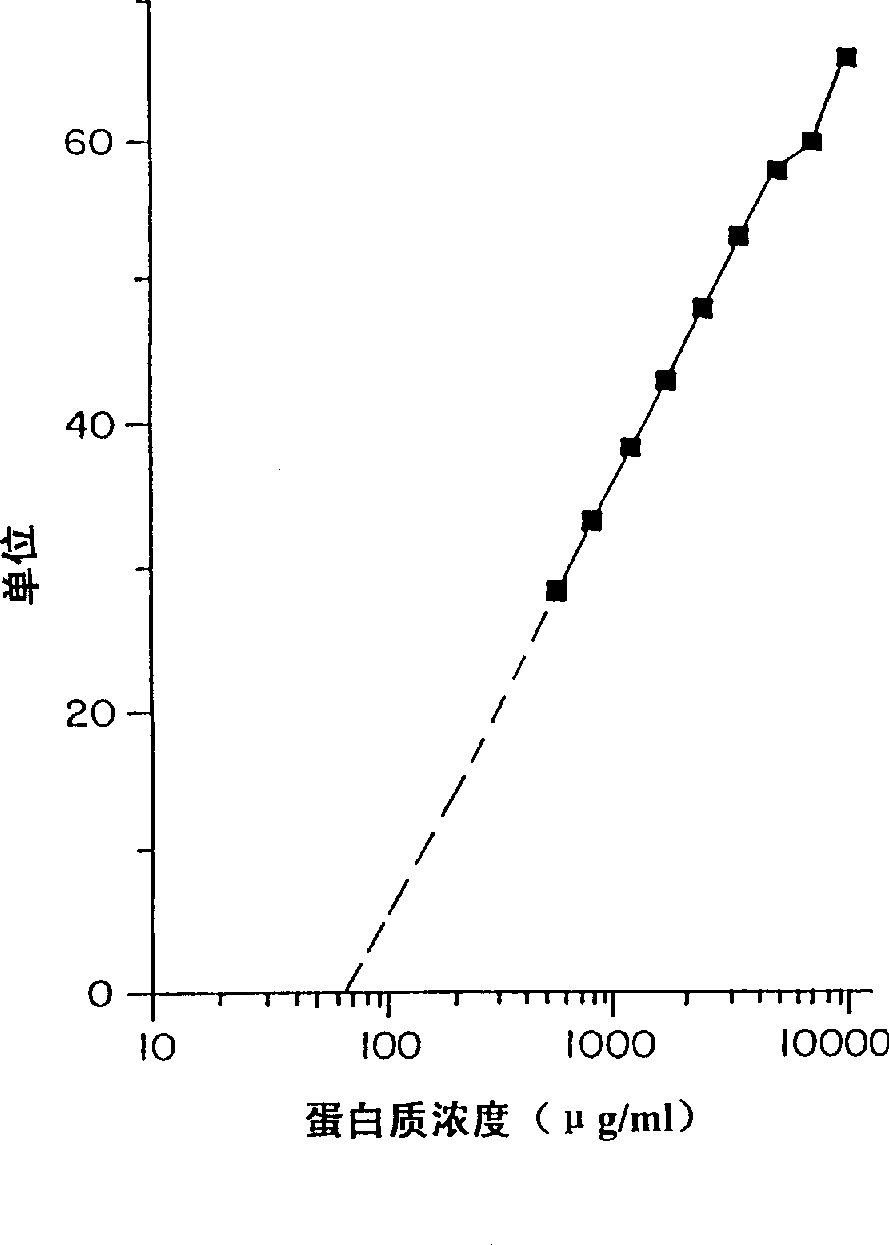
[0066] The antimicrobial activity of human hemoglobin was confirmed by radiation diffusion test, and the results are summarized in Table 1,
[0067] Example 1 and Figures 1-6.
Embodiment 2
[0069] The antimicrobial activity of human hemoglobin was confirmed by the plate test, and the following data were obtained. IC against Candida albicans 50 5-6μg / ml, IC for Escherichia coli 50 It is 8-10μg / ml. IC 50 Indicates the protein concentration required to kill 50% of the detected microorganisms (ie 50% reduction in colony forming units).
Embodiment 3 and 4
[0071] The results of the antimicrobial activity of the hemoglobin α chain without heme are summarized in Table 1 and Example 3, and the results of the antimicrobial activity of the hemoglobin β chain without heme are summarized in Table 1 and Example 4.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com