Plant waveguide and optical fibre low-loss connecting method
A technology of planar optical waveguide and connection method, which is applied in the coupling of optical waveguide, optical waveguide, etc., can solve the problems of increased coupling loss between waveguide and optical fiber, difference in cladding refractive index, etc., and achieves low polarization-dependent loss and good capacitance Poor characteristics, the effect of reducing coupling loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
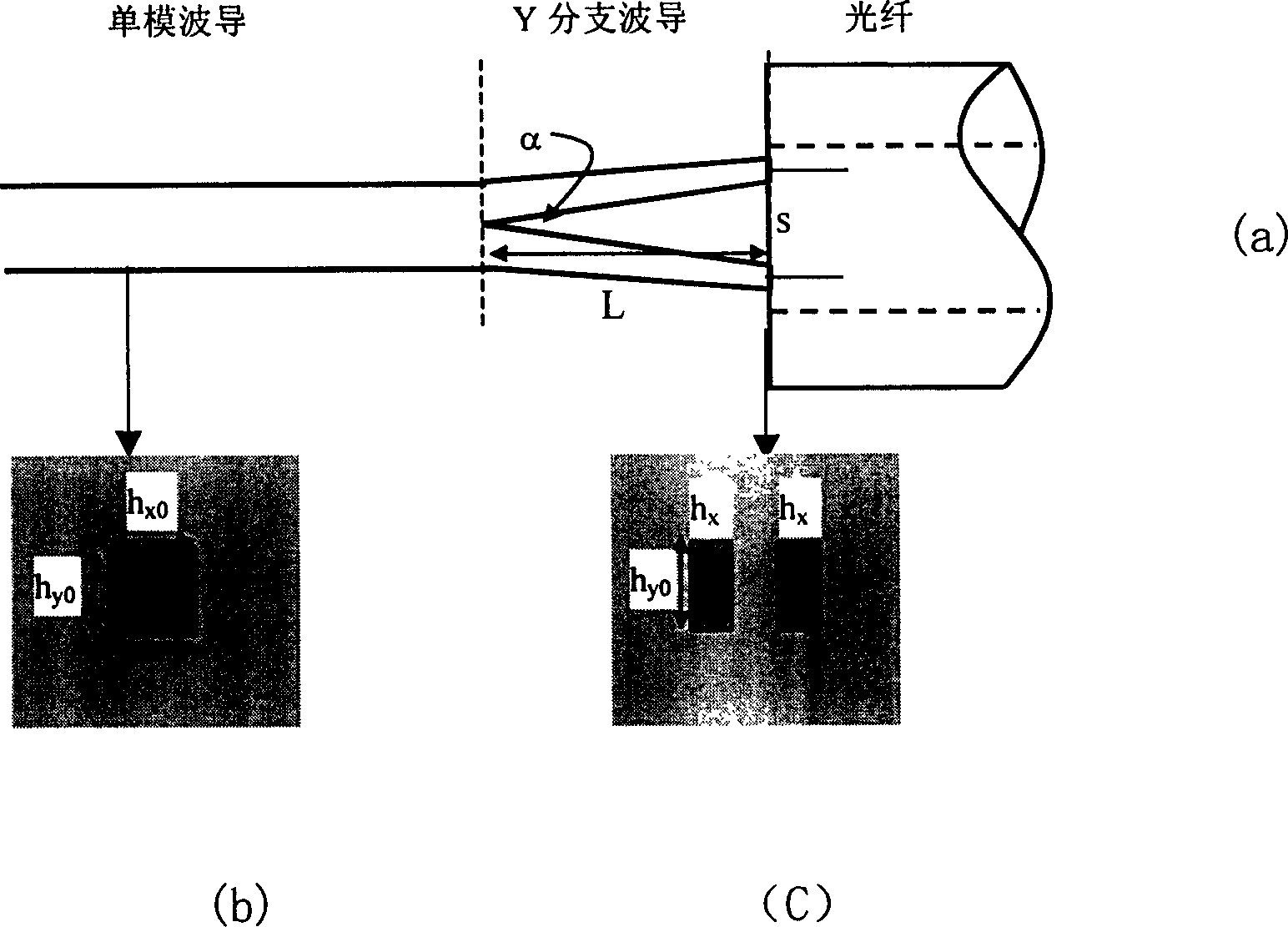
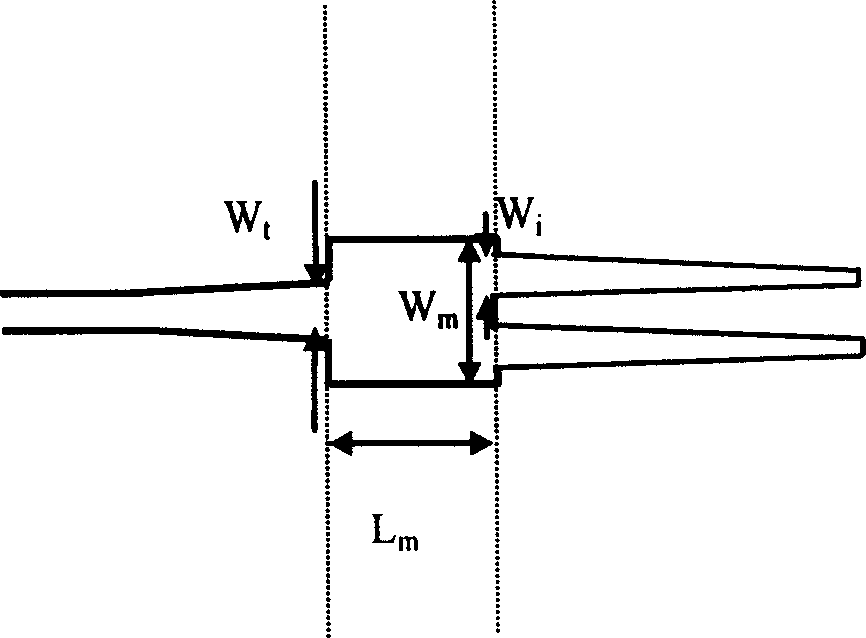
[0023] In the following, the buried waveguide is taken as an example to describe the implementation manner in detail. figure 1 In the specific connection method shown, at the end of the single-mode waveguide connected to the optical fiber, the single-mode waveguide is gradually separated into two waveguides with a certain distance and width to form a Y-shaped branch waveguide, and the branch of the waveguide is a sharp angle. alpha. Suppose the width and height of the original single-mode waveguide are h x0 and h yo , then the parameters of the branched waveguide are: branched waveguide length L, branched waveguide width h x and the distance s between the branch ends.
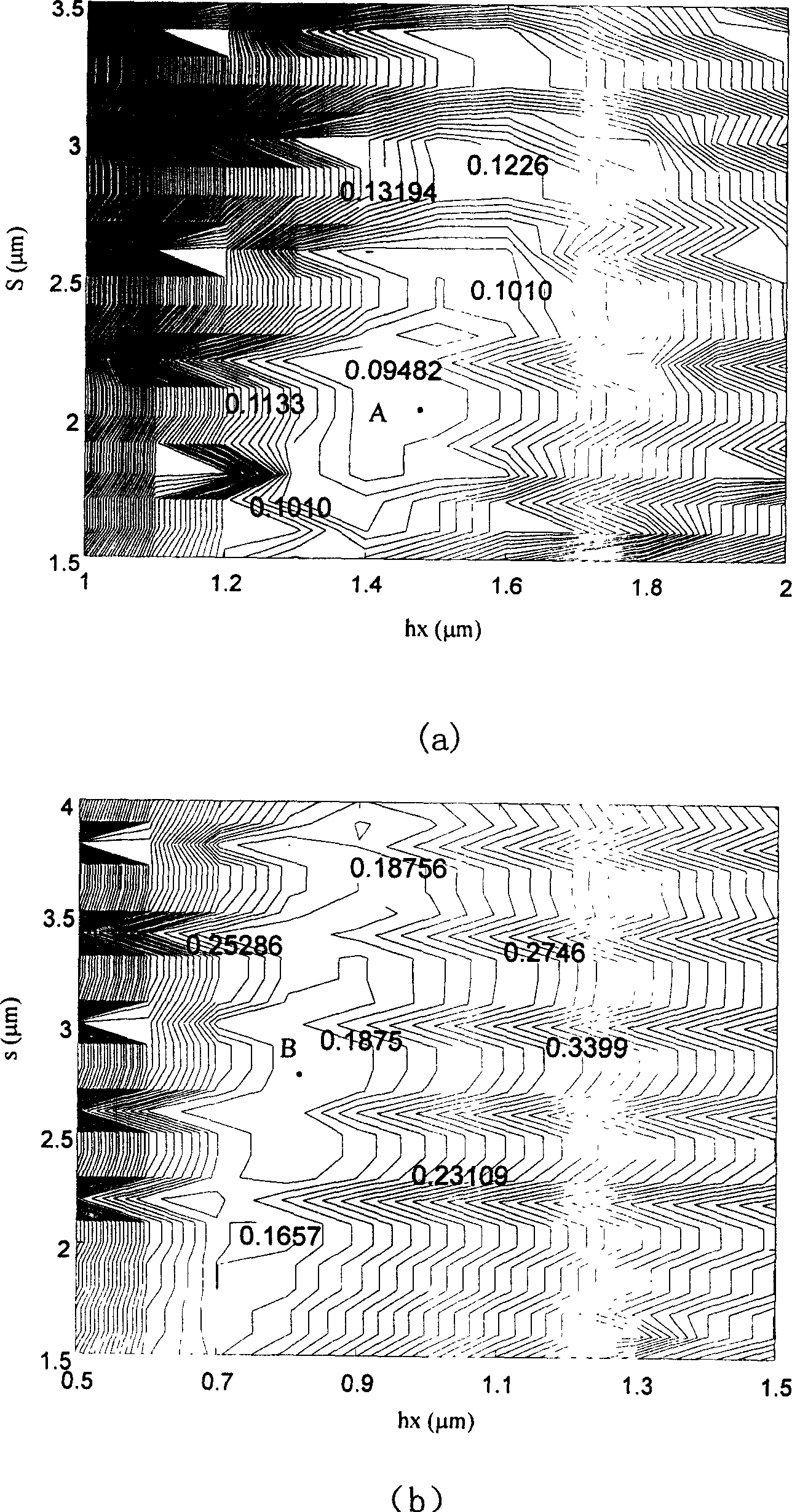
[0024] As for the length L of the branch waveguide, it is sufficient to ensure that the optical field changes slowly during the transmission process, generally in the range of 500 μm to 1000 μm. And the branch waveguide width h x The reasonable selection of the spacing s between the branch end and the bran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com