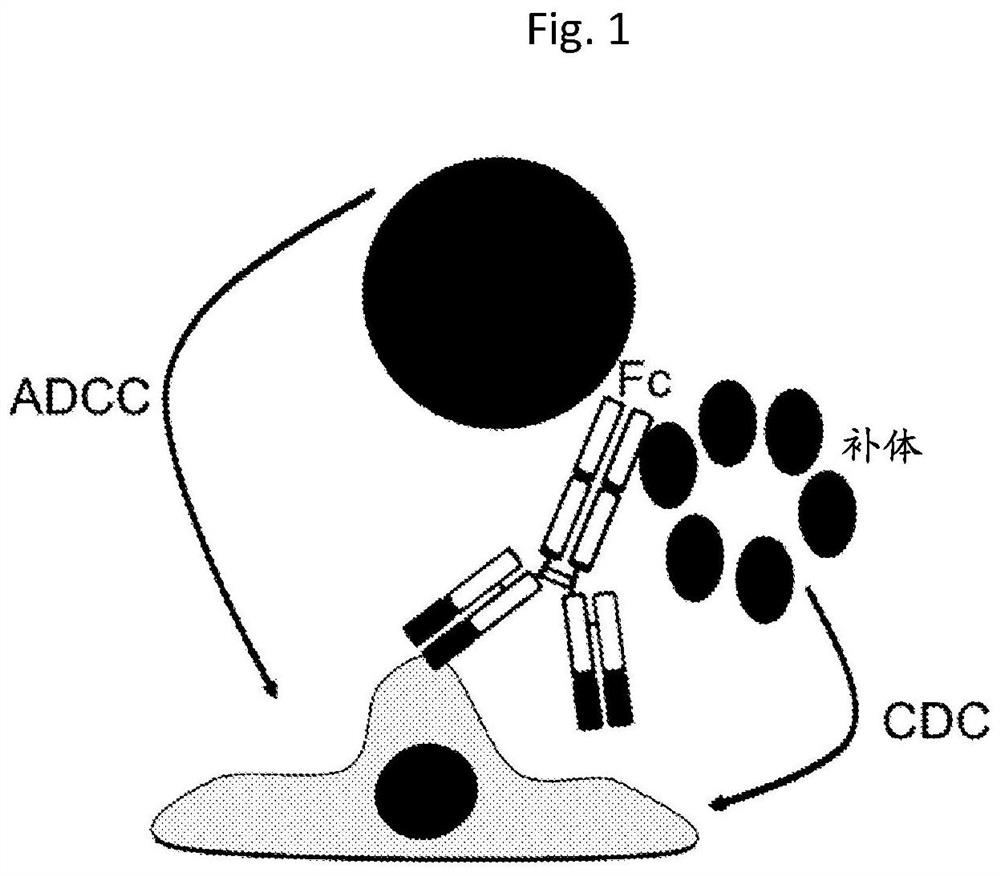
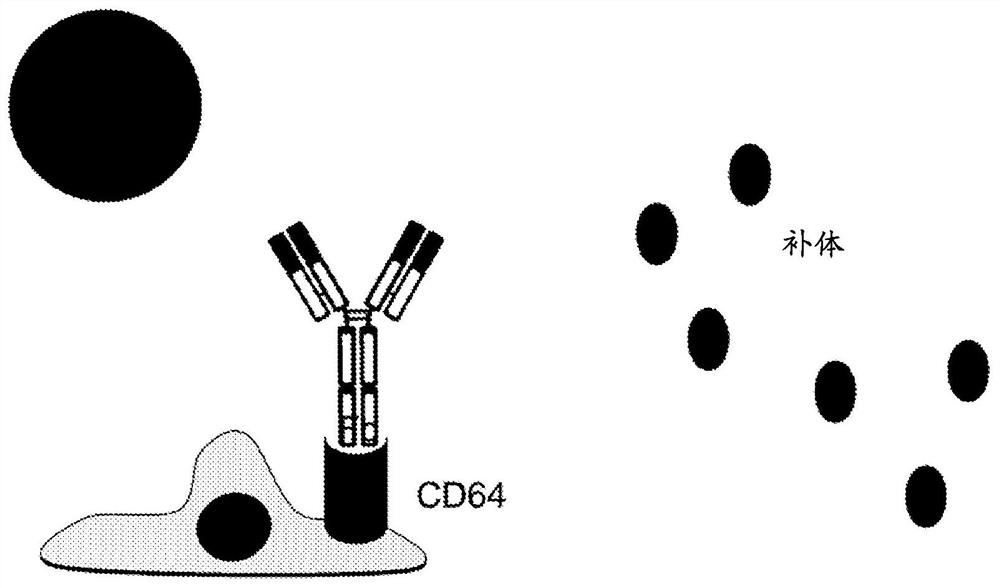
Transplanted cell protection by Fc isolation
A technology of cells and pluripotent cells, applied in the field of regenerative cell therapy, can solve the problem that pluripotent cells have no protective effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0202] HIP, HIPO-, iPSC, iPSCO-, ESC or ESCO- cells of the invention overexpressing CD16, CD32 or CD64 or derivatives thereof can be used for the treatment of eg type 1 diabetes, heart disease, neurological diseases, cancer, blindness, blood vessels disease and other diseases that respond to regenerative medicine therapies. In particular, the present invention contemplates the use of cells to differentiate into any cell type. Accordingly, provided herein are cells that have enhanced CD16, CD32 or CD64 expression and exhibit pluripotency, but do not when transplanted as pluripotent cells or their differentiation products into an allogeneic host such as a human patient Can cause host ADCC or CDC responses.
[0203] In one aspect, the cells of the invention comprise nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) in which CD16, CD32 or CD64 expression has been increased. A CAR can comprise an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling d...
Embodiment 1
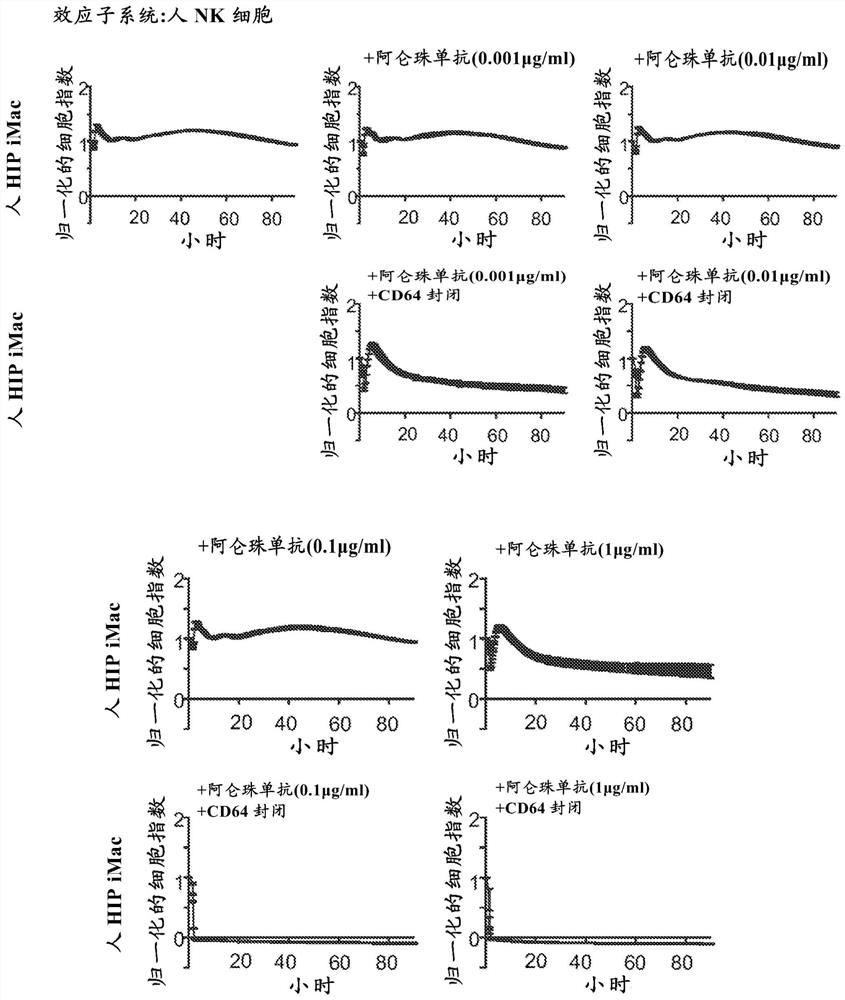
[0265] Example 1: CD64 protects macrophages from NK cell ADCC killing
[0266] Constitutive CD64 expression was shown to protect macrophages that naturally express CD52 from NK cell ADCC when challenged with anti-CD52 antibody. Hypoimmune macrophages (derived from B2M) constitutively expressing CD52 - / - CIITA - / - CD47 tg HIPiPSCs) were plated on the XCelligence platform for in vitro impedance assays (ACEA BioSciences, San Diego, CA). They are attached to plastic petri dishes, forming a confluent layer. The FDA approved humanized IgG antibody alemtuzumab (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, catalog number MCA6101 ) was added at concentrations of 0.001 μg / ml, 0.01 μg / ml, 0.1 μg / ml or 1.0 μg / ml. Alemtuzumab is an anti-CD52 antibody capable of mediating ADCC and CDC. Then, NK cells were added to the assay. Macrophage killing was assessed by measuring the impedance between electrodes on a special 96-well E-plate (ACEA BioSciences).
[0267] image 3 The upper row shows that high concentr...
Embodiment 2
[0268] Example 2: CD64 protects macrophages from CDC killing
[0269] CD64 was shown to protect CD52+ macrophages from CDC challenge when challenged with anti-CD52 antibody. Macrophages were plated on Xcelligence plates and challenged with alemtuzumab as in Example 1. Serum from a blood group A donor (compatible with the blood group of the target cells) was added to avoid the production of additional blood group antibodies in the assay. However, all complement components are present. Figure 5 The first row of shows that macrophages have some constitutive protection against CDC, as lower concentrations of alemtuzumab do not result in major killing. CD64 protection was clearly shown at 0.001 μg / ml and 0.01 μg / ml alemtuzumab. This is because anti-CD64 antibodies cause significant CDC death. ( Figure 5 , bottom row). This suggests that macrophages have constitutive protection against CDC through their CD64 expression, which protection can be suppressed at high antibody con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com