Method for detecting weeding ether pesticide residues in soil
A technology for pesticide residues and detection methods, applied to measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., to achieve the effects of convenient operation, high resolution, and high degree of automation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
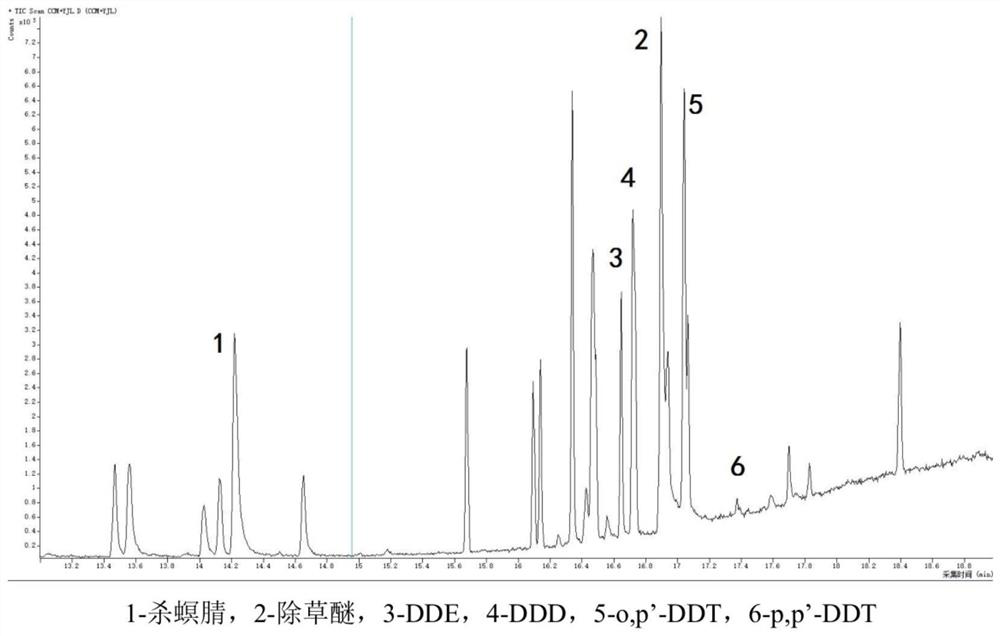
[0041] (2) Preparation and extraction of samples: remove foreign bodies, sticks, leaves, stones, etc. in the soil samples, and mix the samples evenly; at the same time, weigh two soil samples of about 10g (accurate to 0.01g), and one is used for determination Dry matter content, one part is used for extraction with a pressure solvent extractor; the sample used for extraction is added with an appropriate amount of diatomaceous earth and ground to a quicksand-like shape and then loaded into the extraction cell, and the mixed solvent of dichloromethane and acetone (volume Ratio 1:1) pressure extraction of herbicides in soil samples.
[0042] (3) Condition settings of the pressure solvent extractor: carrier gas (nitrogen) pressure 1.0MPa, heating temperature 100°C, pressure 1700psi, preheating equilibrium 5min, static extraction time 5min, solvent rinsing volume 60% pool volume, extraction nitrogen blowing The sweep time was 70s, and the static extraction was performed twice.
[...
Embodiment 1
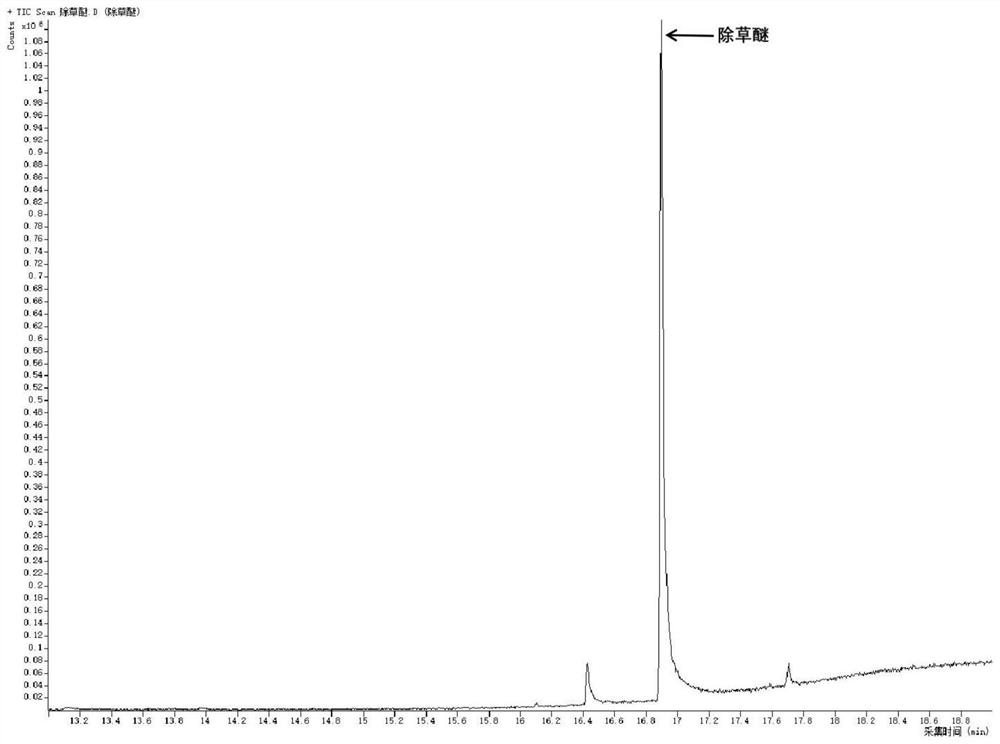
[0057] (1) The detection limit of the method: Dilute the standard solution of herbicide 10 times to become the standard solution of herbicide, refer to the "Technical Guidelines for the Development of Environmental Monitoring Analysis Methods" (HJ 168), and accurately pipette 20 μL with a micropipette In the extraction tank equipped with 10g quartz sand, the standard solution of herbicidal ether was extracted with dichloromethane:acetone (1:1) on the pressure solvent extractor according to the instrument conditions in step (3), and the extract was extracted according to the steps (6) Concentrate by nitrogen blowing to convert the solvent into n-hexane, quantitatively add 100 μL of the internal standard solution, and then use n-hexane to dilute to 1 mL, and send it to the gas chromatograph from the automatic sampler according to the instrument conditions in step (7). Separation and detection by mass spectrometry detector, determination of herbicidal ether content. Repeat the ab...
Embodiment 2
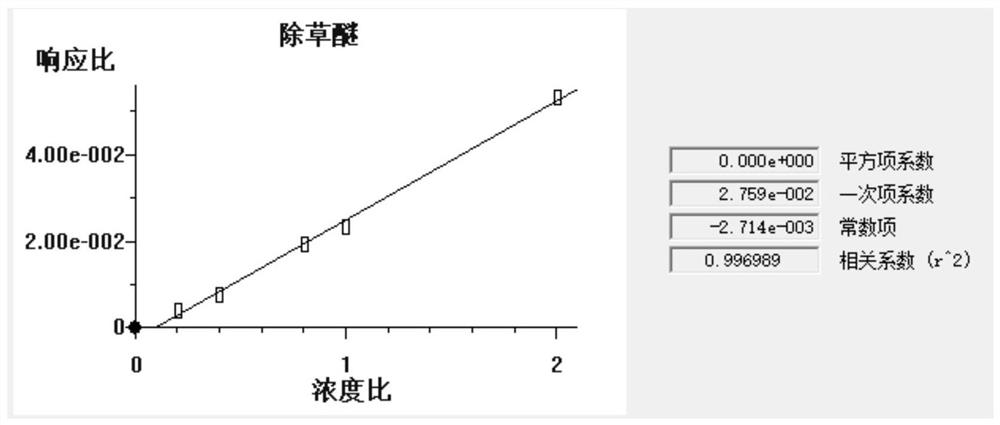
[0064] Method precision: Use a micropipette to accurately pipette different volumes of the standard solution of herbicide into the extraction cell containing 10g of soil matrix samples, and use dichloromethane:acetone (1:1) on a pressure solvent extractor to press In step (3), pressurized extraction is carried out under the conditions of the apparatus, and the extract is subjected to nitrogen blowing and concentration according to step (6) to convert the solvent into n-hexane, quantitatively add 100 μL of internal standard solution, and dilute to 1 mL with n-hexane, and press step (7). ) in the instrument condition is sent to the gas chromatograph by the automatic sampler for separation and detected by the mass spectrometer detector to determine the herbicide content in the soil matrix sample. The above operation was repeated 5 times in the whole process, and the precision was measured. The precision measurement data are shown in Table 1. When the herbicide content in the soil ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com