Construction method and application of condylar bone resorption animal model for temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
A temporomandibular joint and construction method technology, applied in veterinary surgery, veterinary instruments, medical science, etc., can solve the problem of limited anterior displacement of the joint disc, and achieve fast modeling speed, low cost, and simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Evaluation of the effect of temporomandibular joint disc displacement on condylar cartilage and subchondral bone
[0037] 1. Construction of an animal model of condylar bone resorption in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
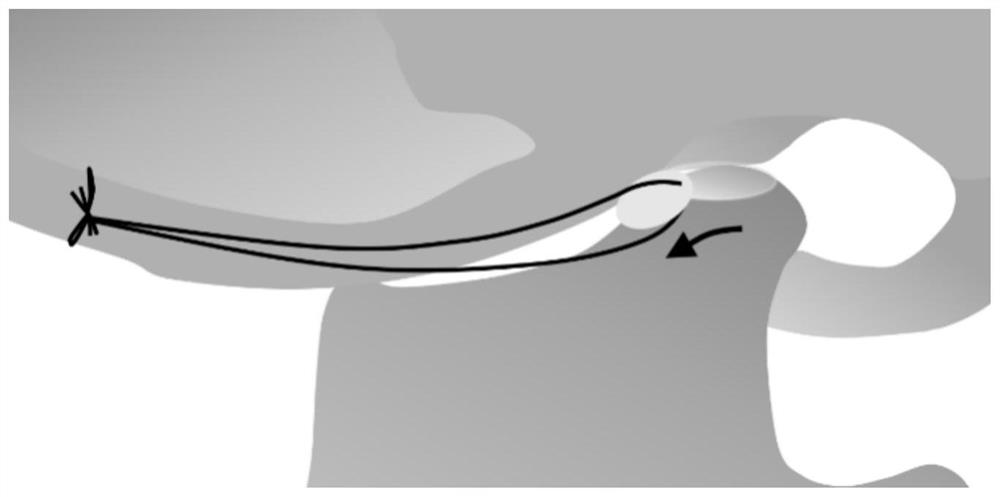
[0038] Rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 1% sodium isopentobarbital (60 mg / kg). A 1.0cm arc-shaped incision was made along the zygomatic arch at 0.5 cm lateral to the lateral canthus of the right eye of the rat. The skin and subcutaneous tissue were incised and entered from the depression between the temporalis muscle, masseter muscle and external auditory canal to expose the zygomatic arch. ; Blunt dissection of the surrounding muscle tissue, exposing the condylar neck to the surgical area. The joint capsule was cut to expose the condyle and articular disc. The tissue attached to the neck of the condyle was cut anteriorly (mandibular anterior attachment), laterally, and posteriorly (mandibular posterior attachm...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Exploring the best treatment period for temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
[0042] 1. Construction of an animal model of condylar bone resorption in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
[0043] Rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 1% sodium isopentobarbital (60 mg / kg). A 1.0cm arc-shaped incision was made along the zygomatic arch at 0.5 cm lateral to the lateral canthus of the right eye of the rat. The skin and subcutaneous tissue were incised and entered from the depression between the temporalis muscle, masseter muscle and external auditory canal to expose the zygomatic arch. ; Blunt dissection of the surrounding muscle tissue, exposing the condylar neck to the surgical area. The articular capsule is incised to expose the condyle and articular disc. The tissue attached to the neck of the condyle was cut anteriorly (mandibular anterior attachment), laterally, and posteriorly (mandibular posterior attachment) with microscissors. P...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3: Exploring the mechanism of articular disc displacement leading to osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint
[0049] 1. Construction of an animal model of condylar bone resorption in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
[0050] Rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 1% sodium isopentobarbital (60 mg / kg). A 1.0cm arc-shaped incision was made along the zygomatic arch at 0.5 cm lateral to the lateral canthus of the right eye of the rat. The skin and subcutaneous tissue were incised and entered from the depression between the temporalis muscle, masseter muscle and external auditory canal to expose the zygomatic arch. ; Blunt dissection of the surrounding muscle tissue, exposing the condylar neck to the surgical area. The joint capsule was cut to expose the condyle and articular disc. The tissue attached to the neck of the condyle was cut anteriorly (mandibular anterior attachment), laterally, and posteriorly (mandibular posterior attachme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com