Novel flavone reductase and application thereof
A technology of reductase and flavone, applied in the field of new flavone reductase and its application, can solve the problem of unclear reaction mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0148] Example 1 Discovery and verification of flavone reductase FLR
[0149] experimental method:
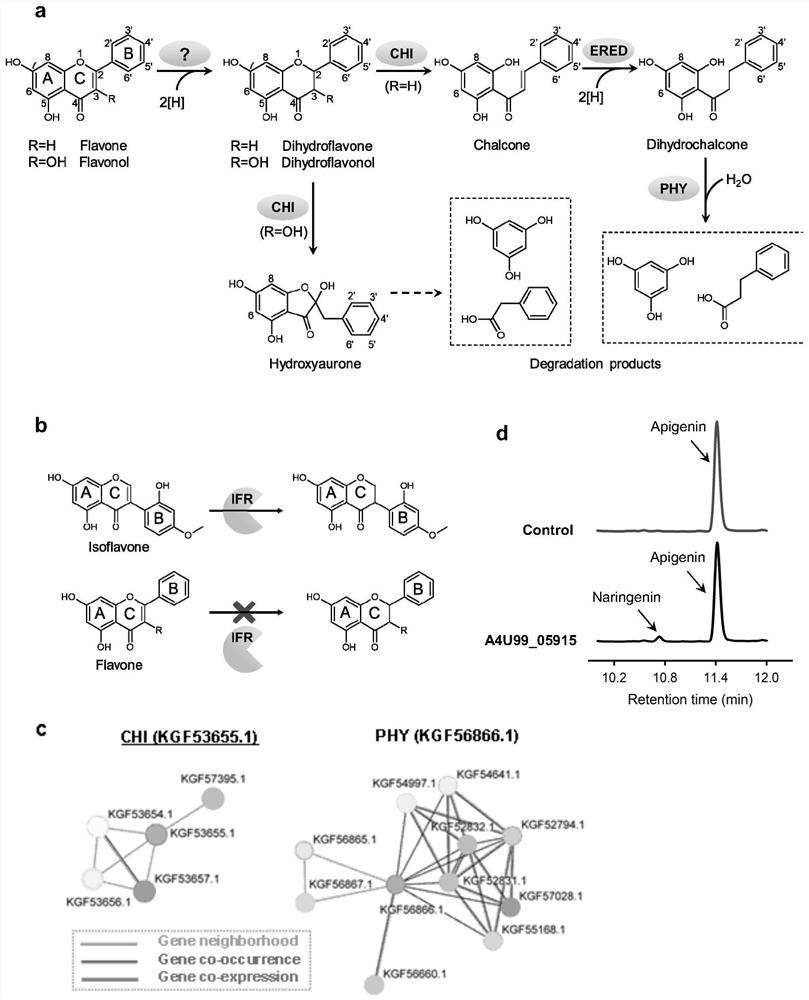
[0150] Human intestinal flora can metabolize flavonoids, and the key enzymes responsible for the initial reaction in the metabolic pathways of the two most important types of compounds—flavonoids and flavonols have not yet been discovered and identified ( figure 1 a). The possible candidate genes of flavone reductase were predicted by the method of comparative genomics, and the candidate genes were cloned into plasmids one by one and introduced into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) for expression, and anaerobic fermentation was carried out in the medium supplemented with apigenin , to determine whether there is target flavonoid generation.
[0151] Experimental steps:
[0152] 1) We tested whether the reported flavonoid reductase - isoflavone reductase IFR can catalyze the reduction of flavones, and found that IFR can only specifically catalyze the reduction of isoflavones. It sh...
Embodiment 2
[0158] The biochemical characteristic analysis of embodiment 2 flavone reductase
[0159] experimental method:
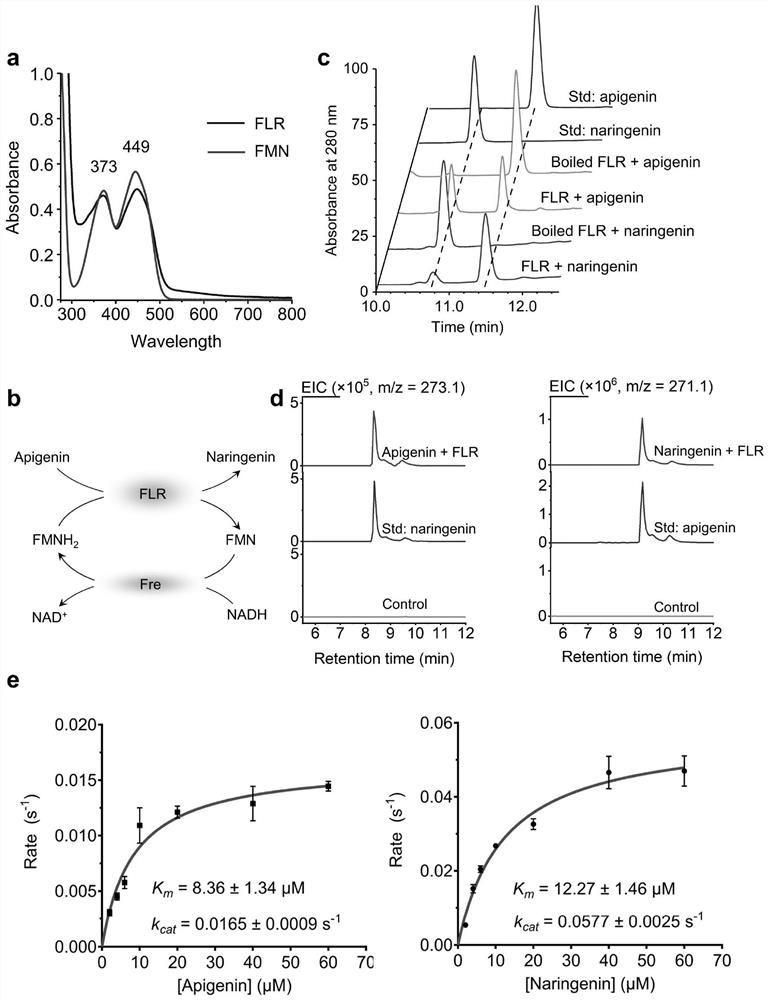
[0160] A coupling reaction system based on flavin cofactors was constructed to realize the catalytic reaction of flavone reductase in vitro, and the catalytic efficiency of flavone reduction reaction and dihydroflavone oxidation reaction of the enzyme was detected at different pH values, different temperatures and different substrate concentrations. To analyze the enzymatic properties of FLR.
[0161] Experimental steps:
[0162] 1), according to the two characteristic absorption peaks of 380nm and 447nm that appear in the full-wavelength scanning result of enzyme extract ( figure 2 a), Preliminary judgment that FLR is a flavin-dependent oxidoreductase.
[0163] 2). A coupled reaction system based on flavin cofactors was constructed to analyze the enzymatic properties of FLR. Such as figure 2 As shown in b, the reaction system produces reduced flavin cofactor...
Embodiment 3
[0168] The universality of embodiment 3 flavone reductase substrates
[0169] experimental method:
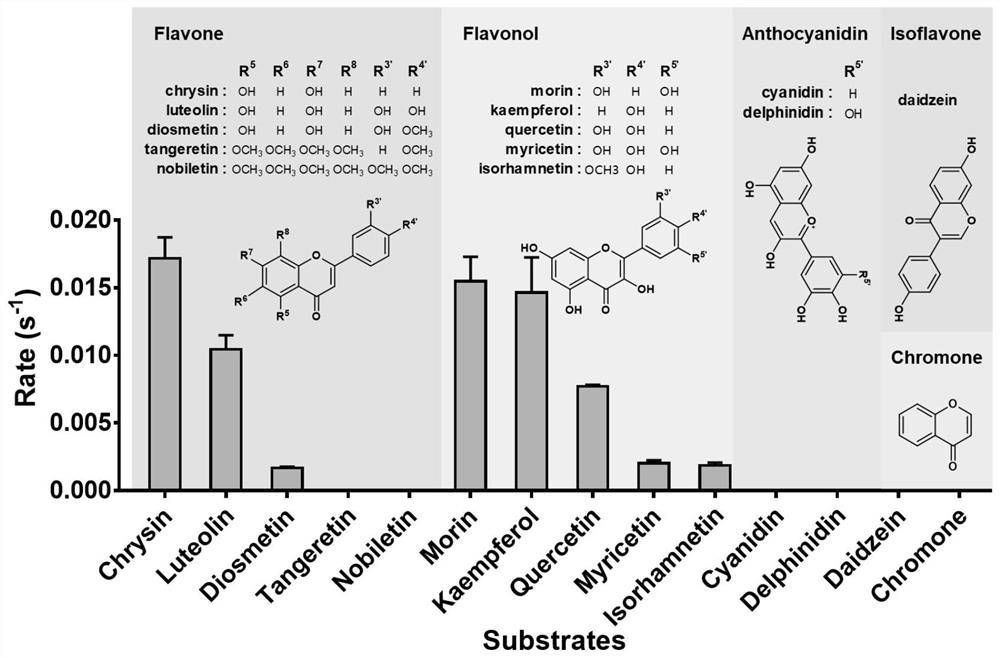
[0170] Under the established enzyme catalytic system, different kinds of representative flavone substrates were selected to test the catalytic activity of flavone reductase.
[0171] Experimental steps:
[0172] We selected 14 representative flavonoids from the main classes of flavonoids (flavonoids, flavonols, isoflavones, anthocyanins and chromones) for enzyme activity testing.
[0173] Experimental results:
[0174] The results showed that FLR had catalytic activity for these several substances, showing good substrate adaptability ( image 3 ). Moreover, it was found through comparison that if more or larger substituent groups appear on the B ring of these flavones, the catalytic efficiency of FLR to the substrate will be reduced. For example, the ability of FLR to catalyze the reduction of chrysin, apigenin, and luteolin shows a decreasing trend, and the efficiency of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com