Treatment of immune platelet disorders using antigen-binding fragments
A technology combining fragments and platelets, applied in the fields of immunology and medicine, can solve the problem of not being effective and unable to eliminate the effective prothrombotic process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0144] Materials and methods
[0145] patient
[0146] Samples were randomly selected from stored serum collected with informed consent from patients with HIT. Diagnosis of HIT was made according to criteria as previously defined (Amiral J et al. (1998) Baillieres Clin. Haematol.). The study was approved by the South-Eastern Sydney Illawarra / Eastern Sydney Area Health Service Ethics Committees. Blood and plasma from healthy donors were obtained with informed consent.
[0147] Molecular cloning and humanization of scFv
[0148] Total RNA was isolated from IV.3 hybridoma cells using the RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions. First strand cDNA using SuperScript for qRT-PCR TM III First-Strand Synthesis SuperMix (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) synthesis. PCR amplification of the heavy and light chains was performed using specific primers. Heavy chain variable region forward primer 5'GGCCAGTGGATAGTCAGATGGGGGTGTCGTTTTGGC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 24)...
Embodiment 2
[0168] Example 2 - Sequence and protein expression of scFv
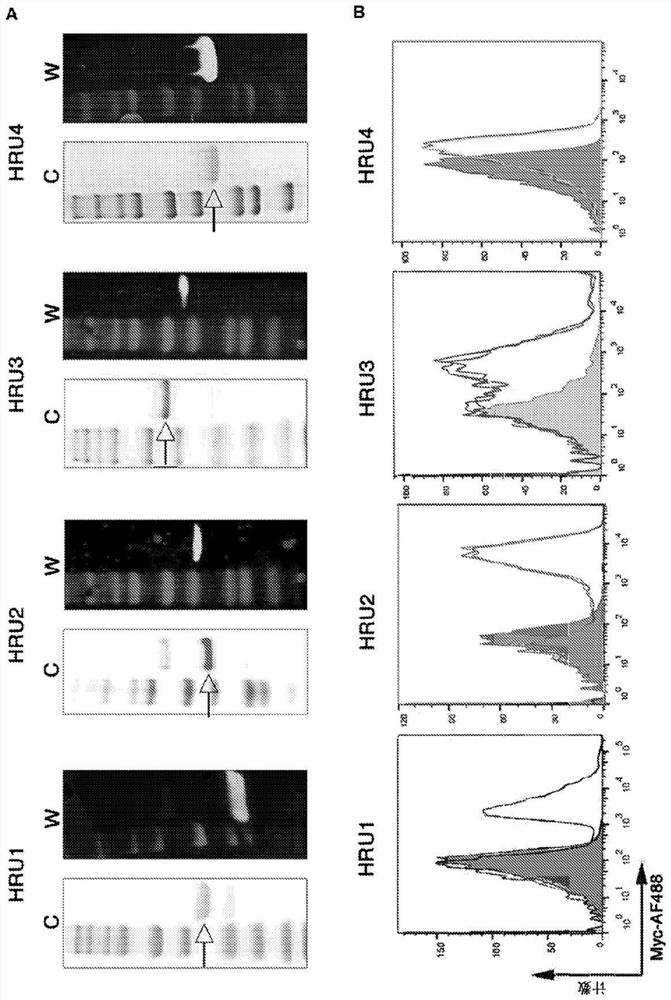
[0169] The sequences of the murine scFv and the variable heavy and variable light regions of the humanized molecules (HRU1 to HRU4) and CTBR1 are shown in Table 1 as SEQ ID NOs: 1-23. Purified protein obtained from bacterial expression in figure 1 Shown in A.
[0170] Table 1: Sequence information
[0171]
[0172]
[0173]
[0174]
[0175]
[0176] *SEQ ID NO: 10, 11-13, 15 and 22 may also each contain a signal peptide sequence to facilitate secretion. In this study, the signal peptide sequence was KSLITPITAGLLLLALSQPLLA. Signal peptide sequences are usually not present in the final protein preparation.
[0177] **SEQ ID NOs: 2 and 10-15 may also each comprise a polyhistidine tag (H 6 ). The final antigen-binding product may or may not contain a polyhistidine tag.
Embodiment 3
[0178] Example 3 - HRU1 to HRU4: Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation and Activation
[0179] The ability of HRU molecules to interact with human platelets in figure 1 Shown in B. These experiments showed that all scFvs exhibited strong binding to human platelets.
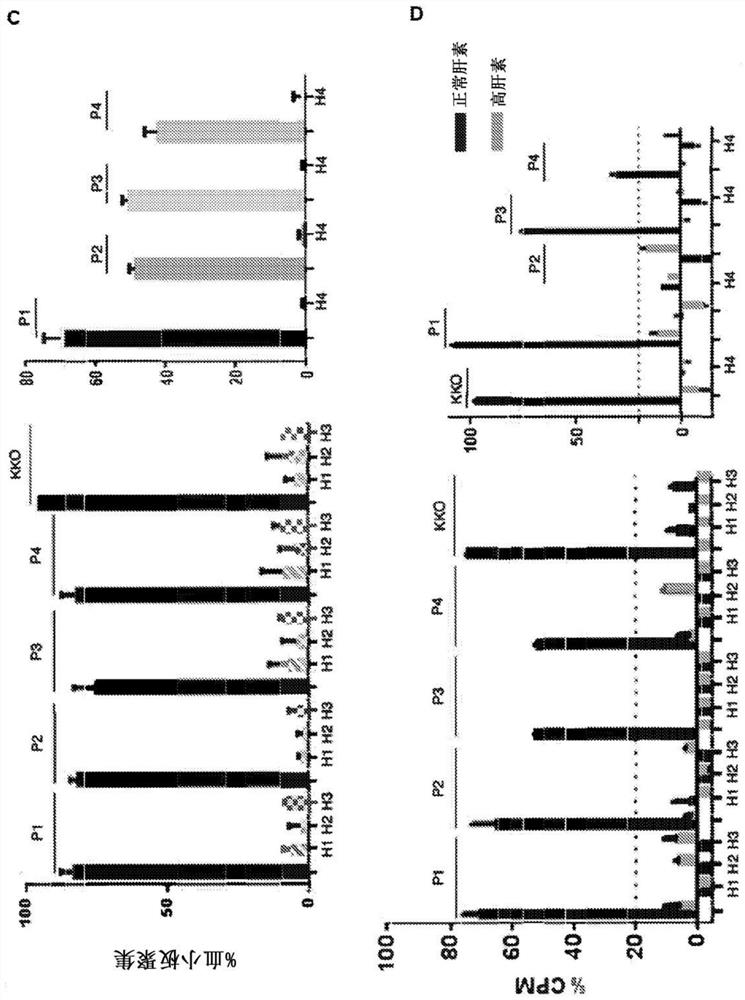
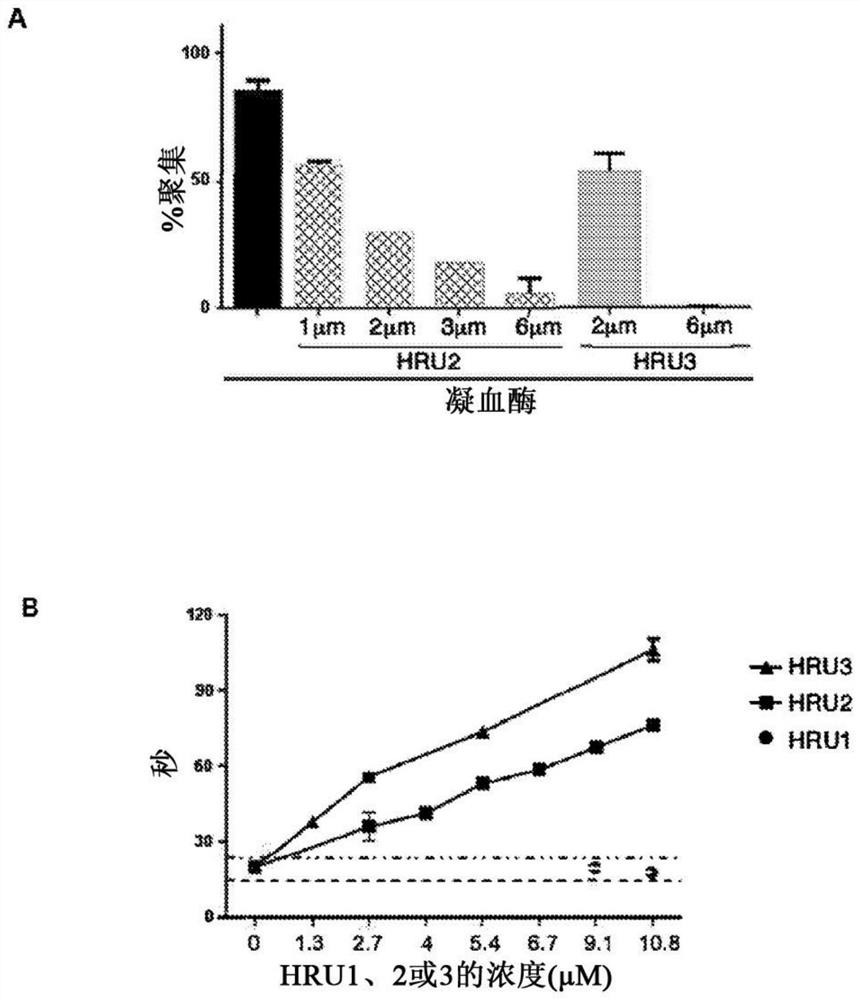
[0180] The ability of scFvs to inhibit platelet aggregation and activation was investigated. To determine whether scFv could inhibit HIT antibody-induced platelet aggregation in vitro, HRU1-4 were added to a reaction consisting of human platelets, HIT IgG or IgG-like monoclonal antibody KKO, and heparin. In the absence of HRU molecules, HIT IgG and KKO induced strong platelet aggregation ( figure 1 C). HRU scFv strongly inhibited HIT IgG-induced aggregation at submicromolar concentrations (2 μM in all cases). These results indicate that these are functional molecules capable of blocking platelet aggregation induced by HIT IgG and heparin. The serotonin release assay (Sheridan D et al. (1986) Blood) for measurin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com