TEAC and ATTAC immunooncology compositions and methods
A technology of immune cells and tumor antigens, applied in chemical instruments and methods, drug combinations, anti-tumor drugs, etc., can solve problems such as cytokine release syndrome and death
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0459] The following numbered items provide embodiments as described herein, but the embodiments cited here are not limiting.
[0460] Item 1. A medicament for treating cancer in a patient, comprising: a first component comprising a targeted T cell engaging agent comprising: binding to a tumor expressed by the cancer a first targeting moiety of an antigen; a first T cell engaging domain capable of T cell engaging activity when it binds a second T cell engaging domain, wherein the second T cell engaging domain is not part of the first component, and wherein said first T cell engaging domain comprises a VH domain or a VL domain; for a first inert binding partner of the first T cell engaging domain, the first inert binding partner binds to the first T cell engaging domain, such that the first T cell engaging domain does not bind to the second T cell engaging domain unless an inert binding partner is removed, wherein if the first T cell engaging domain comprises a VH domain, the i...
Embodiment 1
[0556] Example 1. Anti-CD33 / anti-CD123 TEACs comprising half-life extending moieties
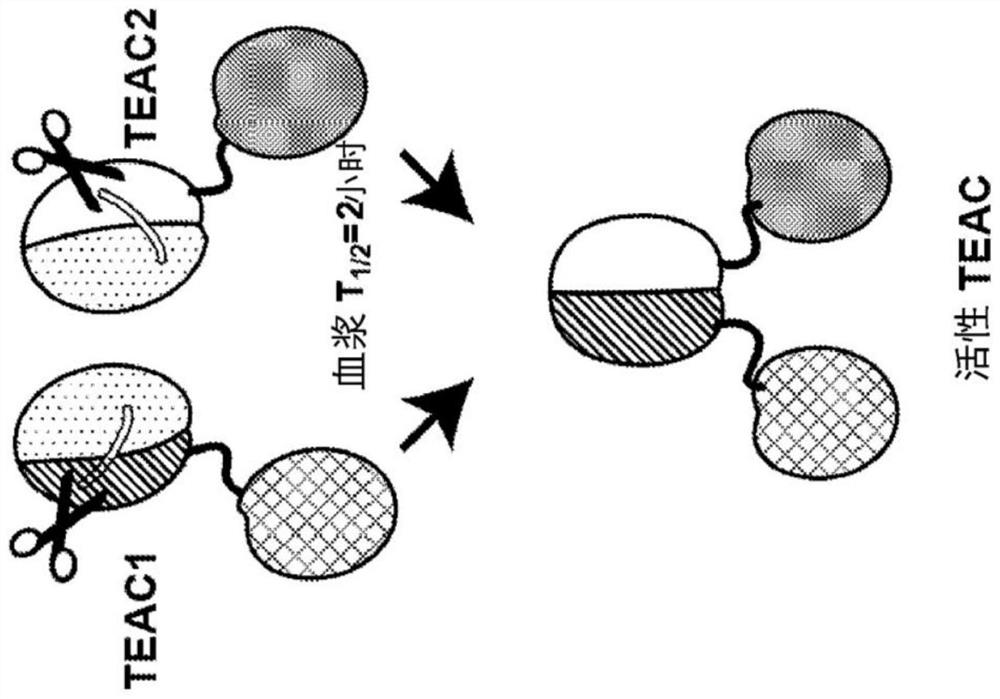
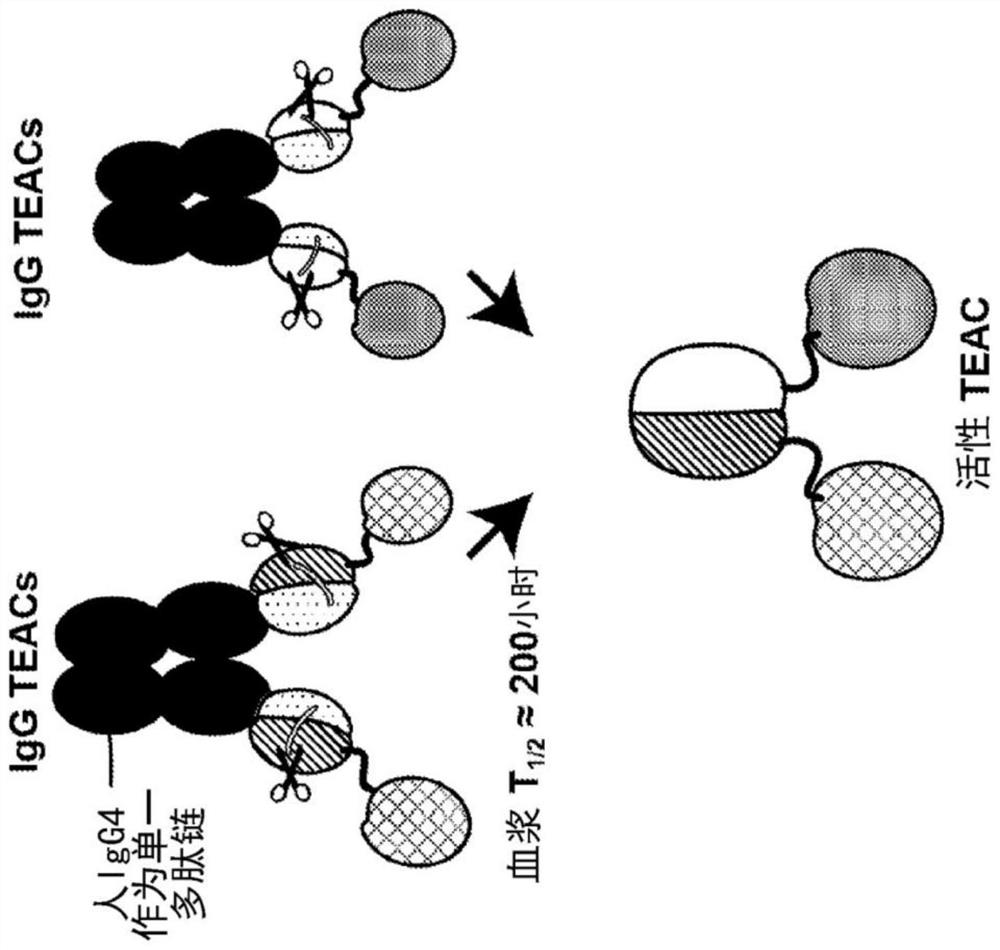
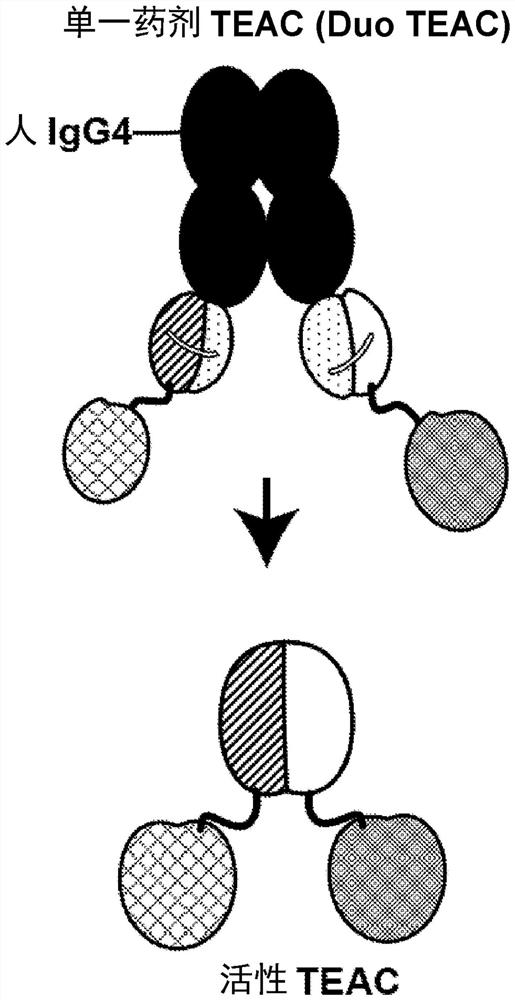
[0557] A two-component dual IgG TEAC was developed, where each component of the two-component system contained an IgG TEAC. Dual IgG TEACs were designed to contain a first component, an IgG TEAC comprising two targeting moieties, each an anti-CD33 antibody, and a second component, is an IgG TEAC comprising two targeting moieties, each of which is an anti-CD123 antibody. Each IgG TEAC also contained two copies of the T cell engagement domain, two copies of the inert binding partner, and two copies of the cleavage site between the T cell engagement domain and the inert binding partner.
[0558] Additionally, both the first and second components together comprise a linker comprising a half-life extending moiety. The half-life extending moiety comprises an Fc domain from IgG4, wherein the Fc domain is directly linked to an inert binding partner. When expressed in HEK293T cells, one copy of TE...
Embodiment 2
[0568] Example 2. Anti-EpCAM TEACs comprising half-life extending moieties
[0569] A variety of TEACs with half-life extending moieties can be designed with EpCAM targeting moieties.
[0570] Design of a two-component dual IgG TEAC comprising a first IgG TEAC comprising two targeting moieties, each an anti-EpCAM antibody, and a second IgG TEAC comprising two targeting moieties , each an anti-EpCAM antibody. Each IgG TEAC also contained two copies of a T cell engaging domain, two copies of an inert binding partner, and two copies of a protease cleavage site between each T cell engaging domain and its inert binding partner.
[0571] Additionally, both the first and second components further comprise a linker comprising a half-life extending moiety (SEQ ID NO: 201 and 202). The half-life extending moiety comprises an Fc domain where one end of the linker is directly linked to an inert binding partner. When expressed in HEK293T cells, one TEAC (EpCAM binding region (scFv) – an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com