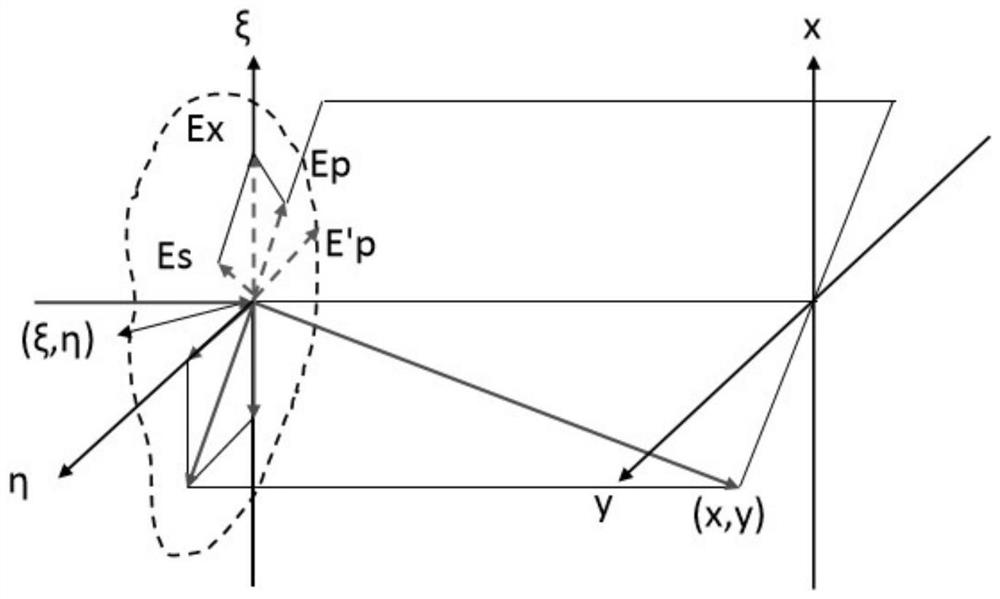
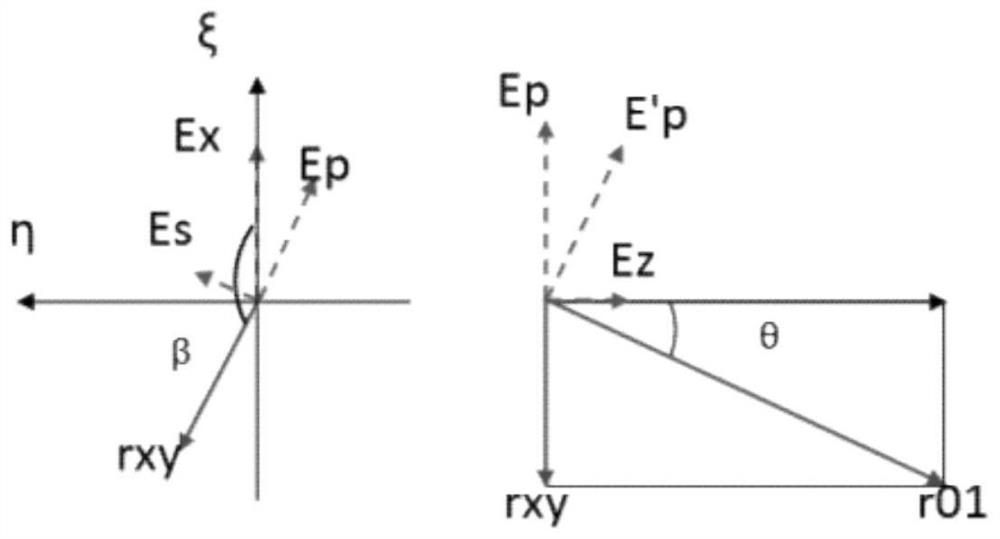
Vector diffraction algorithm based on optical vector decomposition synthesis and Huygens-Fresnel
A technology of Fresnel diffraction and diffraction algorithm, applied in the field of vector diffraction algorithm based on light vector decomposition and Huygens-Fresnel, can solve the problems of inconvenient calculation and unintuitive physical meaning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
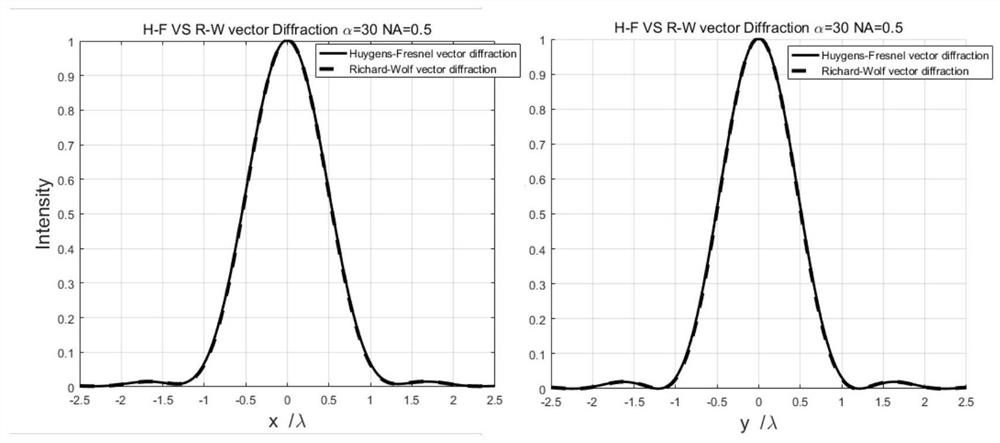
[0063] This embodiment considers the objective lens of NA=0.5 (α=30°), considers that the incident photoelectric vector is linearly polarized light in the x direction, and the x and y total light intensity distributions on the focal plane of the objective lens are shown in the appendix image 3 . Among them, the solid line is the result of Richard-Wolf vector diffraction (formula (11)), and the dotted line is the result of vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction (formula (4)). It can be seen that the light intensity distribution in the x and y directions of the vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction results and the Richard-Wolf vector diffraction results almost completely coincides. attached Figure 6 The first row (α = 30°) shows the light intensity distribution for the x, y and z components of the vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction. attached Figure 7 The first row (α = 30°) shows the comparison of vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction and Richard-Wolf vector diffraction logarithmic ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] This embodiment considers the objective lens of NA=0.87 (α=60°), considers that the incident photoelectric vector is linearly polarized light in the x direction, and the x and y total light intensity distributions on the focal plane of the objective lens are shown in the appendix Figure 4 . Among them, the solid line is the result of Richard-Wolf vector diffraction (formula (11)), and the dotted line is the result of vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction (formula (4)). It can be seen that the light intensity distribution in the x and y directions of the vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction results and the Richard-Wolf vector diffraction results almost completely coincides. attached Figure 6 The second row (α = 60°) shows the light intensity distribution for the x, y and z components of the vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction. attached Figure 7 The second row (α = 60°) shows the comparison of the logarithmic contours of the vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction and the Rich...
Embodiment 3
[0067] This embodiment considers the objective lens of NA=0.97 (α=75°), considers that the incident photoelectric vector is linearly polarized light in the x direction, and the x and y total light intensity distributions on the focal plane of the objective lens are shown in the appendix Figure 5 . Among them, the solid line is the result of Richard-Wolf vector diffraction (formula (11)), and the dotted line is the result of vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction (formula (4)). It can be seen that the vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction results and the Richard-Wolf vector diffraction results almost completely coincide in the light intensity distribution in the x direction, and almost completely coincide in the central part of the light intensity distribution in the y direction, only in the first sub-peak part. nuance. attached Figure 6 The third row (α=75°) shows the light intensity distribution of the vector Huygens-Fresnel diffraction x, y and z components. attached Figure ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com