Method and system for completing karyotype analysis of sample to be detected based on whole genome sequencing and computer readable medium
A genome and sequencing technology, applied in the field of biological information, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, long time, and inaccurate detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] Example 1: library construction and sequencing
[0094] Blood is drawn from the bone marrow of AML or MDS patients, and the bone marrow sample (fresh cells or tissues) is subjected to cell disruption and genomic DNA extraction. After extraction, follow the following method to interrupt and build a library. This embodiment is applicable to all human fresh tissue and cell samples.
[0095] 1. Genomic DNA interruption
[0096] 1) Use the Covaris interrupter to fragment the genomic DNA to the required main band range: PE50 recommends a main band of about 180bp, PE100 recommends a main band of about 280bp, and PE150 recommends a main band of about 420bp.
[0097] Check that the liquid level of the deionized water injected into the Covaris tank reaches or exceeds the running mark, and ensure that the water level is not above the glass part of the broken tube; refer to the Covaris instrument instruction manual for experimental operation;
[0098] Table 1
[0099] ...
Embodiment 2
[0180] Example 2 CNV Detection
[0181] (1) According to the method of Example 1, complete the library sequencing of the samples, obtain off-machine data, filter out low-quality reads, and use the comparison software (bwa) to compare these sequencing reads to the human reference genome .
[0182] (2) Filter the comparison results, require the comparison quality value to be >30, remove duplicate reads, abnormally paired reads, etc. Use the tools in bedtools to get the alignment start position of reads1.
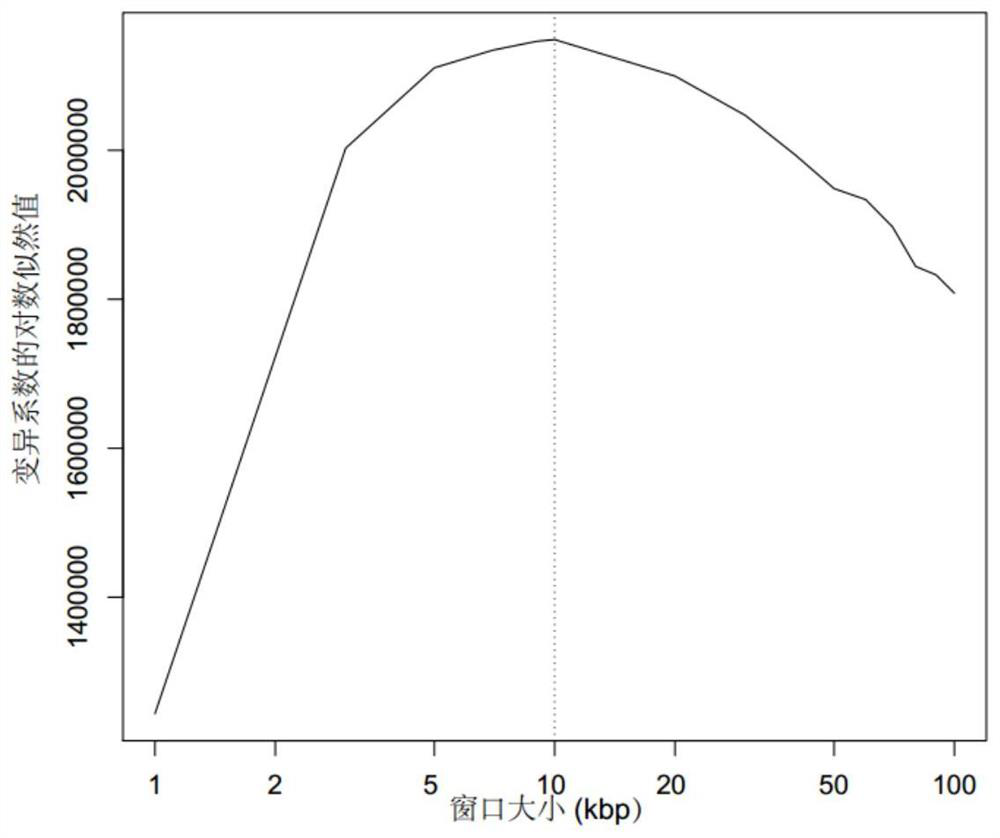
[0183] (3) According to the starting position of the comparison, the inventor calculated the Akaike's information criterion (Akaike's information criterion) and cross-validation logarithmic likelihood estimation corresponding to different intervals through the published method (Gusnanto et al. (2014)) Value (Cross validation Log-likelihood). like figure 2 As shown in , select the interval size corresponding to the minimum AIC value (or the maximum log-likelihood value), a...
Embodiment 3
[0199] Example 3 CNV Large Fragment Variation Type Detection
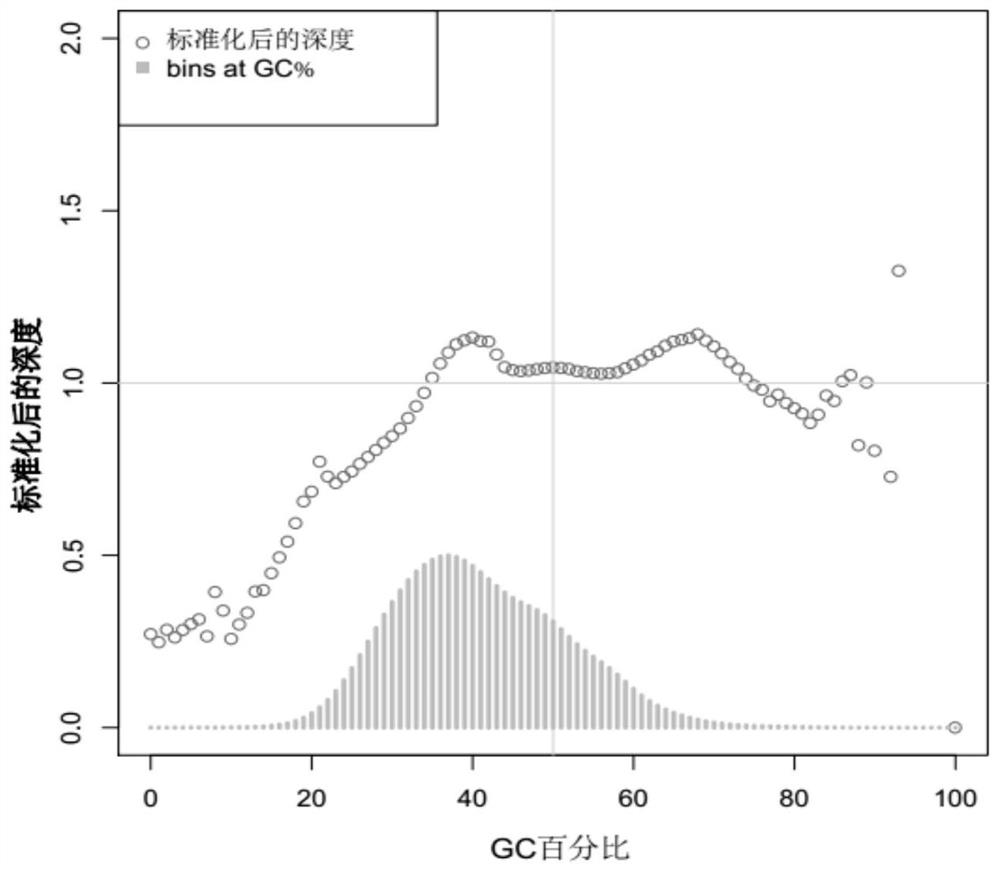
[0200] (1) Obtain the fragment size of CNV (the number of bins contained in the fragment) and the log R ratio corresponding to the fragment based on the analysis method in Example 2. The sample comes from a normal person. According to the above results, it can be seen that the smaller the length, the larger the value of logR (the smaller the negative number becomes). Therefore, a dynamic cutoff method was constructed based on the genome fragments of different sizes and the corresponding logR detected from about 500 normal people (without CNV mutation).
[0201] (2) According to the sequencing analysis results of the normal population, analyze the size of the fragment and the corresponding log R ratio. It is found that as the number of biomarkers contained in the fragment increases (that is, the length of the fragment becomes larger), the fluctuation range of log R ratio is significantly reduced. Therefore, it can b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com