Long-chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) for inhibiting J subtype avian leukosis virus as well as vector and application thereof
A long-chain non-coding, viral technology, applied in viruses/bacteriophages, DNA/RNA fragments, and stably introducing foreign DNA into chromosomes, etc., can solve the problems of no vaccine and effective antiviral drugs, and achieve inhibition of ALV-J Effects of virus infection and replication capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
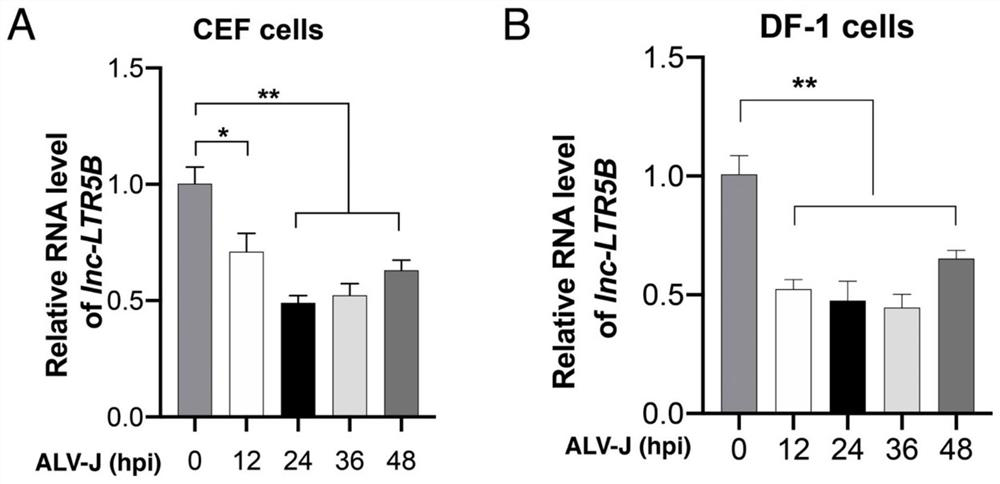
[0032] Effect of ALV-J infection on the expression level of lnc-LTR5B
[0033] ALV-J infected CEF and DF-1 cells, and the expression level of lnc-LTR5B at different infection time points was determined by fluorescent quantitative PCR. Specific steps are as follows:
[0034] CEF and DF-1 cells were spread in 12-well plates, and when the cell confluency reached 70%, the medium was replaced with serum-free DMEM, and ALV-J virus (JS09GY3 strain) at MOI 0.1 was added to incubate at MOI 0.1, and set uninfected control group. After 2 hours of infection, the medium was replaced with maintenance medium containing 2% fetal bovine serum (containing 1% penicillin / streptomycin).
[0035] After 12, 24, 36 and 48 hours of infection, the total RNA of CEF cells and DF-1 cells was extracted, reverse-transcribed into cDNA, and the expression level of lnc-LTR5B was detected by fluorescent quantitative PCR. The primer sequences were as follows:
[0036] Upstream primer q-lnc-LTR5B-F:
[0037] ...
Embodiment 2
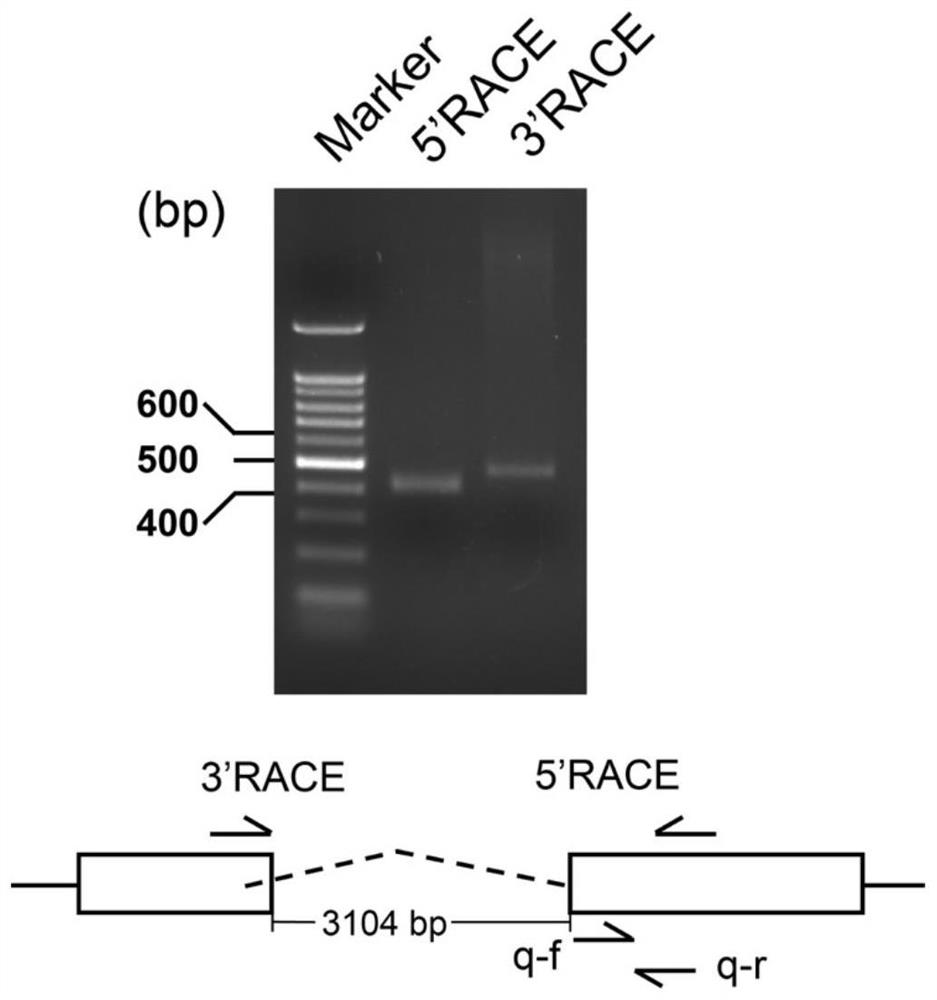
[0042] Amplification of the full-length nucleotide sequence of lnc-LTR5B by RACE method
[0043] (1) RACE technology identifies the 5' and 3' end sequences of lnc-LTR5B
[0044] Depend on RACE 5' / 3'Kit Kit (Takara, #634859) to complete. First, use Reagent was used to extract the total RNA of chicken embryo fibroblast CEF, and then use RNase-free DNase I to remove the genome. Under the action of SMART ScribeReverse Transcriptase (provided by the RACE kit), 1 μg of genome-deleted RNA was reverse-transcribed into 5′- or 3′-RACE products, respectively.
[0045] Then, follow Instructions for the operation of the RACE 5' / 3' Kit kit, using the universal primer UPM and the 5'-end or 3'-end gene-specific primers (gene-specific primer, GSP) for PCR amplification (RACE agarose gel Electropherogram see figure 2 ), cloned and sequenced to obtain the 5' end and 3' end sequences of lnc-LTR5B for later identification of the end sequence of lnc-LTR5B. Wherein, the nucleotide sequen...
Embodiment 3
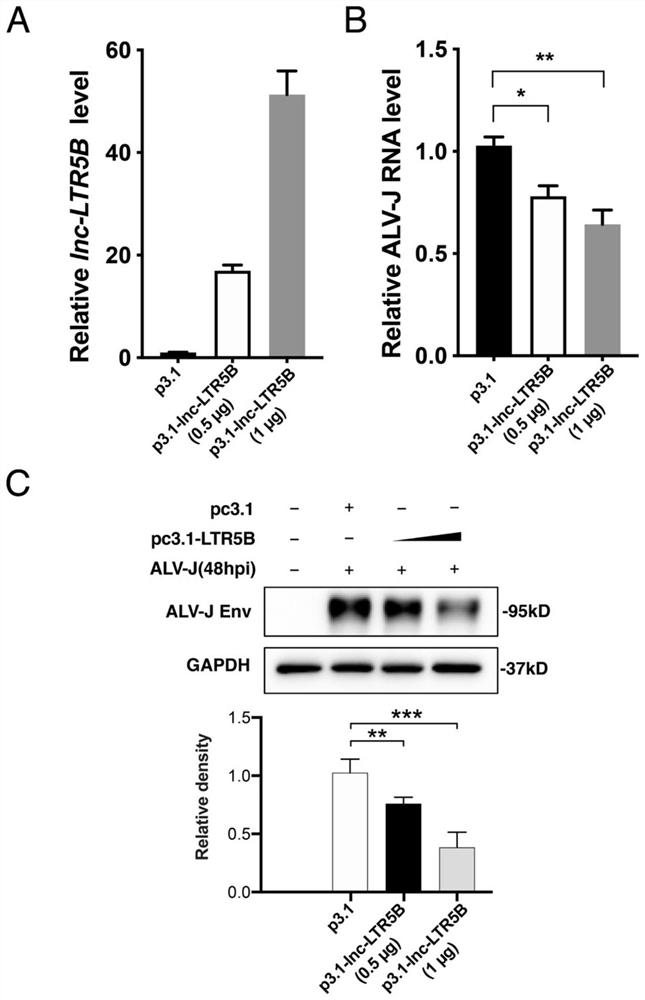
[0058] lnc-LTR5B overexpression vector construction
[0059] In this example, the full-length sequence of lnc-LTR5B obtained in Example 2 was used to design full-length amplification primers to construct an lnc-LTR5B overexpression plasmid. Specifically include the following steps:
[0060] (1) Total RNA was extracted from chicken embryo fibroblast CEF by using TRIzol method, and after the genome was removed with RNase-free DNase I, it was reverse transcribed into cDNA using PrimeScript RT reagent Kit (Takara, #RR047A).
[0061] (2) Using the cDNA product obtained in step (1) as a template, use a high-fidelity enzyme to amplify the full-length sequence of lnc-LTR5B with homology arms, wherein the primers RT-lnc-LTR5B-F and RT-lnc- The nucleotide sequence of LTR5B-R is as follows:
[0062] RT-lnc-LTR5B-F:
[0063] 5'-ACCCAAGCTGGCTAGCGTTTCTCTTGCTGGCTGCACAG-3' (SEQ ID NO.8)
[0064] RT-lnc-LTR5B-R:
[0065] 5'-GGCTGATCAGCGGGTTTTTTCTTTGAGTTGCAGGTTA-3' (SEQ ID NO.9)
[0066] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com