Method and performing blood cell counts
A technology of white blood cells and red blood cells, applied in the field of assessing the components in whole blood samples, can solve the problems of no guarantee, time-consuming and expensive dilution process, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding costs and problems, eliminating purchases and avoiding the possibility of errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
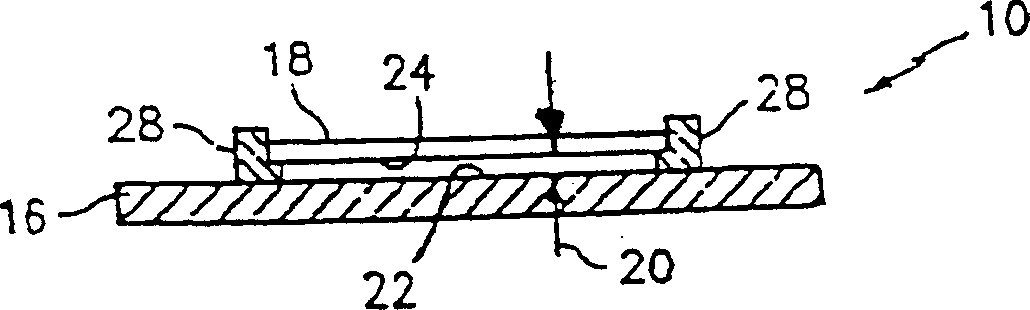
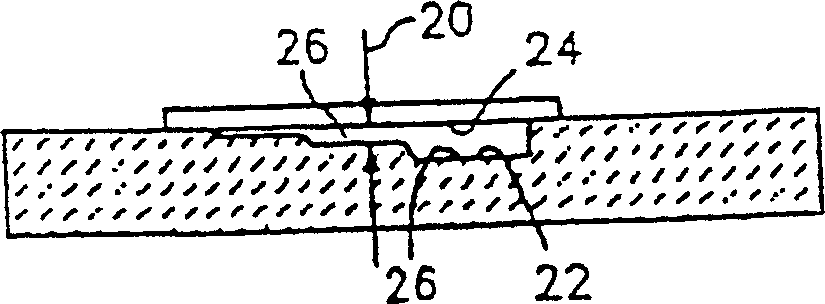
[0036] refer to Figure 5 and 6 , WBC's 34 in anticoagulated whole blood samples admixed with a small amount of sensitive colorant can be assessed within the sample chamber 10 having a through plane approximately equal to 20 μm through the sample chamber 10 or a portion of the sample chamber 10 Thickness 20 (see Figure 2~4 ). EDTA is an example of an applicable anticoagulant, and the brightest fluorescent ultra-reactive stains (such as Acridine Orange, Basic Orange-21, etc.) are examples of applicable sensitive stains. A chamber through-plane thickness 20 of about 20 [mu]m was selected for two reasons. First, the assessment volume contains a suitable number of WBC's 34 for detection; The sample volume being evaluated is generally determined by the cross-sectional area of the evaluation viewing zone 38 and the through-plane thickness 20 of the sample. As previously mentioned, several methods can be applied to optimize the exact through-plane thickness 20 of the viewing ...
Embodiment II
[0038] The method described in Example 1 can be used to assess platelets 36 in anticoagulated whole blood samples. Since platelets are present in much greater quantities than WBC's 34, a chamber region with a through-plane thickness 20 of about 5 [mu]m in size is used. Each viewing zone 38 having a one square millimeter cross-sectional area within a chamber region with a through-plane thickness 20 of 5 μm represents a sample volume of .005 μl, so a typical individual will contain about 1250 platelets 36 . Platelets can be assessed using the same brightest fluorescent hyperactive stains and methods used for WBC's34. Platelets 36 can be assessed in the same chamber 10 as used to assess WBC's 34, provided that the chamber has regions of varying through-plane thickness dimensions, such as those described above with sloped, stepped, and / or arcuate walls.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com