Oil cooling structure of driving motor and processing method thereof
A driving motor and oil cooling technology, applied in the manufacture of motor generators, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of high processing cost, limited motor thermal load, limited motor volume, etc., to achieve Reduce the influence of tolerances, avoid misalignment of oil passages, and improve adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
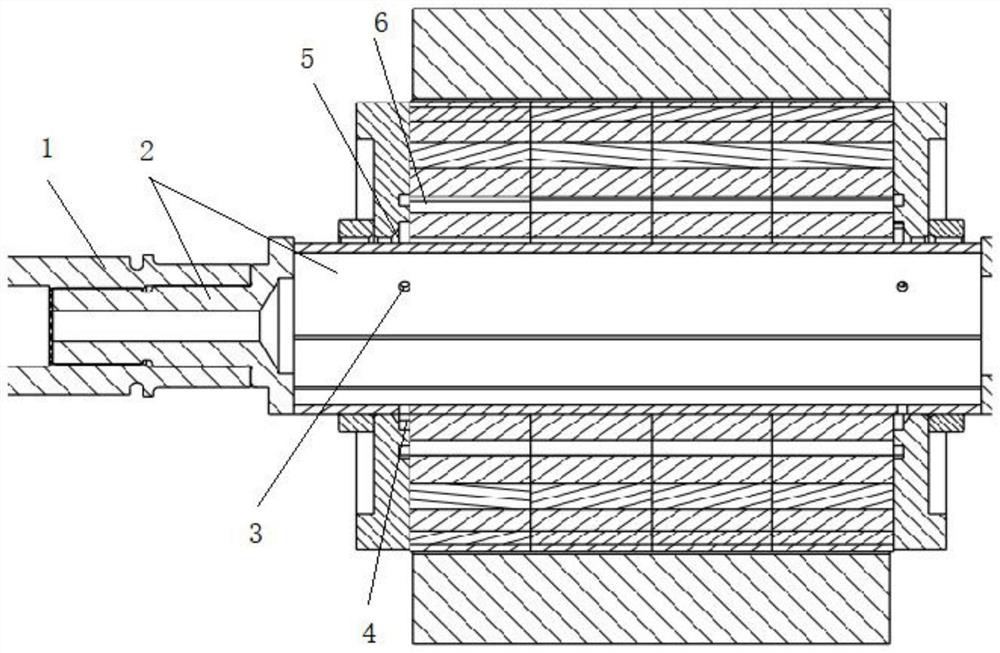
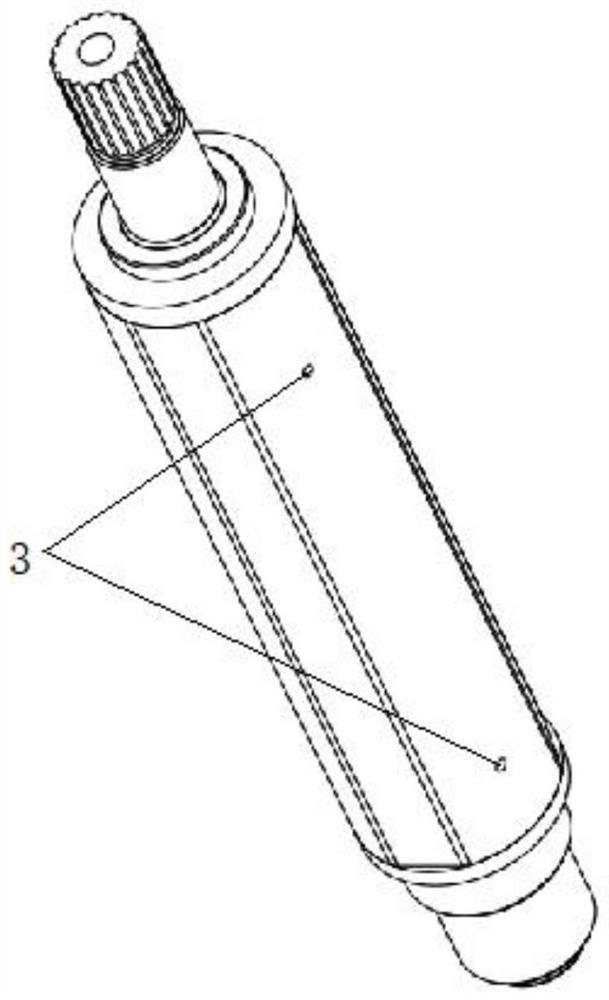
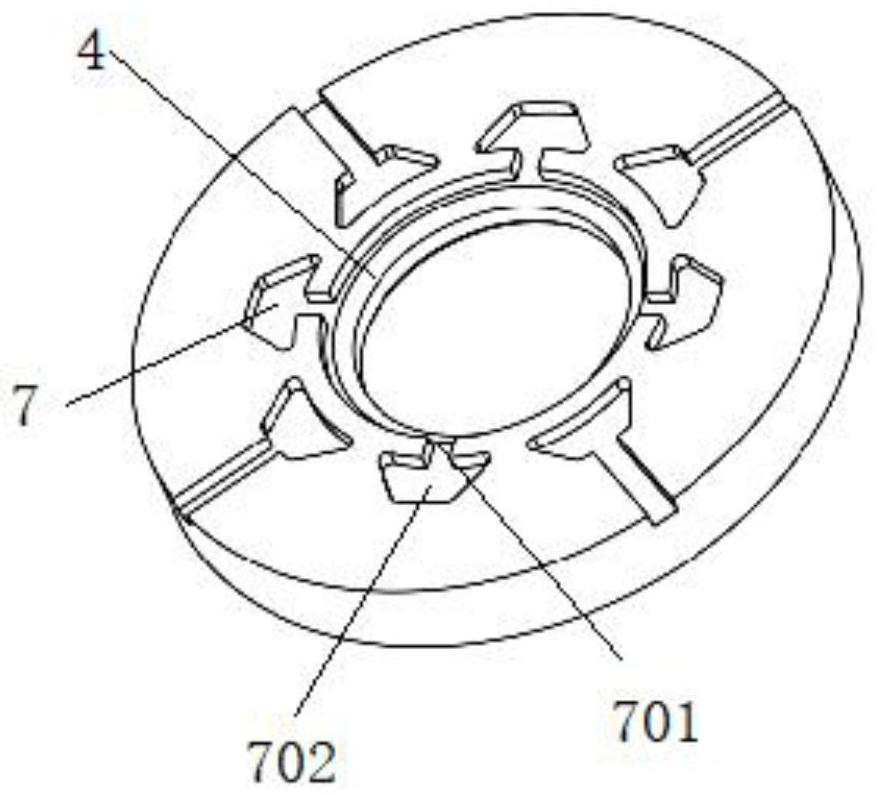
[0062] Embodiment one, see appendix Figure 1-3 The outer surface of the rotor shaft 2 is provided with a first spline, the inner surface of the reducer shaft 1 is provided with a second spline matching the first spline, and the reducer shaft 1 is sleeved on the second part of the rotor shaft 2 In addition, because it is installed outside, it does not extend into the first part of the rotor shaft 2, so it is staggered with the axial position of the balance plate, and the oil guide hole 3 will be directly opened on the inner wall of the rotor shaft 2, and the second oil hole of the balance plate will be directly opened. Corresponds to the location of Road 7.
[0063] See attached Figure 4 , the arrow part is the flow direction of the cooling oil. After the external cooling oil enters the first oil passage in the rotor through the oil inlet passage of the reducer, under the rotation of the rotor, it is dispersed to the inner wall of the rotor shaft 2 due to the centrifugal for...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment two, see appendix Figure 5-7The inner surface of the rotor shaft 2 is provided with a first spline, the outer surface of the reducer shaft 1 is provided with a second spline matching the first spline, and the reducer shaft 1 is sleeved on the first part of the rotor shaft 2 In the first oil passage, in order to further reduce the axial size of the reducer shaft 1 and the rotor shaft 2, the reducer shaft 1 will extend into the first part of the rotor shaft 2, and at this time it will coincide with the axial position of the balance plate, The oil guide hole 3 corresponding to the radial position of the second oil passage 7 (or the first ring groove 4) of the balance disc on the inner surface of the rotor will be blocked, so that the oil cannot circulate, so in this embodiment, the rotor shaft 2 The first spline on the reducer shaft 1 and the second spline on the reducer shaft 1 are disconnected at the same position, so that when the two splines cooperate, a ga...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment three, see appendix Figure 9-11 , the same as the second embodiment, the reducer shaft 1 is sleeved in the first oil passage of the first part of the rotor shaft 2, and extends into the first part of the rotor shaft 2, and coincides with the axial position of the balance plate, blocking the The oil guide hole 3 on the inner surface of the rotor corresponding to the radial position of the second oil channel 7 (or the first ring groove 4 ) of the balance plate prevents oil from circulating.
[0071] The difference from Embodiment 2 is that in this embodiment, the second oil guide hole 302 on the wall surface of the first oil passage includes a first sub-path 30201 and a second sub-path 30202 that intersect, and the first sub-path 30201 has a diameter of The second sub-channel 30202 is axially arranged on the second part of the rotor shaft 2 and communicates with the second oil passage 7 and the rotor shaft 2 outer walls. One end of the first sub-channel 3020...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com