Rated capacity type selection method for commercial vehicle valve-regulated lead-acid storage battery
A technology of lead-acid battery and rated capacity, which is applied in the direction of measuring electrical variables, measuring electricity, and measuring devices, which can solve the problems of high cost of selection and long selection cycle, and achieve accurate and reasonable calculation results, good adaptability, and calculation precise effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
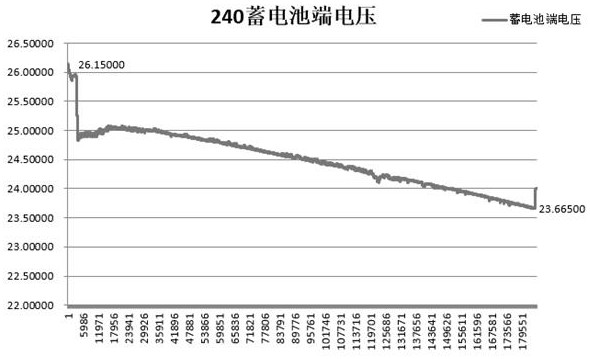
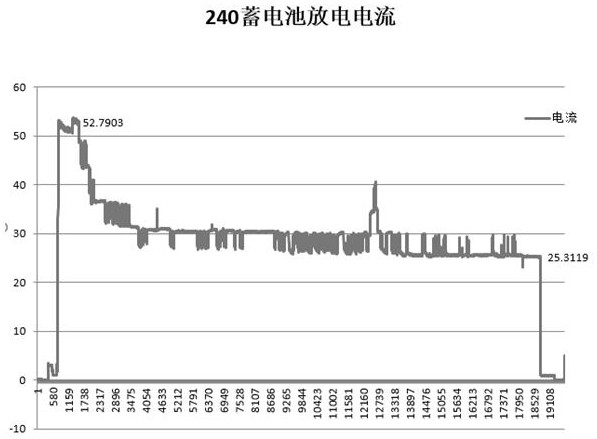
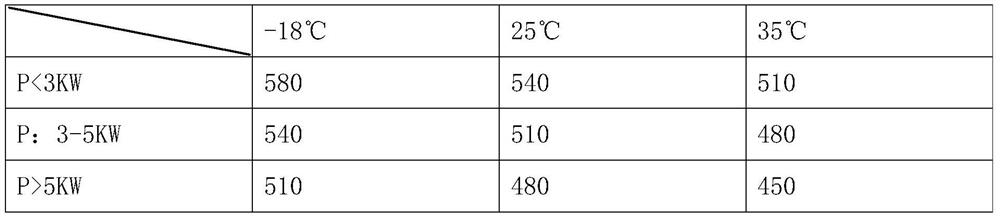
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0136] A method for selecting a rated capacity of a commercial vehicle valve-regulated lead-acid battery, comprising the following steps:
[0137] The first step is data collection and sorting: collect the power consumption information of each electric device for the vehicle to be selected, sort out and classify the battery power consumption items and power consumption time;
[0138] The second step is to establish a demand model: to establish a power consumption model required to meet the specific needs of high-power electrical equipment. Electricity demand and parking high-power equipment power demand are respectively established according to the power demand: start-up power demand model, static power demand model and conventional power consumption and parking high-power equipment power demand model;
[0139] The third step is to calculate the power consumption: according to the characteristics of the battery and the geographical distribution information, calculate separatel...
Embodiment 2
[0142] Embodiment 2 is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and its difference is:
[0143] In the first step, during data collection and sorting, the power consumption information collected for different types of power consumption equipment on the vehicle to be selected is different, and the specific content is as follows:
[0144] For conventional power demand equipment, it collects: working rated current, use frequency coefficient and 4-hour power consumption information;
[0145] For starting electrical equipment, collect its: starter power information;
[0146] For the static power demand, collect the static current information of each electrical appliance on the vehicle to be selected, and sum the static current of all electrical appliances to obtain the static current I of the whole vehicle S ;
[0147] According to the power demand of parking high-power equipment, collect its power consumption information in different use environments: rated power, rated current, work...
Embodiment 3
[0197] Embodiment 3 is basically the same as Embodiment 2, and its difference is:
[0198] In the first step, during data collection and sorting, the power consumption information collected for different types of power consumption equipment on the vehicle to be selected is different, and the specific content is as follows:
[0199] For conventional power demand equipment, collect its: working rated current, use frequency coefficient and 4-hour power consumption information; in ACC mode, the working parameters of electrical equipment are as follows: Table 3:
[0200] Regular electrical equipment Current (A) Frequency coefficient 4h consumption of C A (Ah)
ECU 0.005 1 0.02 T-BOX 0.005 1 0.02 Smart car 2 0.3 2.4 meter 0.08 1 0.32 BCM logic circuit 0.21 1 0.84 ACC relay 0.08 1 0.32 heater relay 0.08 1 0.32 cigarette lighter 5 0.0025 0.05 Interior lights (night) 0.63 0.5 1.26
[0201] Fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com