Safe low-concentration electrolyte for lithium battery and application of safe low-concentration electrolyte
A lithium battery and electrolyte technology, which is applied in the field of low-concentration electrolyte for lithium batteries, can solve the problems of not being able to balance high performance and high safety, and reduce the cost of electrolyte, so as to improve cycle stability and reduce the amount of free solvent molecules , the effect of high commercialization prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
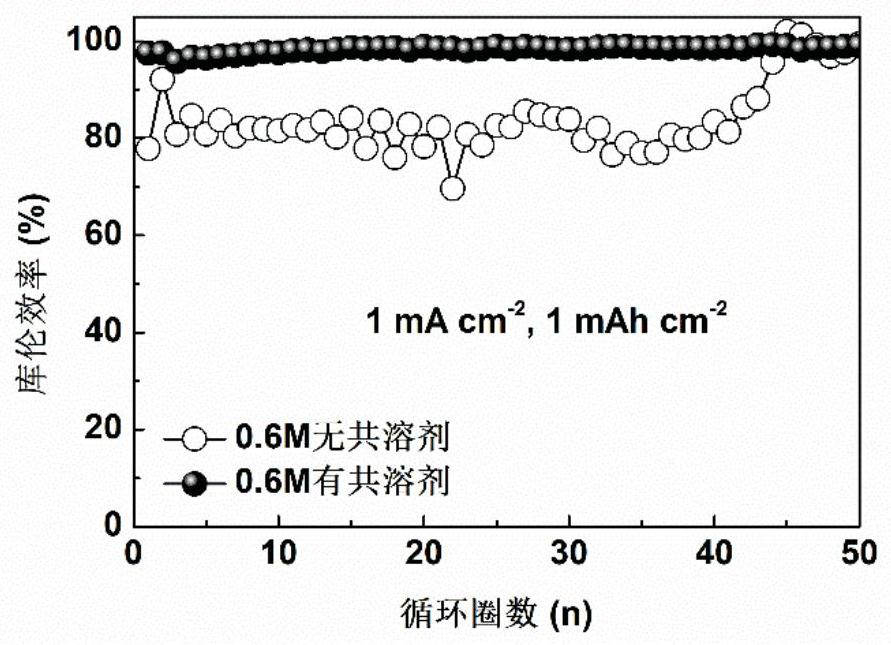
[0043] The lithium salt concentration is respectively configured as 0.6M without co-solvent (specifically 0.3M LiDFOB+0.3M LiBF 4 dissolved in FEC solvent) and 0.6M added co-solvent (specifically 0.3M LiDFOB+0.3M LiBF 4 Dissolved in the mixed solvent of FEC / TTE, the volume ratio of FEC and TTE is 1:1) low-concentration electrolyte, using the above electrolyte, lithium sheet, copper sheet, and diaphragm to assemble into a lithium-copper half-cell, and at 1mA cm -2 The Coulombic efficiency test is carried out under the current density, such as figure 1 As shown, in the 0.6M no co-solvent control group, the average coulombic efficiency of the lithium anode was lower than 90%, while in the 0.6M co-solvent addition experimental group, the average coulombic efficiency of the lithium anode was close to 100%. This example demonstrates that the addition of co-solvents has an important effect on the properties of low-concentration electrolytes.
Embodiment 2
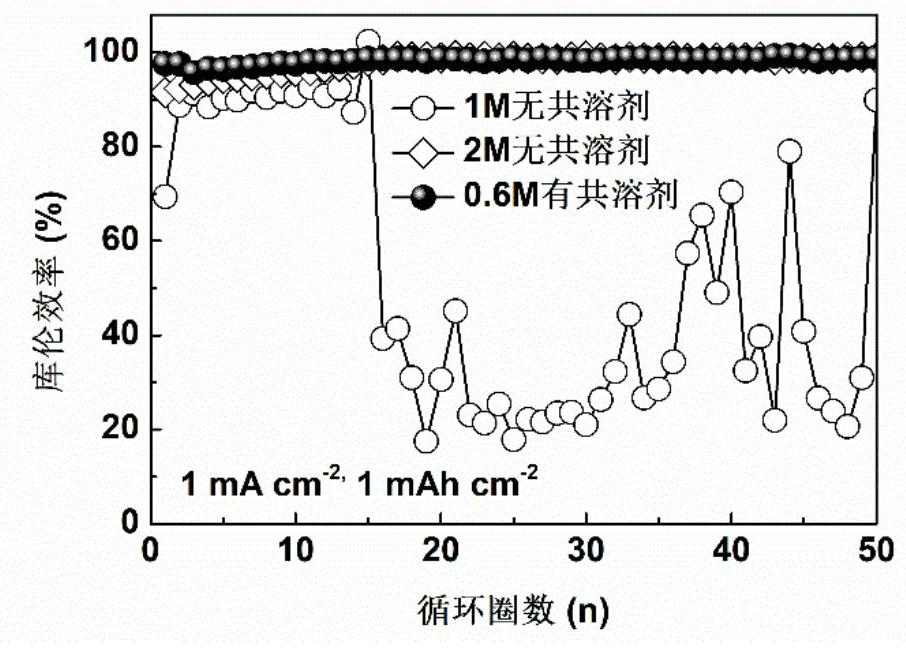
[0045] The concentration of lithium salt is respectively configured as 1M without co-solvent (specifically 0.5M LiDFOB+0.5M LiBF 4 soluble in FEC solvent), 2M without co-solvent (specifically 1M LiDFOB+1M LiBF 4 dissolved in FEC solvent) and 0.6M added co-solvent (specifically 0.3M LiDFOB+0.3M LiBF 4 Dissolved in the FEC / TTE solvent, the volume ratio of FEC and TTE is 1:1) low-concentration electrolyte, using the above electrolyte, lithium sheet, copper sheet, and diaphragm to assemble into a lithium copper half-cell, and at 1mA em -2 The Coulombic efficiency test is carried out under the current density, such as figure 2 As shown, in the 1M no co-solvent control group, only 10 weeks of stable circulation can be achieved, while the performance of the 0.6M co-solvent addition experimental group and the 2M no co-solvent control group is similar, and the lithium anode can be stably circulated. This example shows that by adding a co-solvent to a low-concentration electrolyte, e...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Configure the lithium salt concentration as a single lithium salt (specifically 0.6M LiBF 4 Dissolved in FEC / TTE solvent, the volume ratio of FEC and TTE is 1:1) and mixed lithium salt (specifically 0.3M LiDFOB+0.3M LiBF 4 Dissolved in the solvent of FEC / TTE, the volume ratio of FEC and TTE is 1:1) low-concentration electrolyte, using the above electrolyte, lithium sheet, copper sheet, and diaphragm to assemble into a lithium copper half-cell, and at 1mA cm -2 The Coulombic efficiency test is carried out under the current density, such as image 3 As shown, in the single lithium salt control group, the coulombic efficiency of the lithium anode gradually decreases, while in the mixed lithium salt experimental group, the coulombic efficiency of the lithium anode can remain stable. This example shows that the use of mixed lithium salts in low-concentration electrolytes has superior performance over single lithium salts.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com