Method for preparing hydrogen or reducing gas by ammonia cracking through two-stage process
A hydrogen and method ammonia technology is applied in the petrochemical field to achieve the effect of saving heat source, pressure energy consumption and heat source.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] The flow process of the two-stage ammonia cracking hydrogen production of the present embodiment is as follows:
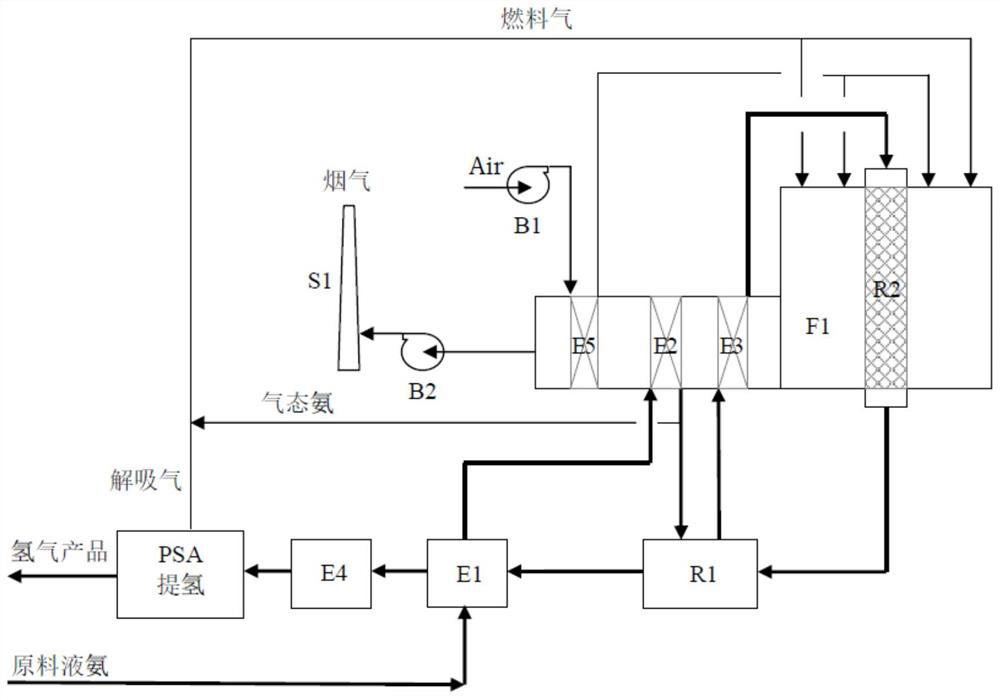
[0050] Process such as figure 1 shown. In this example, the raw material liquid ammonia has a flow rate of ~50800kg / h, a temperature of normal temperature, and a pressure of ~1.5MPa(G). It is first partially gasified by the raw material preheater (E1) and then heated by the raw material gasifier (E2). The high-temperature flue gas of the furnace completely vaporizes the raw material liquid ammonia. Except a small part of gaseous ammonia is used as supplementary fuel gas (flow rate ~ 800kg / h), the rest is sent to the first heat exchange ammonia cracking reactor (R1) for partial ammonia cracking reaction. The first-stage heat exchange ammonia cracking reaction system (R1) is set as a reactor with heat exchange, the reactor is equipped with a catalyst, and the required heat source is provided by heat exchange of the second-stage high-temperature ammonia crack...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The flow process of the two-stage ammonia cracking hydrogen production of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0055] Process such as figure 2 shown. In this embodiment, the raw material liquid ammonia has a flow rate of ~50000kg / h, a temperature of normal temperature, and a pressure of ~3.0MPa(G). It is first partially vaporized by the raw material preheater (E1) and then heated by the raw material gasifier (E4). The high-temperature flue gas of the furnace completely vaporizes the raw material liquid ammonia. The gaseous ammonia enters the first-stage heat exchange ammonia cracking reaction system, and the first-stage heat exchange ammonia cracking reaction system is set as a separate secondary raw material heater (E2) and a separate first-stage adiabatic reactor (R1). Gaseous ammonia enters the secondary raw material heater (E2), is heated to 550-650°C by the reaction gas at the outlet of the second-stage high-temperature reactor, and then sent to the adiabatic...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The flow process of reducing gas produced by the two-stage ammonia cracking of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0060] Process such as image 3 shown. In this example, the raw material liquid ammonia has a flow rate of ~6400kg / h, a temperature of normal temperature, and a pressure of ~0.8MPa(G). It is first partially vaporized by the raw material preheater (E1) and then heated by the raw material gasifier (E3). The high-temperature flue gas of the furnace completely vaporizes the raw material liquid ammonia. The gaseous ammonia enters the first-stage heat exchange ammonia cracking reaction system, and the first-stage heat exchange ammonia cracking reaction system is set as a separate secondary raw material heater (E2) and a separate one-stage adiabatic reactor (R1), and the reactor is equipped with catalyst. Gaseous ammonia enters the secondary raw material heater (E2) and is heated by the reaction gas at the outlet of the second-stage high-temperature reactor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com