QSPR method and system for constructing interpretable XGBoost regression model to predict PCE based on SHAP value
A regression model and model technology, applied in the field of prediction of power conversion efficiency, can solve problems such as the difficulty of understanding the internal principles of machine learning models, and achieve the effects of shortening R&D time, high performance, and reducing R&D costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
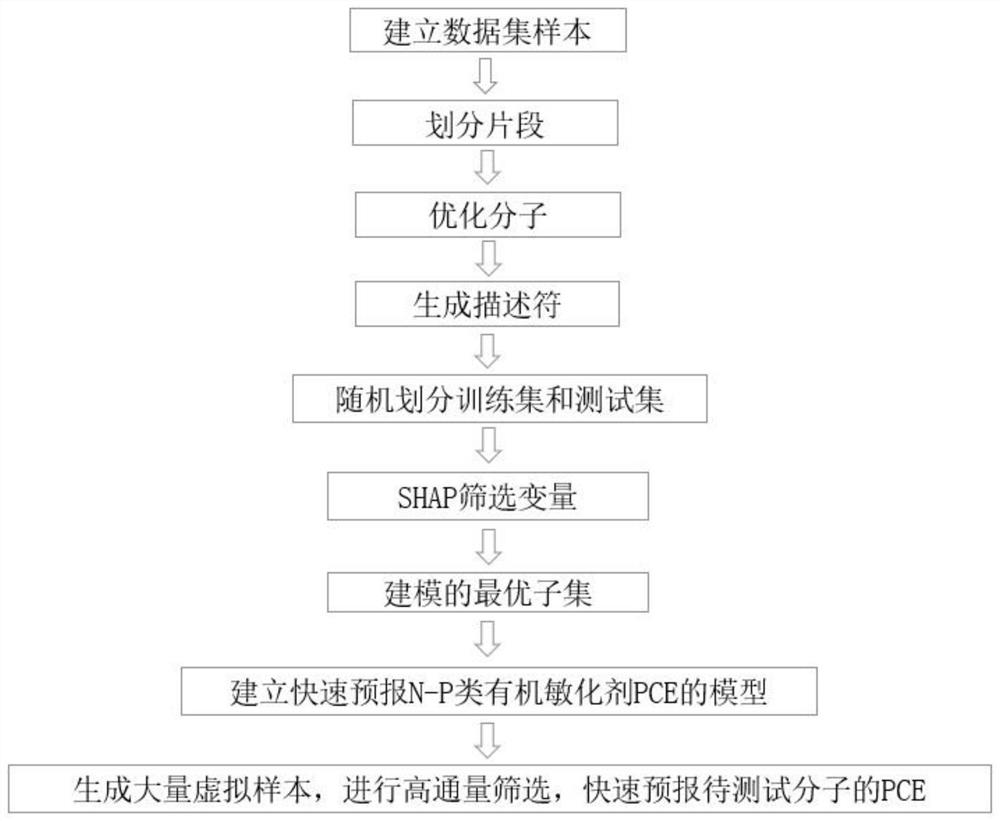
[0041] In this example, see figure 1 , a QSPR method for constructing an interpretable XGBoost regression model to predict PCE based on SHAP values, including the following steps:
[0042] 1) Use a computer system to search for literature, and search for the structure of N-P dye molecules, electrolyte conditions and their corresponding PCE values from the literature;
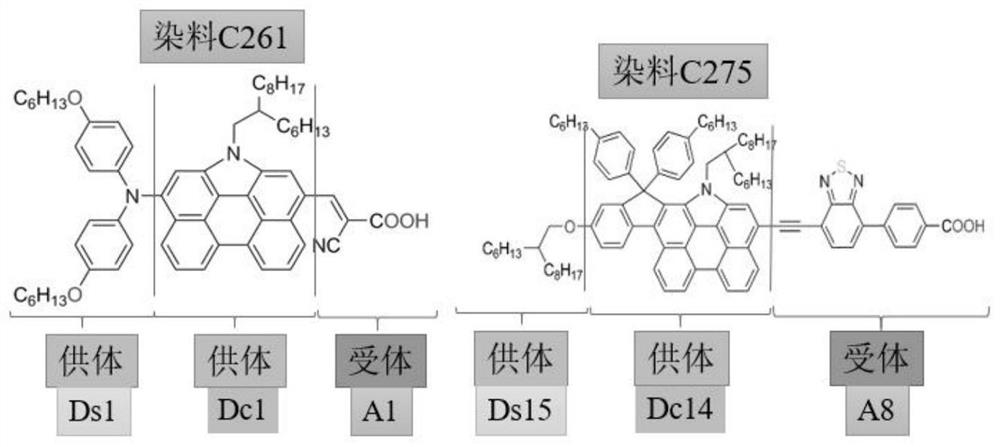
[0043] 2) Divide the collected dye molecules into three fragments, the first two fragments are Ds (Doner Space) and Dc (Doner Core), the first two fragments are donors with electron-pushing groups, and the last fragment is A (Accepter ), an acceptor with an electron-withdrawing group, and the last fragment prepares for subsequent interpretation of fragment effects and high-throughput screening;
[0044] 3) Use ChemDraw to draw the fragment structure of the dye molecule, optimize the molecule through MM2-Minimize energy in chem3D, and then use Dragon software to generate a descriptor; optimize the molecule thr...
Embodiment 2
[0055] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
[0056] In this embodiment, in the step 1), after searching for documents, the obtained data samples are preprocessed, including sorting out the molecular structure, electrolyte conditions and PCE of the samples, and determining the number of sample data.
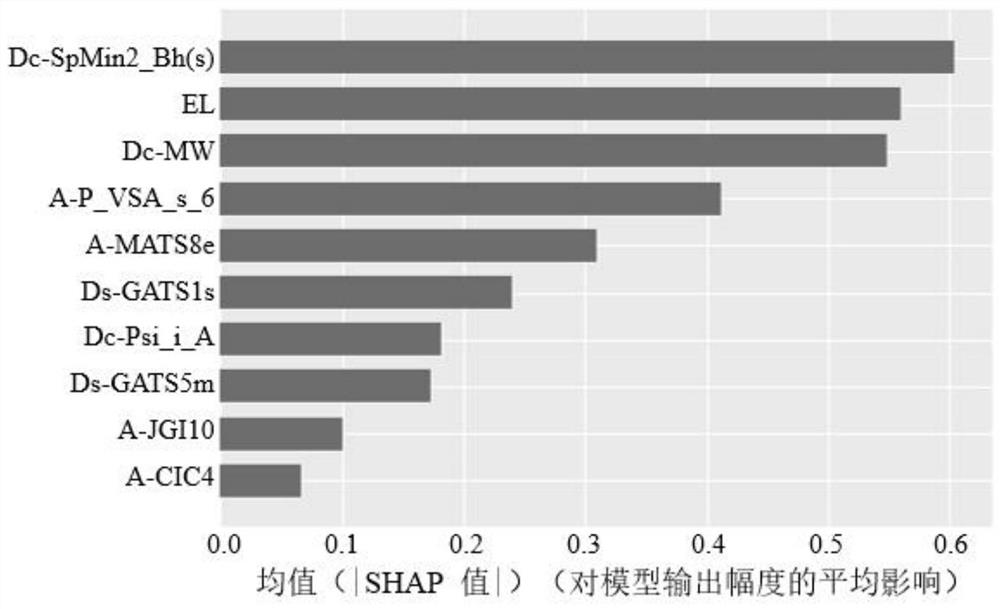
[0057] In this embodiment, in the step 6) and step 7), for a certain characteristic variable, use TreeSHAP to calculate the SHAP value corresponding to the variable in all samples, and use its average value as the importance value of the characteristic variable , so as to get a global explanation; use the SHAP nested XGBoost method to screen variables, start from an initial naive model, based on the error of the observation value in the sample set, build a new model for fitting, and add it to the existing model in the form of addition, and iterate this model repeatedly The process forms an integrated model.
[0058] In this example, the opti...
Embodiment 3
[0065] This embodiment is basically the same as the above-mentioned embodiment, and the special features are:
[0066] In this embodiment, the step 2) divides the collected dye molecules into three segments according to the group empirical rules of electron-withdrawing and electron-pushing abilities, the Ds and Dc fragments are electron-pushing donors, and the A fragment is Electron-withdrawing acceptors are prepared for subsequent interpretation of fragments and high-throughput screening; the junctions of fragments are replaced by free radicals. For examples of specific division methods, see figure 2 , instances of subsequent fragments are replaced by letters.
[0067] In this embodiment, in the step 3), use ChemDraw to draw the 2D structure of the collected N-P dye molecules, then simply calculate the optimal structure of the molecule in Chem3D-Calculations-MM2-Minimize Energy, and finally use the Dragon software Generate corresponding descriptors.
[0068] In this embodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com