Path planning method, path planning system, robot and storage medium
A technology for path planning and robotics, applied in the field of robotic algorithms, it can solve problems such as slow planning of large maps, and achieve the effects of improving preprocessing efficiency, improving search efficiency, and reducing search space.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] A path planning method provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
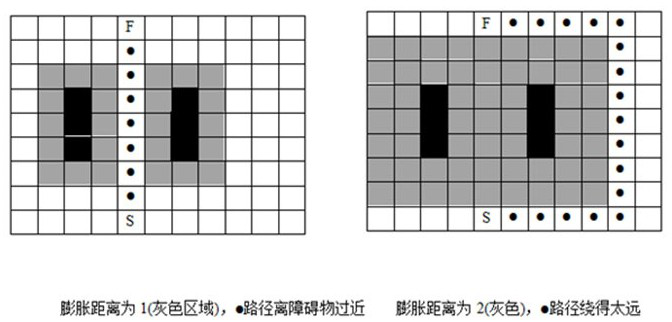
[0057] Step 1: Set the minimum expansion distance d_min and the maximum expansion distance d_max.
[0058] Step 2: Accept the original grid map that needs to be planned, and generate a new map type distmap according to d_min and d_max. Step 2 includes the following steps:
[0059] Step 2.1: Add all occupied grids in the original grid map to the pending queue occ_list, and initialize the dist value of the unoccupied grid to d_max, where the dist value is the distance from the unoccupied grid to the occupied grid The minimum distance, d_max is the maximum expansion distance;
[0060] Step 2.2: Record each occupied grid in occ_list as grid point p_i, add surrounding unoccupied grids to dist_expand_list, and calculate the dist value of each unoccupied grid from p_i; for example: if The coordinates of p_i are (p_i_x, p_i_y), and the unoccupied grid is (x_, y_), then dist is the distance betw...
Embodiment 2
[0073] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a path planning system, adopting the path planning method provided in Embodiment 1, including the following modules:
[0074] Setting module: set the minimum expansion distance d_min and the maximum expansion distance d_max;
[0075] Mapping module: accept the original grid map that needs to be planned, and generate a new map type distmap according to d_min and d_max;
[0076] Input module: input the start point and end point in the distmap, and list the start point as the current point P';
[0077] Calculation module: judge whether the adjacent grid of the current point P' is passable, and calculate the cost value of the adjacent grid according to the new heuristic function O(x);
[0078] Heap building module: Add passable points near P' to the openlist queue, and build a minimum heap according to the cost value of each point;
[0079] Judging module: judging whether P' is the end point, otherwise repeatedly exec...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Those skilled in the art can understand this embodiment as a more specific description of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2.
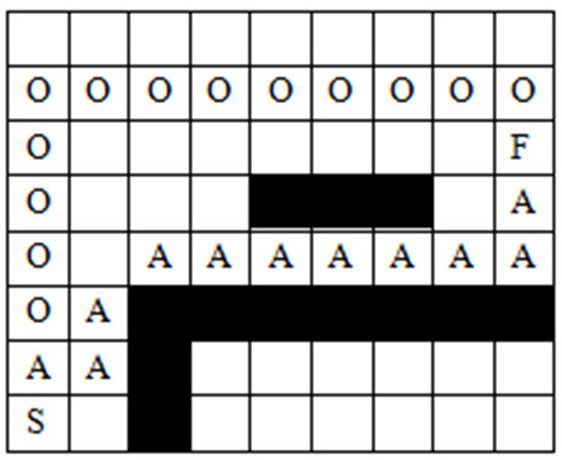
[0082] Such as Figure 1~3 As shown, a path planning method provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0083] Step 1: Set the minimum expansion distance d_min and the maximum expansion distance d_max;
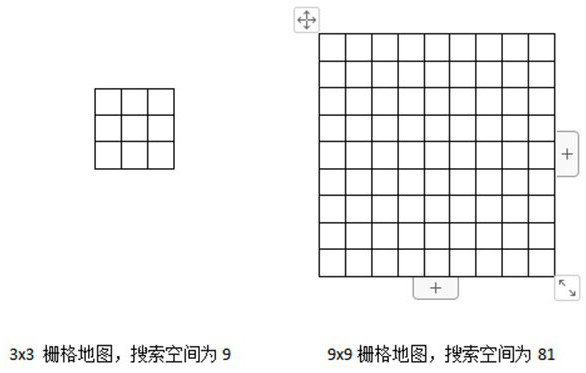
[0084] Step 2: Accept the original grid map that needs to be planned, and generate a new map type distmap according to d_min and d_max (in this step, the search space for path planning is dynamically reduced);
[0085] Step 3: Enter the start point and end point, and list the start point as the current point P’;
[0086] Step 4: Determine whether the adjacent grid of the current point P’ is passable, and calculate the cost value of the adjacent grid according to the new heuristic function O(x) (where O(x) is the key to ensure the shortest route and path safety);
[0087] Step 5: Add the passable points near P' to the openlist queu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com