Compound fungicide containing N-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxyl)phenyl)-3-(difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-amide and procymidone
A technology of chlorophenyl ether amide and fungicides, applied in the direction of fungicides, biocides, biocides, etc., can solve the problems of difficult research and development of fungicides, difficult to launch, etc., to achieve drug resistance, simple use, and good effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1, the bacteriostatic activity of chlorphenamide to boscalid resistance and sensitive strains:
[0030] The sensitivity of boscalid-resistant (R) and sensitive (S) Botrytis cinerea strains (Table 1) to chlorphenamide and other SDHIs was determined by mycelial growth method. Results: The 10 boscalid-resistant (R) strains all showed resistance (R) to flufenapyridine, which is also SDHI, that is, there was complete cross-resistance. 8 of the 10 boscalid-resistant (R) strains, the ratio was 80%, also showed resistance (R) to fluopyram, which is also SDHI. It shows that DHI such as fluopyram and flufenapyr can not effectively control Botrytis cinerea which has developed resistance to boscalid.
[0031] Unexpectedly, the 10 boscalid-resistant (R) strains were all sensitive (S) to chlorphenamide, which is also SDHI. Sensitivity of 10 boscalid-sensitive (S) strains to chlorphenamide, which is also SDHI (EC 50 ) between 1.03-2.28mg / L, with an average of 1.465mg / L; ...
Embodiment 2
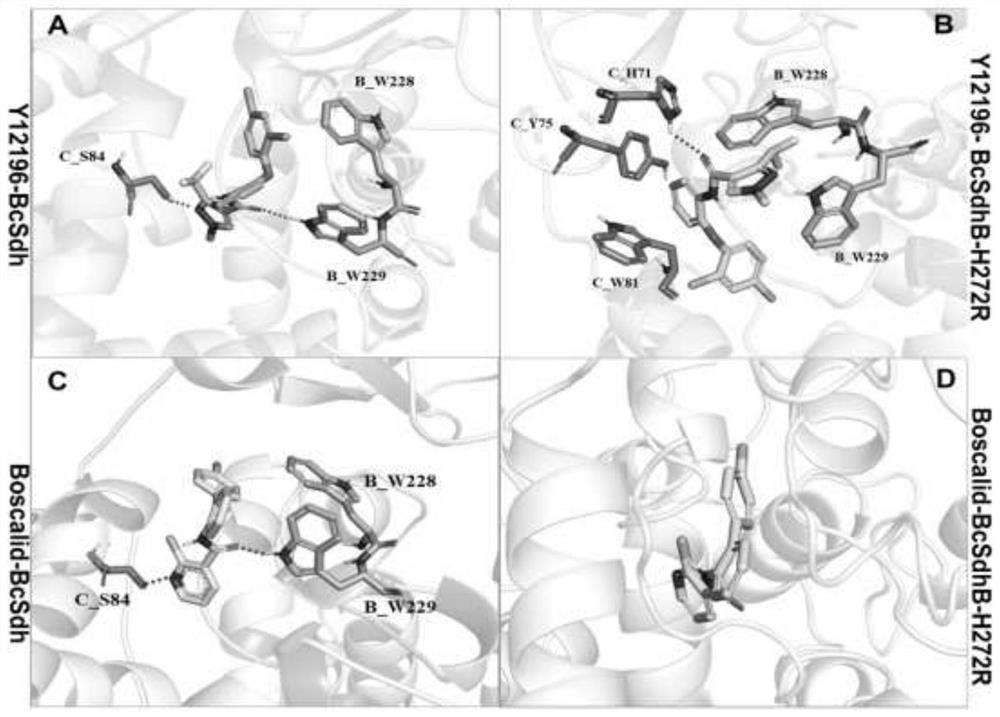
[0034] Example 2. Molecular docking of chlorphenamide and boscalid with SDH proteins of boscalid resistant and sensitive strains
[0035] Chlorphenamide and boscalid belong to the same class of drugs SDHI. Generally speaking, there is cross-resistance between the same type of pesticides, that is, the Boscalid boscalid produced by Botrytis cinerea has developed resistance, so chlorophenyl ether amide can no longer be used for the effective control of resistant botrytis. . However, the present invention unexpectedly finds that the fact does not conform to the general situation, and there is no cross-resistance between chlorphenamide and other SDHIs such as boscalid and flufenapyridine. Existing studies have shown that the resistance of Botrytis cinerea to boscalid is caused by the mutation of the B subunit of succinate dehydrogenase, but there are many related mutation types, among which H272 R / L and P225L / F / T more common. The present invention further analyzes the molecular ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3, Botrytis cinerea population is sensitive to chlorophenyl ether amide
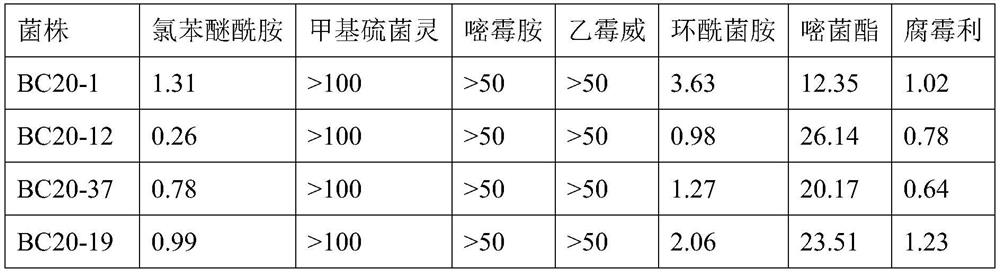
[0038] Collect Botrytis cinerea from grapes, strawberries, tomatoes and other crops, and measure the sensitivity of 239 strains of Botrytis cinerea to chlorophenyl ether amide, and find that 7 (2.9%) bacterial strains cannot be inhibited by chlorophenyl ether amide (Table 2), EC 50 The value is between 12.45-33.85mg / L.
[0039] The present invention selects 4 strains from the above-mentioned 7 gray mold bacterial strains that cannot be inhibited by chlorophenyl ether amide, and selects 4 strains from 232 strains that can be inhibited by chlorophenyl ether amide, and further measures the effect of these bacterial strains on other gray mold Sensitivity of commonly used agents for mildew, the results showed that the strains were more sensitive to procymidone, while thiophanate-methyl, pyrimethanil and diethofocarb had almost no inhibitory activity on these strains, fenhexamid and azoxystr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Ec50 value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com