Mechanical arm kinematics self-calibration method based on binocular vision
A technology of binocular vision and manipulators, which is applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, manual participation, and cumbersome calibration process, achieve accurate readings, reduce the impact of absolute positioning accuracy, and search wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
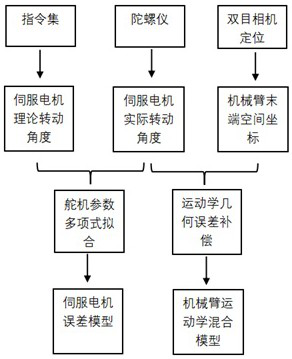
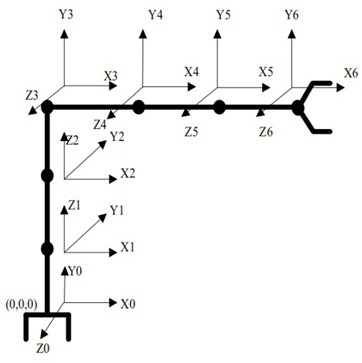
[0052] The embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail below, an example of a binding method based on a binocular visual manipulation figure 1 Down. The embodiments described below are illustrative of the embodiments described with reference to the accompanying drawings, and is not to be construed as limiting the invention.
[0053] Collecting the position information of the robot arm, the engine theory rotation angle, the actual rotation angle of the servo motor, the acquisition method is as follows:
[0054]Optionally, according to the mechanical structure of the robot arm Determines the range of each servo motor command, 50 sets of data is quoted, for any N axis rigid body arm. 50 sets of instructions are randomly generated, each set of instructions contain N servo rotation information, convert the instruction to an angle as a servo motor theoretical rotation angle.
[0055] During the execution of the instruction, the robot uses the gyroscope to collect the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com