Saccharomyces cerevisiae, starter cultures and their use in winemaking
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and leavening agent, which is applied in the field of fermentation to achieve the effects of low content of undesired flavor substances, good flavor and fast fermentation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0037] Its preparation method can be a conventional preparation method in the art.
[0038] The third aspect of the present invention provides a method for preparing a starter, the method comprising carrying out fermentation and cultivation of the above-mentioned Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a fermentation medium.
[0039] According to the present invention, the fermentation medium can be various conventional mediums for cultivating Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the art, for example, it can be YPD medium, WL medium or grape juice simulated medium as mentioned above. Medium suitable for culturing Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
[0040] According to the present invention, Saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No. 22616 can be fermented and cultivated in the fermentation medium, and the number of live bacteria can reach 10 8 More than CFU / mL, the fermented liquid obtained can be used as a liquid starter.
[0041] Preferably, the conditions of the fermentation culture include: the temperature ...
Embodiment 1
[0063] This example illustrates that Saccharomyces cerevisiae ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) separation, purification and identification.
[0064] The grape juice from the Huaizhuo Basin production area was used for laboratory small-scale fermentation. The unsterilized grape juice was added to the fermentation container and fermented at a constant temperature of 25°C. The reducing sugar content is detected during the fermentation process, and samples are taken at different stages of fermentation according to the consumption of reducing sugar. The samples were serially diluted and spread on the WL medium plate. After the wine yeast grew out, the strains with good growth and obvious characteristics were selected for colony morphology and molecular biological identification (5.8 S-rDNAITS method) , and then used the high-throughput platform to carry out tolerance screening experiments on the identified Saccharomyces cerevisiae. After evaluating the production of ethanol, glucose,...
Embodiment 2
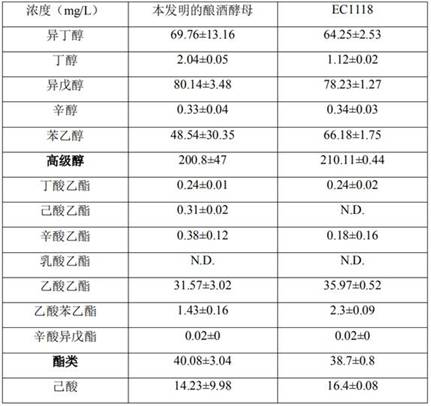
[0067] This embodiment is used for brewing yeast described in the present invention ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) strains were evaluated for tolerance and hydrogen sulfide production performance.
[0068] A single colony of the strain was inoculated in a 96-well plate containing sterile YPD liquid medium, and cultured overnight at 30°C and 200 rpm to obtain an activated strain.
[0069] The activated strain was transferred to YPD culture containing 0%, 6%, 8%, 10%, 12%, 14%, 16%, 18% ethanol concentration (v / v) with 3% inoculum After culturing overnight at 30°C and 200 rpm in medium, measure the OD with a microplate reader 600 nm value. The results showed that with the increase of ethanol concentration, the strain showed a trend of deepening inhibition, and the strain could tolerate 14% ethanol concentration.
[0070] The activated strain was transferred to YPD medium containing 200g / L, 300g / L, 400g / L, 500g / L, and 600g / L glucose concentration with 3% inoculum, and after ove...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com