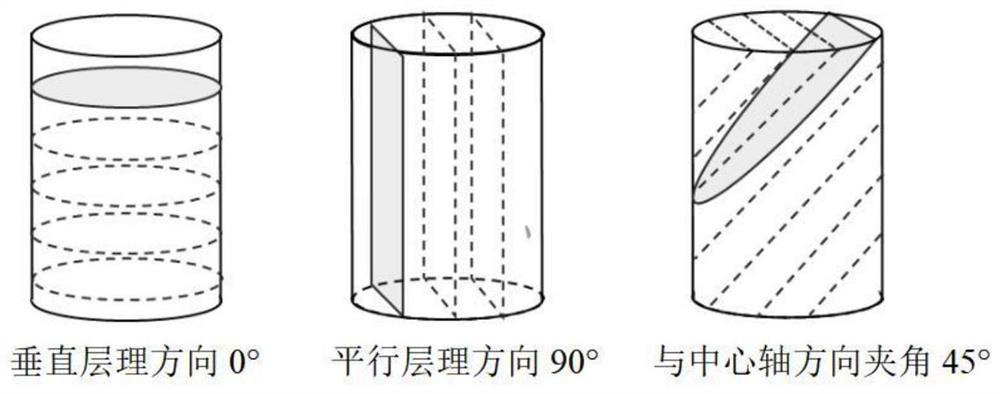
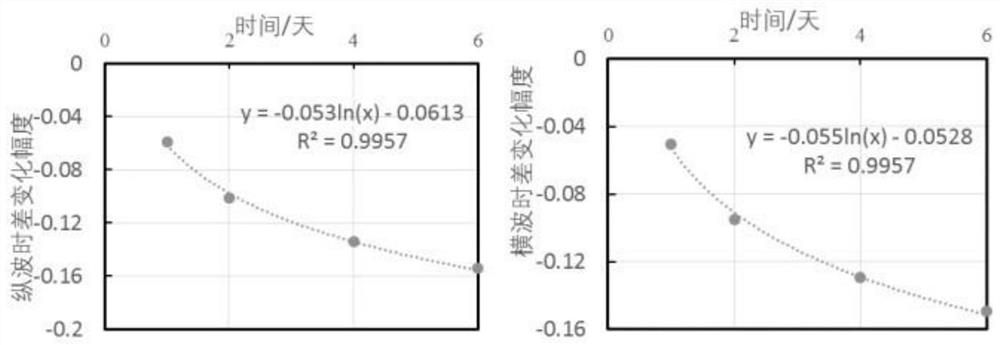
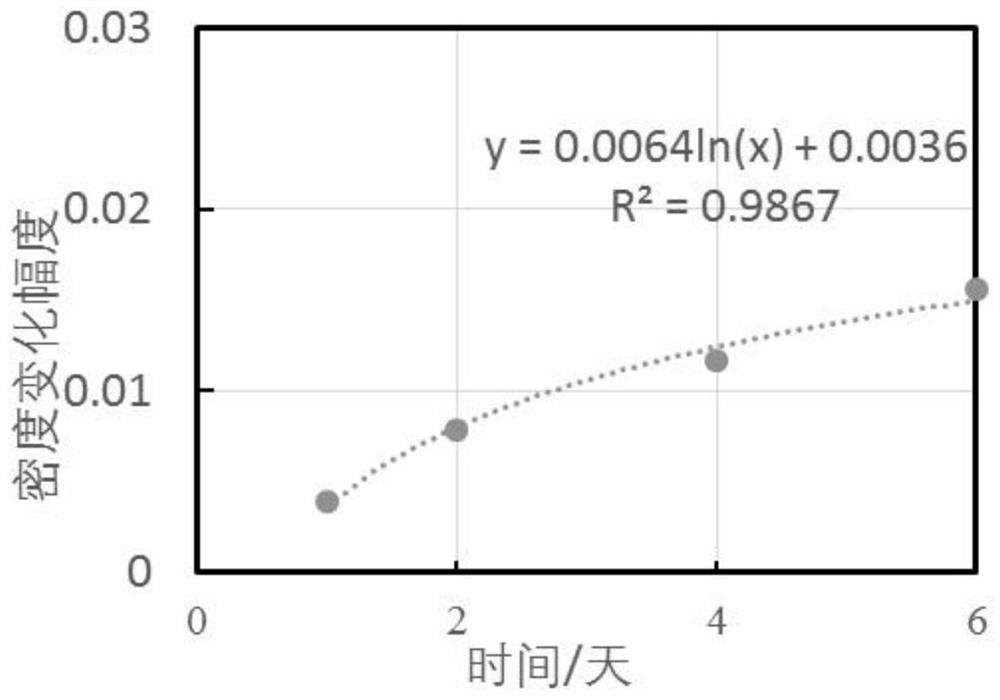
A method for correcting in-situ stress of shale formation
A technology of formation in-situ stress and correction method, applied in the field of oil drilling, can solve the problems of rock sound wave time difference change, deviation, inability to provide stress information for drilling and completion, etc., and achieve the effect of improving prediction accuracy and reasonable in-situ stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0102] A method for calibrating the in-situ stress of shale formations. After the hydration correction of the formation acoustic time difference and the hydration correction of the elastic stiffness coefficient based on the transverse isotropic model, the elastic modulus and Poisson's ratio are calculated, and finally the formation is calculated. ground stress.
[0103] Include the following steps:
[0104] Step 1: Collect experimental core data, geological data, logging data, drilling fluid for on-site drilling, and drilling and completion reports in the research area;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com