Tea-fragrance electronic atomized liquid and preparation method thereof
An electronic atomization and fragrance technology, which is applied in the processing of tobacco, tobacco, and other applications, can solve the problems of atomized liquid flavor and quality impact, and achieve the effect of good smoking experience, tight combination, and stable properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
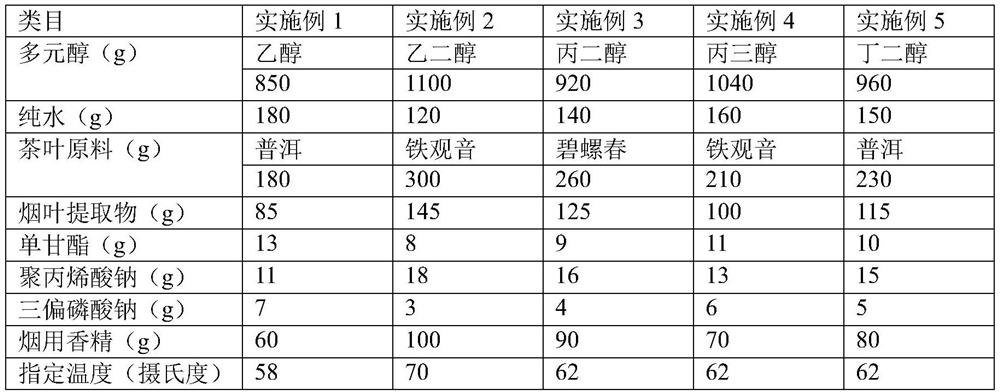
Embodiment 1-5
[0039] A tea-flavored electronic atomization liquid prepared from a mixture, which includes the following raw materials: polyol, pure water, tea raw material, tobacco leaf extract, monoglyceride, sodium polyacrylate, sodium trimetaphosphate and Tobacco flavor.
[0040] Polyhydric alcohols include one or more of ethanol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, glycerol, and butanediol.
[0041] The tea leaves are one or more of commercially available Pu'er, Tieguanyin and Biluochun.
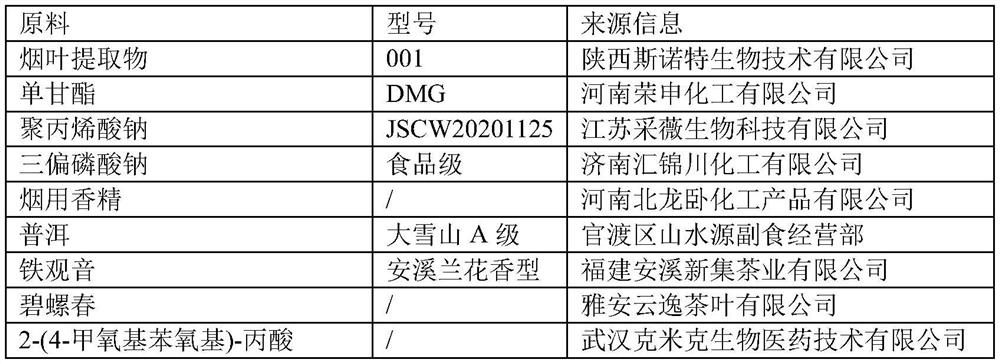
[0042] Refer to Table 2 for the selection and dosage of specific raw materials.
[0043] A method for preparing a tea-flavored electronic atomization liquid, comprising the following steps:
[0044] Step 1): Add monoglyceride and sodium polyacrylate into pure water, heat to the specified temperature shown in Table 2, and stir until dissolved at a rotation speed of 72r / min to obtain an initial mixture.
[0045] Step 2): Add polyhydric alcohol into the primary mixture, stir for 8 minutes at a speed of...
Embodiment 6-7
[0050] A tea-flavored electronic atomizing liquid differs from Example 5 in that the polyhydric alcohols are propylene glycol and glycerin, and the specific amounts of glycerin and propylene glycol are shown in Table 3.
[0051] table 3
[0052] Glycerol (g) Propylene glycol (g) Weight ratio of glycerol to propylene glycol Example 6 738 222 1:0.3 Example 7 640 320 1:0.5
Embodiment 8-10
[0054]A tea-flavored electronic atomization liquid, the difference from Example 7 is that the mixing material also includes a sweetness inhibitor, and the sweetness inhibitor is 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-propionic acid , 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-sodium propionate, and 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-zinc propionate. Refer to Table 4 for the selection and dosage of specific raw materials.
[0055] Table 4
[0056]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com