Lactic acid bacterium with a reduction of sensitivity to cos-type bacteriophages
A bacteriophage, sensitive technology, applied in the field of lactic acid bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0269] The lactic acid bacteria of the present invention can be used in the preparation of food products such as confectionary products, dairy products, meat products, poultry products, fish products, or bakery products.
[0270] For example, the bacteria can be used as an ingredient in the preparation of soft drinks, fruit juices or drinks containing whey protein, tea, cocoa drinks, milk drinks and lactic acid bacteria drinks, yoghurt, drinking yoghurt and red wine.
[0271] Preferably, the food as described herein is a dairy product. More preferably, the dairy product as described herein is one or more of: yoghurt, cheese (e.g. Cottage cheese, hard cheese, semi-hard cheese, cottage cheese), buttermilk, quark Cheese, sour cream, kefir, fermented whey-based drinks, kefir, milk drinks, yogurt drinks, fermented milk, cooked cream, cottage cheese, cottage cheese, milk, dairy residues, processed cheese, ice cream desserts, or baby milk.
[0272] Preferably, the food as described...
example
[0303] Materials and methods
[0304] Bacterial Growth and Phage Propagation
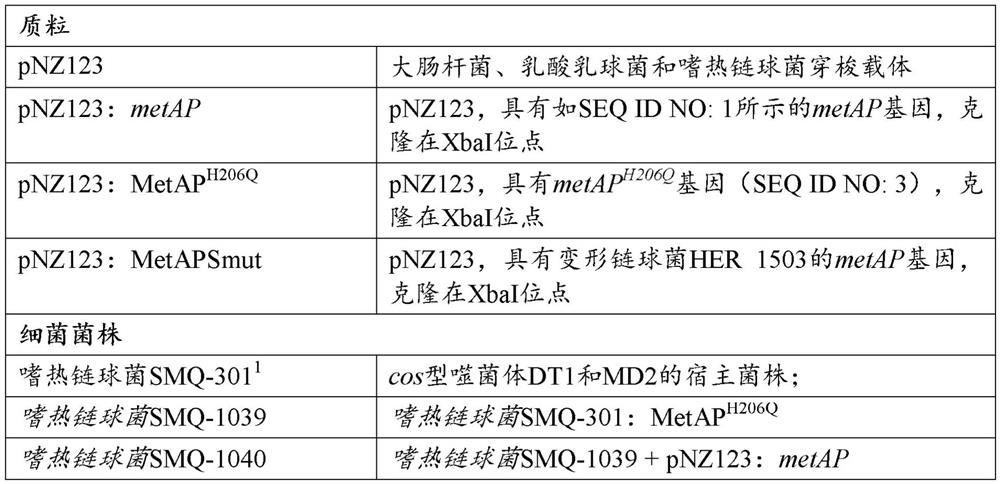
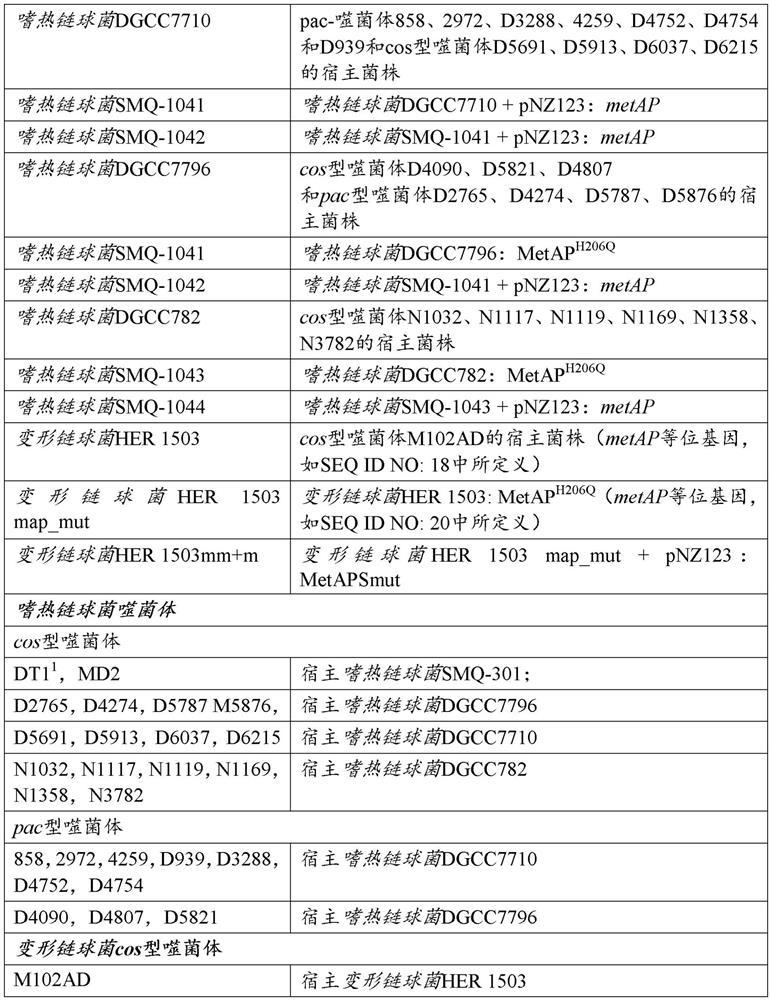
[0305] Bacterial strains, phages and plasmids are listed in Table 1. S. thermophilus was grown in M17 medium (Oxoid, Nepean) supplemented with 0.5% lactose (LM17) at 37°C or 42°C. When needed, chloramphenicol (Sigma, Oakville) was added to a final concentration of 5 μg / mL for growth and selection of S. thermophilus strains containing pNZ123 (DeVos et al., 1987) and derivative. Agar (LabMat, Quebec) was added to a final concentration of 1% in the solid medium. E. coli was grown for selection at 37°C with agitation in Luria Broth (LB) supplemented with 30 μg / mL kanamycin and 20 μg / mL chloramphenicol. Streptococcus mutans HER1503 at 37 °C and 5% CO 2 (BHI, Difco) (supplemented with 10 μg / mL chloramphenicol when selecting pNZ123+ cells). Phage propagation was as previously described (Hynes et al., 2017).
[0306] Isolation of phage-insensitive mutants
[0307] Phage-insensitive mutants (BIMs) ...
example 1
[0327] Mutations in the gene encoding methionine aminopeptidase reduce susceptibility to phages
[0328] Several BIMs of S. thermophilus SMQ-301 with reduced susceptibility to phage DT1 were isolated according to the protocol described above in the section entitled "Isolation of phage-insensitive mutants". More than 95% of BIMs acquired novel spacers targeting the CRISPR locus in the phage DT1 genome. Nine SMQ-301 BIMs that did not acquire the new spacer were selected, presumably mutated elsewhere in the bacterial genome to provide reduced susceptibility to phage DT1. The genomes of these nine non-CRISPR BIMs were sequenced. By comparing these sequences with the genome of S. thermophilus SMQ-301 (Labrie et al., 2015), several mutations were found. Although many of these mutations may be related to phage infection, the same mutation (T->G) occurred at position 618 of the metAP gene in three of the nine BIMs. This gene encodes methionine aminopeptidase (MetAP), and this mutat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com