Method for judging astringent taste grade of matcha by using near-infrared technology
A grade discrimination, near-infrared technology, applied in the field of tea research, can solve the problems of uncertain quality of matcha, difficulty in judging the astringency level of matcha, unscientific and unstable, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Utilizes near-infrared technology to establish a matcha astringency grade discrimination method
[0041] (1) Identify the astringency of different batches of matcha according to the sensory evaluation method, and establish a database of astringency grades of matcha samples. The astringency level is graded by professional judges as "Strong" (Astringency 4), "Medium" (Astringency 3), "Weak" (Astringency 2) and "Very Weak" (Astringency 1).
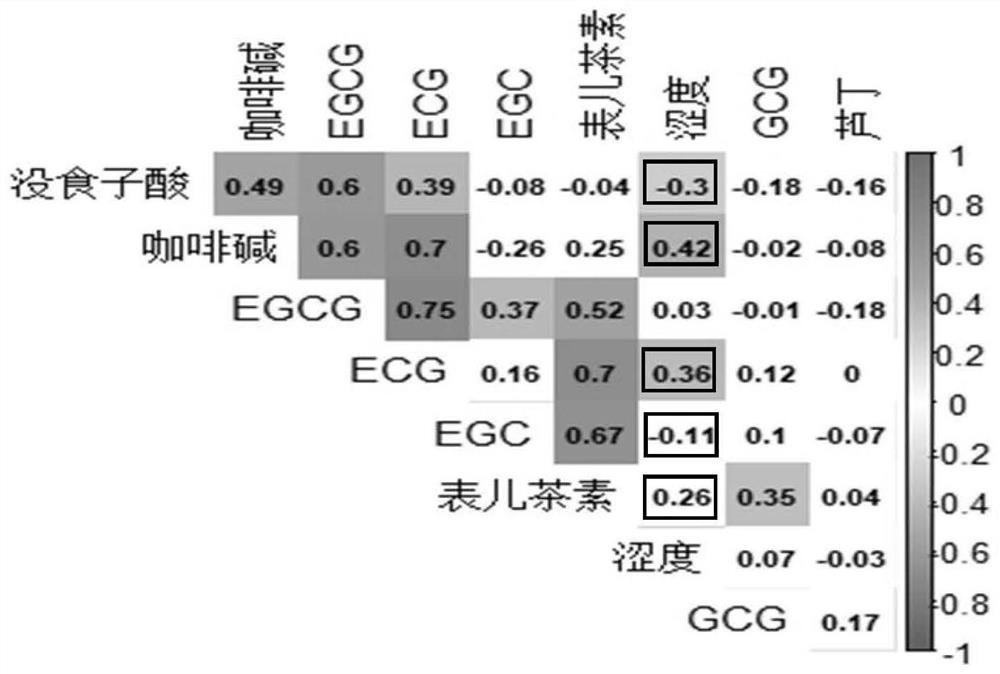
[0042] (2) Using high-performance liquid chromatography to determine gallic acid, epigallocatechin (EGC), caffeine, epicatechin (EC), epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), and epicatechin in matcha samples. Determinations of chlorogallate (ECG), gallic catechin gallate (GCG) and rutin were carried out at least three times.
[0043] (3) Pass the matcha of each grade of astringency in step (1) through a 300-mesh sieve, number them, carry out multi-index component quantification and correlation analysis research, and analyze the o...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Utilizing near-infrared technology to establish a method for discriminating matcha astringency grades
[0049] (1) Based on the tea sensory evaluation method, the astringency of matcha samples was identified.
[0050] (2) Determination of gallic acid, epigallocatechin (EGC), caffeine, epicatechin (EC), epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), and epicatechin in matcha samples by HPLC Component contents of chlorogallate (ECG), catechin gallate (GCG) and rutin.
[0051] (3) Establish the astringency-related component system of matcha.
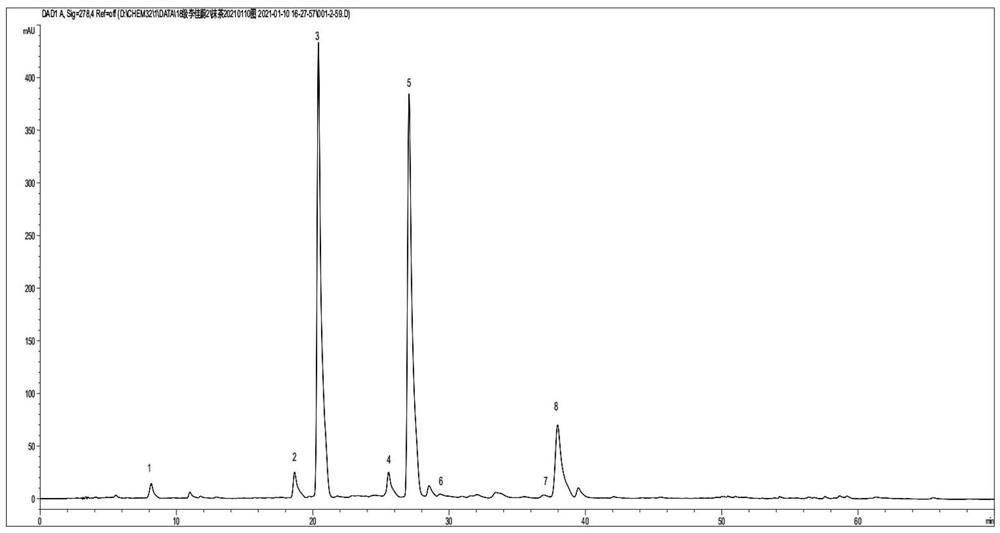
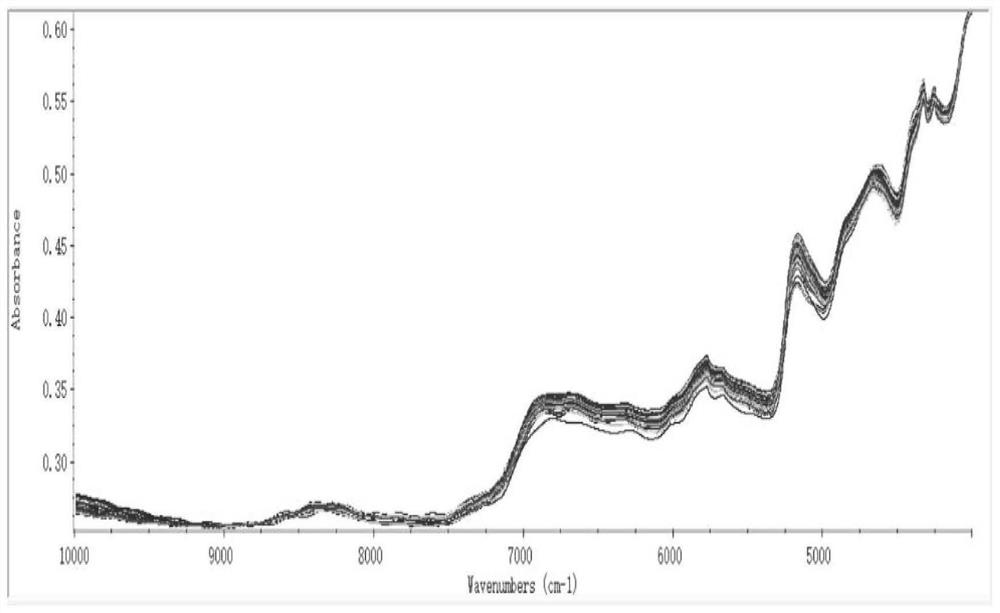
[0052] (4) Scan the matcha sample with a near-infrared spectrometer.
[0053] (5) Select the spectral preprocessing method for the matcha sample.
[0054] (6) Establish a discriminant model by using the spectrogram, classify the astringency level of matcha, and use the model to predict the astringency level of unknown matcha.
[0055] (7) Using the matcha sample spectrum, correlate the astringency-related components of the matcha s...
experiment example
[0056] Experimental example: in order to further verify the feasibility of the present invention, the inventor has carried out a series of tests, specifically as follows:
[0057] Based on the near-infrared technology to establish a new method for judging the astringency level of matcha, first establish the sensory evaluation of traditional experience, through the traditional sensory evaluation, provide an intuitive and simple astringency level standard for the astringency classification of matcha. Then, quantitative analysis of multi-index components and correlation analysis were carried out to reflect the differences among Matcha with different astringency grades as much as possible. Through the astringency grade scoring method, the astringency grade and astringent components were combined, and the near-infrared spectral analysis technology was used to scan and collect the spectra of matcha with different astringency grades, and finally a model for distinguishing the astringe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com