Vegan food composition and method of making thereof
A composition and food technology, applied in food science, dairy products, plant protein processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0131] Example 1: Beverage obtained by processing raw chickpeas and raw sunflower seeds
[0132] Chickpeas are derived from Vivien Paille (France). The chickpeas were dehulled using a laboratory dehuller (F.H. SCHULE Mühlenbau GmbH, Germany) at 90% of maximum speed for 90 seconds.
[0133] The chickpeas were then roasted using a Salvid fired steam CSC oven (Germany) operating at 160° C. for 40 minutes.
[0134] Biological sunflower seeds were purchased from Migros (Switzerland). Sunflower seeds were defatted using a hand press (Rommelsbacher OP 700 "Emido", Germany). Obtain the sunflower cake and the oily phase.
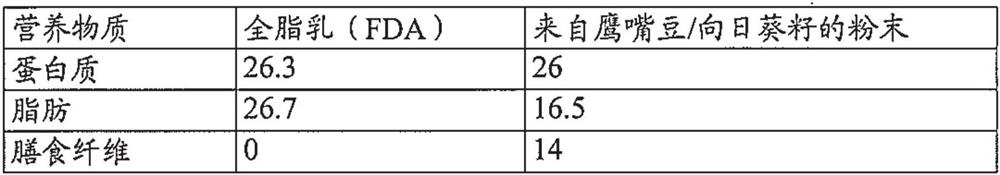
[0135] 60% by weight of hulled roasted chickpeas were dry blended with 40% by weight of defatted sunflower to obtain a composition close to milk. Particles were reduced in size using a hammer mill (Retsch ZM1, Switzerland) operating at speed 2 with a mesh size of 1 mm.
[0136] The 12% by weight solids mixture was added to 88% by weight water and introduced in...
Embodiment 2
[0153] Example 2: Spray drying of ready-to-drink milk substitute
[0154] The ready-to-drink milk substitute of Example 1 was spray dried.
[0155] Spray drying was then carried out using a Tower Niro SD 6.3N (GEA, Denmark) with an inlet temperature of 160°C and an outlet temperature of 85°C and operated at 15 kg / hour.
[0156] Using the CamSizer instrument (Camsizer XT Retsch Xdry, using a pressure of 120Pa, the results are based on volume with X 面积 Indicates that a manual Camsizer) determines the size of the particles, corresponding to a D90 of 52 μm and a D50 of 24 μm.
[0157] Add 9% of this powder to water for a delicious alternative to reconstituted milk. In this drink, add two coffee spoons of Nescafé to 250ml. In another experiment, Milo was added. In another experiment, apple puree was added. It is also served with strawberry puree.
[0158] 9% of the powder was dispersed in water using a Polytron PT3000 for 2 minutes. Viscosity was measured using a Physica M...
Embodiment 3
[0161] Example 3: Low-fat powder obtained by processing raw chickpea and defatted sunflower flour
[0162] Chickpeas were supplied by Zwicky (Switzerland). The chickpeas were dehulled using a laboratory dehuller (F.H. SCHULE Mühlenbau GmbH, Germany) at 90% of maximum speed for 90 seconds.
[0163] The chickpeas were then roasted using a Salvid fired steam CSC oven (Germany) operating at 160° C. for 40 minutes.
[0164] 50% by weight of dehulled roasted chickpeas was dry blended with 50% by weight of defatted sunflower flour (Heliaflor 55, Austrade, Germany) to obtain a composition close to that of skim milk. The particles were reduced in size by hammer milling (Retsch ZM1, Switzerland). Jet milling (Fluid Jet Mill J-70, Techologica mechanica, Italy) was then applied at a feed rate of 600 g / hour at a Venturi pressure of 10 bar and an annular pressure of 11 bar.
[0165] The 12% by weight solids mixture was added to 88% by weight water and introduced into a Tetra Almix B200...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com