Vegetation restoration method for high-altitude ecologically fragile area
A technology for ecological fragility and vegetation restoration, applied in botany equipment and methods, planting substrates, horticulture, etc., can solve the problems of no restoration method for alpine Rhododendron shrubs and poor thermal insulation effect of the substrate, so as to improve the survival rate of planting and prevent Effect of root rot, increasing hydrophobicity and adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A method for restoring vegetation in high-altitude ecologically fragile areas, comprising the following steps:
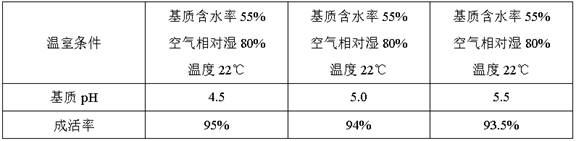
[0031] S1. Transplant appropriate amount of Alpine Rhododendron from an area with an altitude of 4500-4700m to a place with an altitude of 3500-3700m, and plant it under the conditions of a greenhouse with a substrate moisture content of 55%, relative air humidity of 80%, and a temperature of 22°C. After the plant survived, cut semi-lignified branches with a new diameter of 0.6-0.7 cm from the well-growing female parent material as the cutting material. Keep 1 complete leaf on the top, keep the terminal bud, cuttings have 2 nodes, cuttings with a length of 5cm, trim the lower end into a horseshoe shape, and finally insert into the cutting medium with pH=4.5 until the cuttings survive and take root;
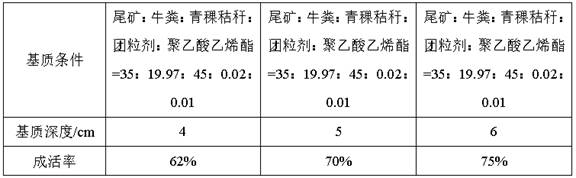
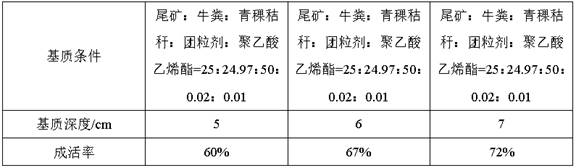
[0032] S2. Then transplant the surviving and rooted cuttings in step (1) to the substrate with outdoor tailings, cow dung, highland barley stalks, pellets, and p...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A method for restoring vegetation in high-altitude ecologically fragile areas, comprising the following steps:
[0036] S1. Transplant appropriate amount of Alpine Rhododendron from an area with an altitude of 4500-4700m to a place with an altitude of 3500-3700m, and plant it under the conditions of a greenhouse with a substrate moisture content of 55%, relative air humidity of 80%, and a temperature of 22°C. After the plant survived, cut semi-lignified branches with a new diameter of 0.6-0.7 cm from the well-growing female parent material as the cutting material. Keep 1 complete leaf on the top, keep the terminal bud, the cuttings have 2 nodes, the cuttings are 5cm in length, the lower end is trimmed into a horseshoe shape, and finally inserted into the cutting medium with pH=5 until the cuttings survive and take root;
[0037] S2. Then transplant the surviving and rooted cuttings in step (1) to the substrate with outdoor tailings, cow dung, highland barley stalks, pel...
Embodiment 3
[0040] A method for restoring vegetation in high-altitude ecologically fragile areas, comprising the following steps:
[0041] S1. Transplant appropriate amount of Alpine Rhododendron from an area with an altitude of 4500-4700m to a place with an altitude of 3500-3700m, and plant it under the conditions of a greenhouse with a substrate moisture content of 55%, relative air humidity of 80%, and a temperature of 22°C. After the plant survived, cut semi-lignified branches with a new diameter of 0.6-0.7 cm from the well-growing female parent material as the cutting material. Keep 1 complete leaf on the top, keep the terminal bud, the cuttings have 2 nodes, the cuttings are 5cm in length, the lower end is trimmed into a horseshoe shape, and finally inserted into the cutting medium with pH=5.5 until the cuttings survive and take root;
[0042] S2. Then transplant the surviving and rooted cuttings in step (1) to the substrate with outdoor tailings, cow dung, highland barley stalks, p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com