Glutathione-rich yeast extract and preparation method thereof as well as application
A yeast extract and glutathione technology, applied in the field of yeast extract, can solve the problem of poor whitening and antioxidant effect, low free radical scavenging ability and tyrosinase activity inhibition strength, and low glutathione content And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
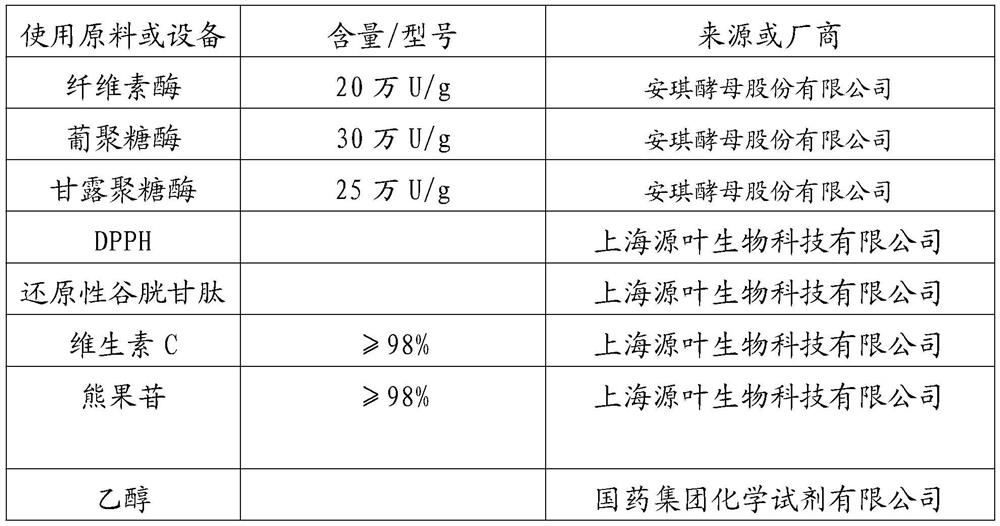
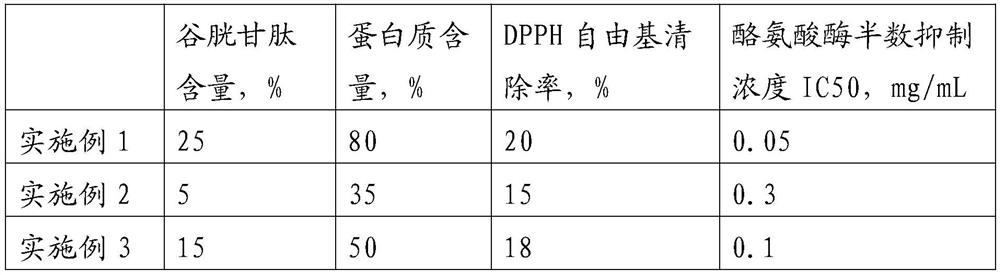
[0031] In the preparation method of glutathione-rich yeast extract of the present invention, the reduced glutathione can be quickly released from the cells through high-pressure homogeneous wall breaking first, because the reduced glutathione is easily absorbed by the body. Source enzyme decomposition, compared with autolytic wall breaking, the use of high-pressure homogeneous wall breaking can retain as much reduced glutathione as possible; Yeast cell wall contains mannan, β-glucan and protein, etc. The inventors found through experiments that two or more of cellulase, glucanase and mannosidase can be used to make mannan and β-glucan degradation to separate glutathione from the yeast cell wall. Since glutathione is easily degraded by protease, compared with protease degradation, the compound enzyme of the present invention can retain more reduced glutathione in yeast and improve the anti-oxidation and whitening effect of yeast extract.
[0032] The present invention also pro...
Embodiment 1
[0054] Yeast preparation method:
[0055] The yeast strain is a yeast strain (saccharomyces cerevisiae) rich in reduced glutathione, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 205130. The nutrient solution is 1% of yeast extract, 2% of peptone and 2% of glucose. For glutathione yeast strains, the normal culture temperature is 30°C. During the fermentation process, the nutrient solution is added in a fed-batch manner, and the first stage is cultivated for 6 hours; the flow rate of the nutrient solution added in the second stage is 20% of the flow rate added in the first stage. Cultivate for 8h. After the cultivation, the fermentation broth is separated to obtain yeast.
[0056] In the batching tank, the yeast is prepared into 10% (yeast dry matter content) yeast milk, the pH is adjusted to 3.0, the temperature is raised to 30° C., and then the homogeneous wall breaking treatment is carried out, and the homogeneous pressure is 50 MPa. Put the above solution into a reaction tank, a...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Yeast preparation method is the same as embodiment 1.
[0059] In the batching tank, the yeast prepared above was formulated into 15% (yeast dry matter content) yeast milk, adjusted to pH = 7.0, cooled to 4°C, and then subjected to homogeneous wall breaking treatment with a homogeneous pressure of 5 MPa. Put the above solution into a reaction tank, adjust the pH=1.0, raise the temperature to 10° C., add 0.05% cellulase and 0.05% mannosidase, and perform enzymatic hydrolysis for 15 hours. Then heat up to 70°C, keep warm for 3 hours to inactivate the enzyme, then centrifuge the enzymolysis solution to take the supernatant, and then use the multi-effect evaporation process to concentrate the above supernatant to a dry matter concentration of 60% to obtain a paste rich in glutathione Glycerin yeast extract, the evaporation temperature is 65°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com