Composite microbial agent for fermenting and degrading cellulose in straw
A composite microbial inoculum and cellulose technology, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of poor treatment effect, reduced enzyme activity, limited degree of cellulose degradation, etc., to achieve the best treatment effect, speed up The effect of cellulose degradation and optimal bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Cellulase Activity Determination and Filter Paper Disintegration Experiment
[0037] 1. Experimental materials
[0038] (1) Compound microbial agent
[0039] Bacillus subtilis, Microbacterium, and Cellulomonas were respectively cultured in beef extract peptone medium to logarithmic growth phase, Aspergillus and Rhizopus oryzae were respectively cultured in PDA medium to logarithmic growth phase, and the The culture solution is formulated into a compound microbial bacterial agent according to the following proportions.
[0040] Experimental group-1, the volume ratio of Bacillus subtilis, Aspergillus, Microbacterium, Cellulomonas, Rhizopus oryzae is 2:2:1:1:1;
[0041] In experimental group-2, the volume ratio of Bacillus subtilis, Microbacterium and Cellulomonas was 2:1:1.
[0042] (2) Filter paper degradation experiment
[0043] The above two groups of composite microbial agents were added to the medium with filter paper as the only carbon source, and the ...
Embodiment 2
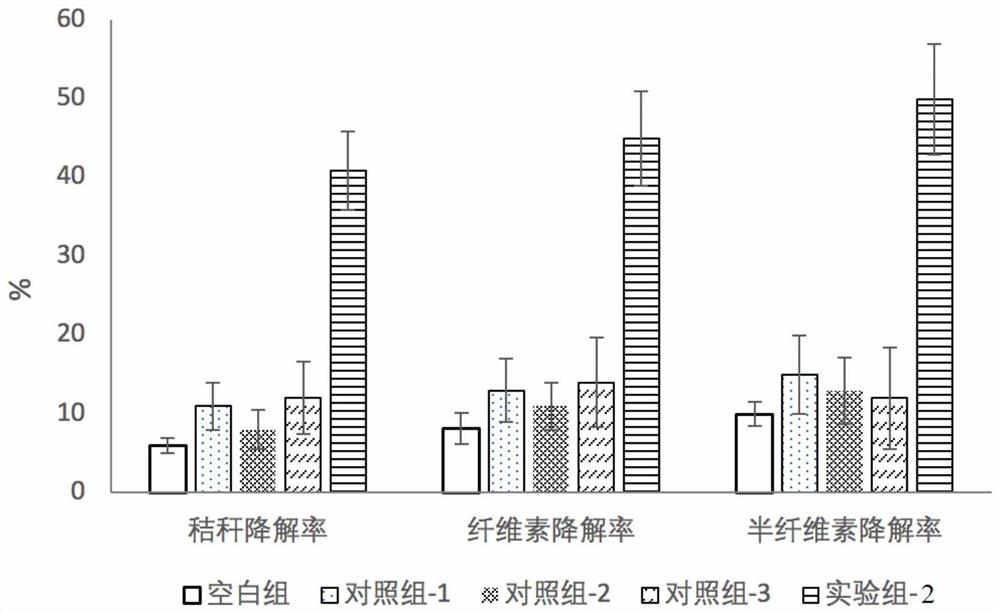
[0065] (1) Fermentation and degradation of corn stalks by compound microbial agents
[0066] Take the pretreated corn stalk 25g and put it into the Erlenmeyer flask, adjust the initial water content to be 70%, add the composite microbial inoculant (experimental group-2) described in Example 1 of the total water 2%, the logarithm of it comprises The volume ratio of the culture solution of Bacillus subtilis, Microbacterium and Cellulomonas in the growth phase is 2:1:1 respectively, and the treatment is 20 days. The experiment set up the blank group without adding bacterial agents, the control group-1 (only added 2% of Bacillus subtilis), the control group-2 (only added 2% of microbacteria) and the control group-3 (only added 2% of fiber Monas), each treatment was done in 3 parallels.
[0067] (2) Determination of cellulose and hemicellulose content by differential gravimetric method
[0068] Weigh 1.5 g of straw, and bake at 60°C to constant weight W1. Add 150mL of 2mol / L HCl...
Embodiment 3
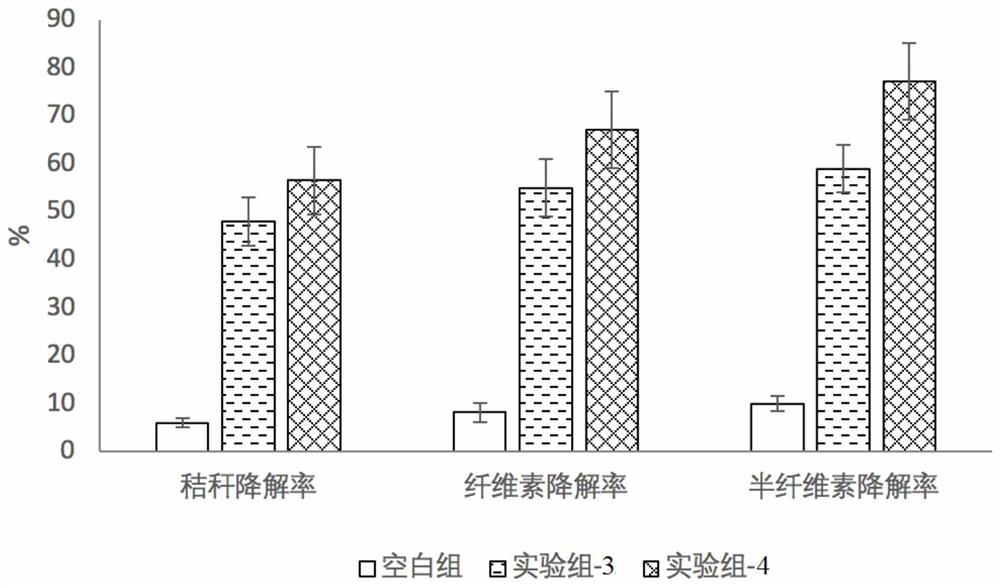
[0072] (1) Fermentation and degradation of corn stalks by compound microbial agents
[0073] Take the pretreated corn stalk 25g and put it into the Erlenmeyer flask, adjust the initial water content to be 60%, add 2% composite microbial bacterial agent (experimental group-3) and 2% composite microbial bacterial agent (experimental group-4) respectively ), the composition of the experimental group-3 is that the volume ratio of the logarithmic growth phase Bacillus subtilis, microbacteria, and cellulomonas culture solution is 1:1:1 respectively, and the composition of the experimental group-4 is the logarithmic growth phase Bacillus subtilis The volume ratio of Bacillus, Microbacterium, Cellulomonas and Streptomyces culture solution is 2:2:2:1 respectively, and the treatment is 30 days. In the experiment, a blank group without adding bacterial agents was set up, and 3 parallels were done for each treatment.
[0074] (2) Determination of cellulose and hemicellulose content by di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com