Calculation method of fvfd far-field integral boundary condition with reduced grid usage
A technology of boundary conditions and far-field integration, applied in the field of numerical solution in the frequency domain of electromagnetism, can solve problems such as increased grid size and calculation burden, difficult application, and influence on numerical calculation accuracy, and achieves convergence standards with reduced iteration steps, The effect of reducing the number of spatial grids and improving non-reflection performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
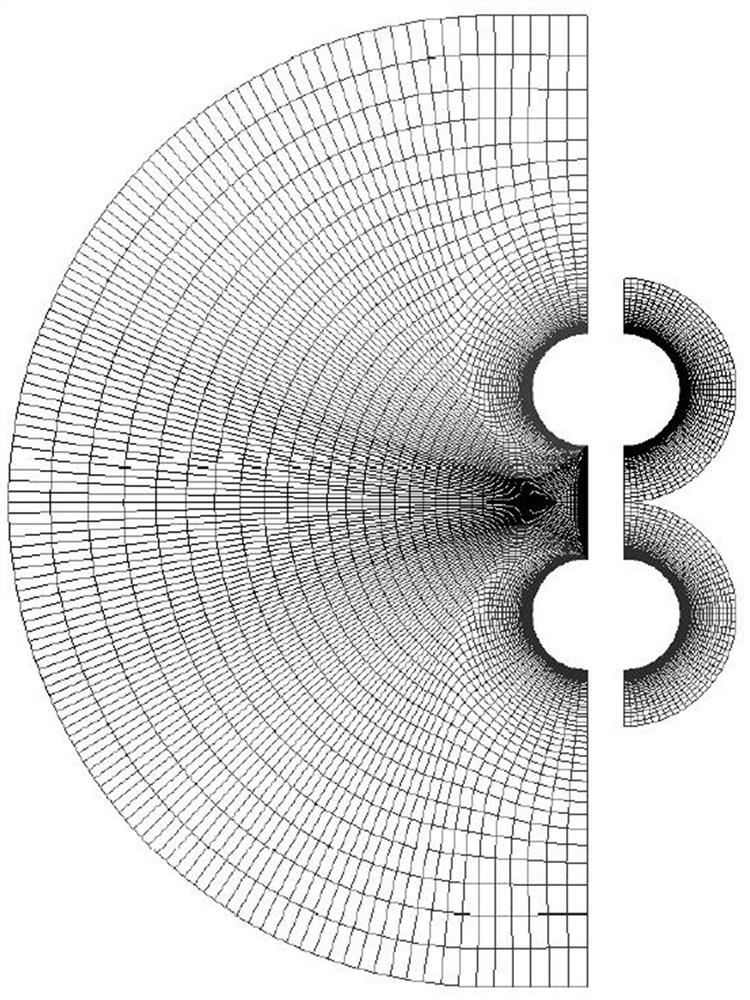
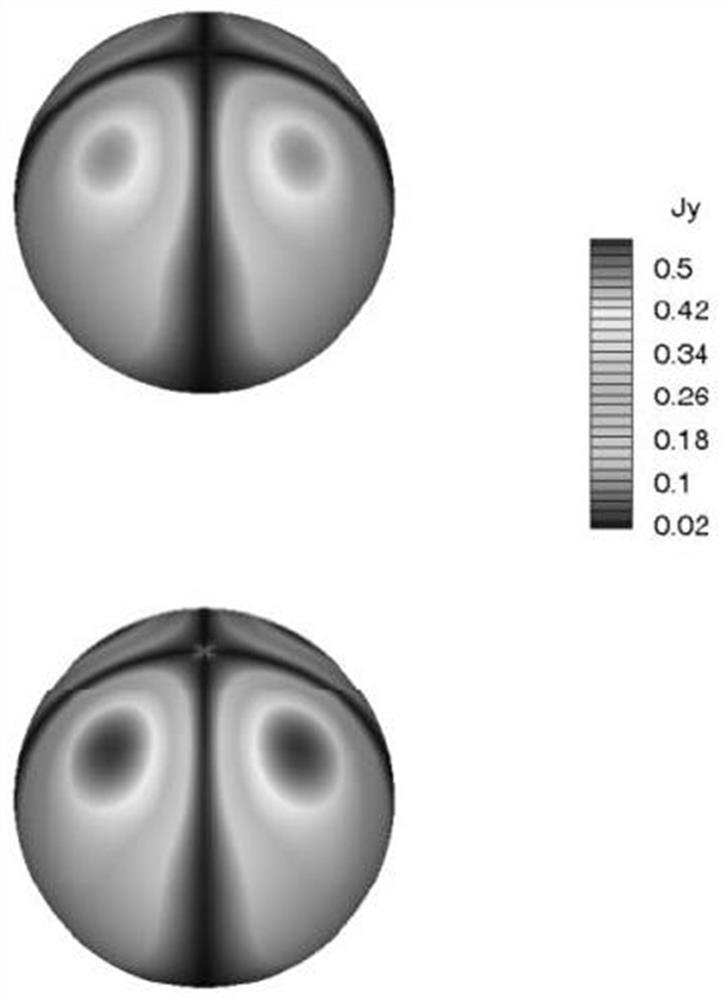
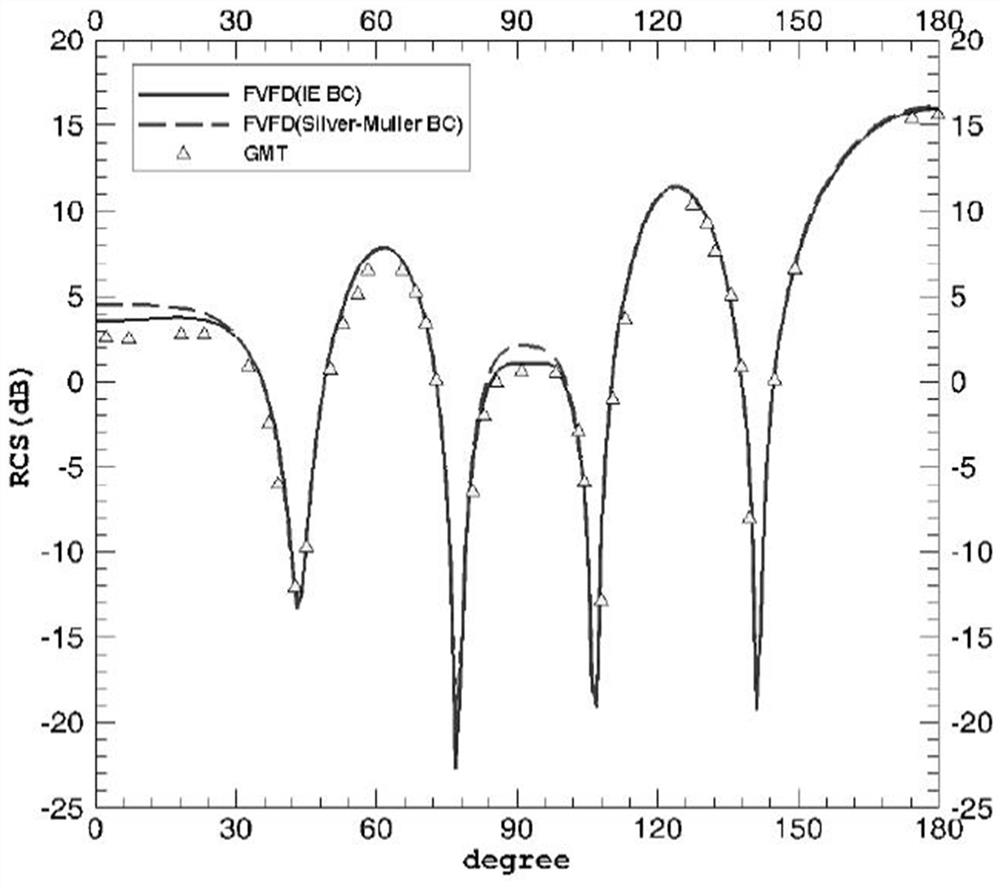
[0083] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 6 The embodiment of the FVFD far-field integral boundary condition calculation method with reduced grid usage in the present invention is further described.
[0084] Refer to attached figure 2 , the entire frequency-domain finite volume method calculation electromagnetic field software can be divided into three parts according to the structure: preprocessing, electromagnetic field calculation and postprocessing. Preprocessing mainly includes three modules: grid data input, calculation parameter data input, and control parameter input, which are mainly used to read grid data, calculation parameter data input, and control parameter files, and on this basis, perform preprocessing for The electromagnetic field calculation provides calculation support; the electromagnetic field calculation includes: space electromagnetic field MUSCL format interpolation, element interface flux calculation, time advancement, and convergence judgment modules; pos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com