Fan active noise control system and method based on virtual error sensing
A technology of active noise control and virtual sensing, which is applied in the direction of sound-emitting devices and instruments, and can solve problems such as installation restrictions of electro-acoustic devices, cost loss, and inability to effectively control low-frequency noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
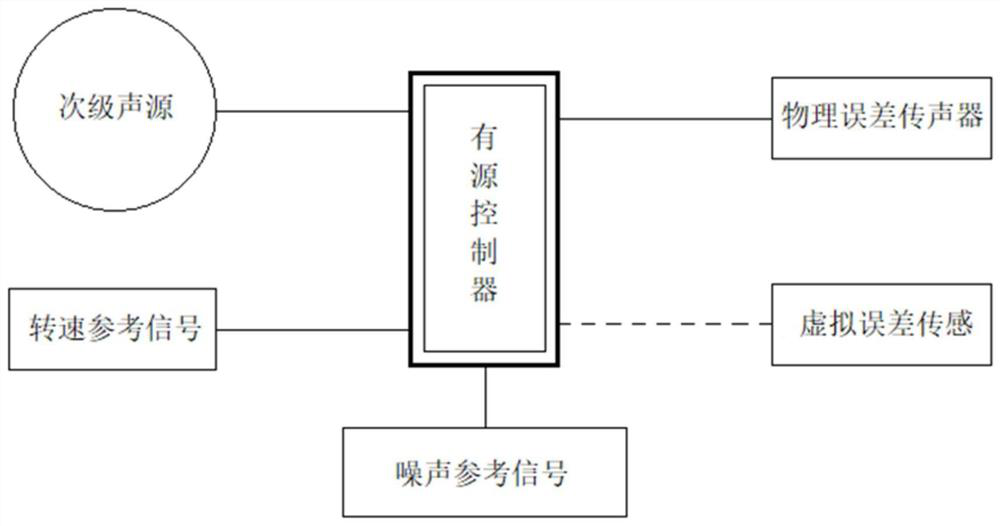
[0031] Such as figure 1 A fan active noise control system based on virtual error sensing is shown, including: an active controller and a secondary sound source connected to the active controller, a physical error microphone, a virtual error sensor, and a speed reference signal , noise reference signal, and a fan model and a pipeline connected to the fan model are also established. A plurality of the physical error microphones are installed on the fan, and a plurality of virtual sensing positions are evenly distributed on the fan, and the secondary sound source is arranged on the fan. and on the pipeline.
[0032] The active controller: the main function is to receive the input signal picked up by the physical error sensor, first preprocess the signal, calculate the transfer function from the physical error microphone to the virtual sensing position, and estimate the virtual error sensor through the transfer function Then the controller takes the signal at the virtual sensor a...
Embodiment 2
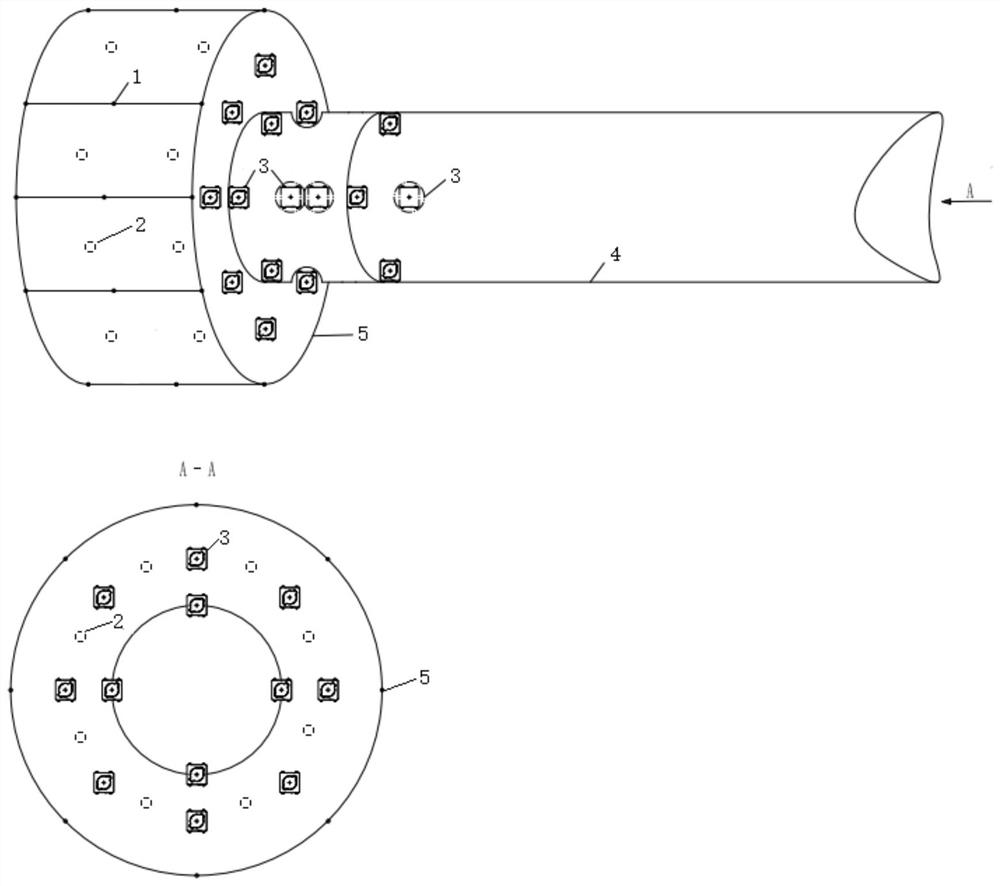
[0039] Such as figure 2 As shown, the positions of the physical error microphone 1 and the virtual sensing are arranged around the control area in a surrounding manner, that is, multiple physical error microphones are installed on the side of the fan, and a plurality of virtual sensing positions are evenly distributed on the side of the fan. The secondary sound source is arranged on the casing of the fan and the nearby pipelines.
[0040] The system is not limited to figure 2 Fan duct model shown, other fan types still applicable;
[0041] The location and number of secondary sound sources and physical error microphones in the fan duct are just examples and not limited to figure 2 The position and number shown;
[0042] The reference signal adopts the combined reference signal of speed and noise for the first time, but it is not limited to speed and noise;
[0043] The location and number of virtual error sensors are examples and are not limited to figure 2 location and...
Embodiment 3
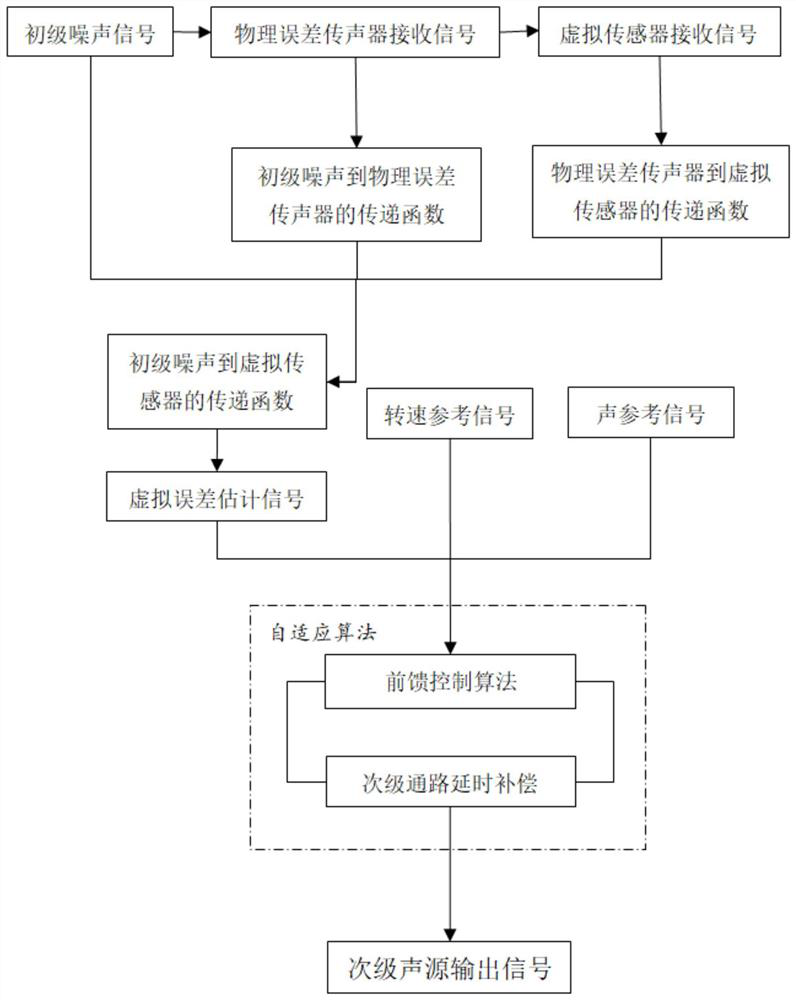
[0045] Such as image 3 As shown, an active noise control method for wind turbines based on virtual error sensing first collects the primary noise signal through the physical error microphone, calculates the acoustic transfer function from the primary noise to the physical error microphone, and then takes the signal at the physical error microphone as input , the signal at the virtual error sensor is used as the output signal, and the acoustic transfer function from the physical error microphone to the virtual error sensor is estimated by the built-in algorithm of the active controller, and then the acoustic transfer function from the primary noise to the virtual error sensor is calculated, and then Estimate the noise signal in the virtual error sensing area as the control target, and perform noise control through the built-in adaptive algorithm of the active controller to obtain a secondary sound source signal equal to the target noise and opposite in phase, and then sent to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com