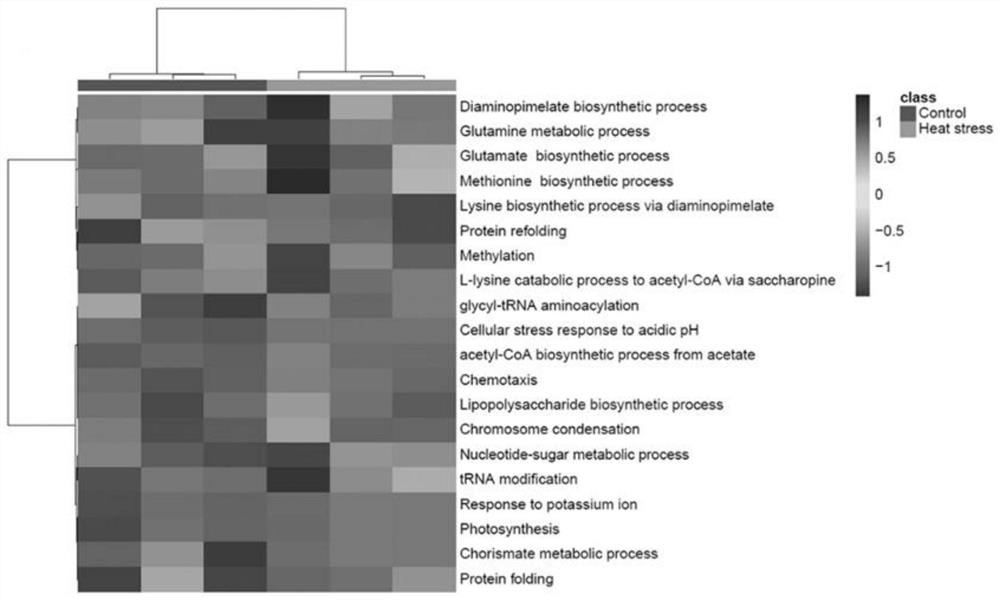
Macro-proteome mining method and application of macro-proteome mining method in obtaining hydrolysis characteristics of intestinal microbial proteins
A technology of proteolysis and proteome, which is applied in the metaproteome mining method and its application in obtaining the proteolysis characteristics of intestinal microorganisms, can solve the problems that the changes of proteolysis characteristics of intestinal microorganisms have not been studied, and reduce false positives. Effect of positive identification, lower confidence, good accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1 Different software executes search performance
[0034] Using the MLI dataset and a large metaprotein database, we compared different commercial software (ProteomeDiscoverer, PEAK, ProteinPilot, and Byonic) and open source software (MaxQuant, MSFragger, and pFind) on several 36-core servers (installed with 192G memory) Properties of hemitryptic peptides. Proteome Discoverer, Byonic, MaxQuant, pFind, and ProteinPilot did not complete searches in a month, while MSFragger crashed with an out-of-memory error. Only PEAK completed the analysis within one month, so further high-throughput analysis was performed using a 156-core HPC cluster, which completed the database search within 2 weeks.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2 Database Search
[0036] The database search process generally includes two main steps: (1) de-novo sequencing, and use a large macroprotein database (large database) and PEAKS software to perform the first search to obtain at least one peptide identified Protein and generate a corresponding small protein database (reduced database); (2) Use the reduced database and various software to perform a second search to improve the accuracy of identifying the semitrypsin polypeptide.
[0037] In order to cope with the increased search space and time in the identification of metaproteomic semitryptic peptides, the search was first performed using PEAKS DB on a cluster configured with an Intel(R) Xeon(R) 156-core processor and 1.5TB 2666MHz memory, the software De novo sequencing was first performed, followed by a database search using the following parameters: mass bias of 10 ppm for precursor ions and 0.02 Da for fragment ions; aminomethylation of cysteine was set a...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3 Semitrypsin Polypeptide Identification and Classification and Functional Analysis
[0043] 1. Identification principle of semitrypsin polypeptide
[0044] Peptides whose first amino acid is not R or K before the identified sequence are semi-tryptic N-terminal peptides (excluding the N-terminal of the protein). The lack of R or K in the last amino acid of the identified sequence is a half-tryptic C-terminal peptide (excluding the C-terminal of the protein). In-source CID fragments were distinguished from proteolytically derived hemitryptic polypeptides based on elution time. Most in-source fragments showed different retention times compared to their theoretical retention times (predicted using SSRCalc). The microbial hemitrypsin polypeptides were distinguished from peptides of human origin and peptides of food origin by the corresponding accession numbers in the FASTA sequence entry.
[0045] 2. Combining semi-trypsin and complete trypsin data to quantify th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com