Linear fast change PRI sequence design method based on Staggered SAR system
A sequence design and linear technology, applied in the field of microwave remote sensing, can solve the problems of missing pulses and non-uniform sampling in azimuth, achieve good imaging focusing performance, optimize system parameters, and solve the problems of missing pulses and non-uniform sampling in azimuth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
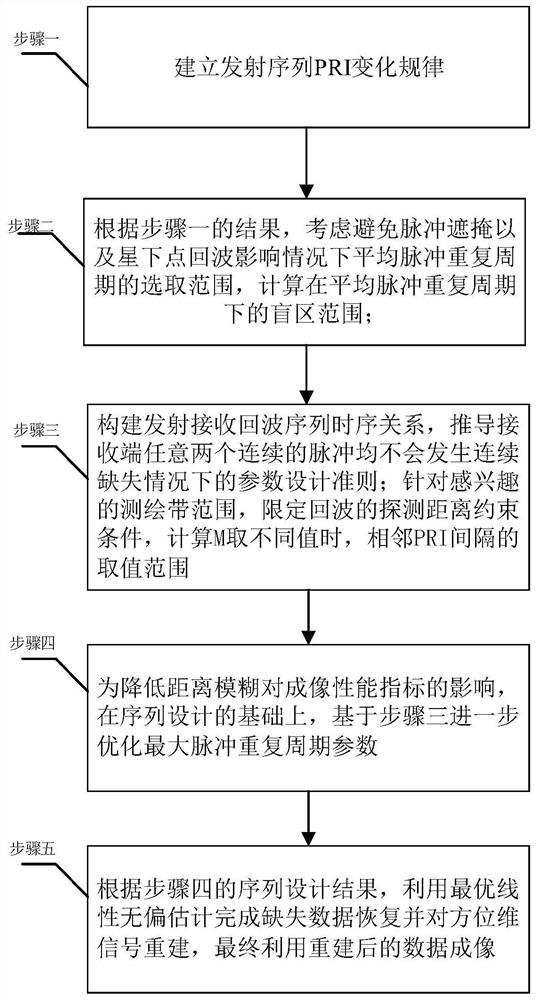
[0037] DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS 1. This embodiment is based on the fast-changing PRI sequence design method of the Staggered SAR system, and is carried out according to the following steps:
[0038] Step 1: establish the variation law of the transmission sequence PRI;
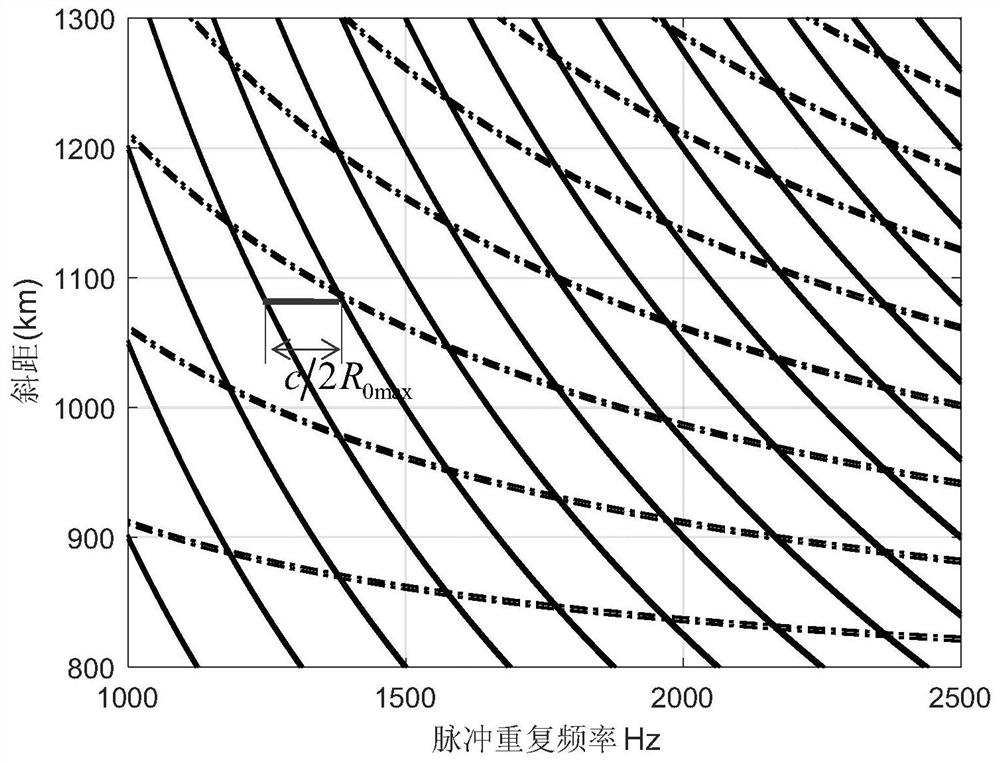
[0039] Step 2: According to the results of Step 1, consider the selection range of the average pulse repetition period (the range of PRF values in the zebra diagram) under the circumstance of avoiding pulse occlusion and the influence of sub-satellite echoes. The selection range of the available value interval) calculates the blind zone range under the average pulse repetition period;
[0040] Step 3: According to the result of Step 2, construct the timing relationship of the transmit-receive echo sequence (the timing relationship of the transmit-receive echo sequence is as follows: Figure 5 and Image 6 shown), deduce the design criteria of parameters (M and Δ) in the case of no c...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048]Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, a change rule of the transmission sequence PRI is established;
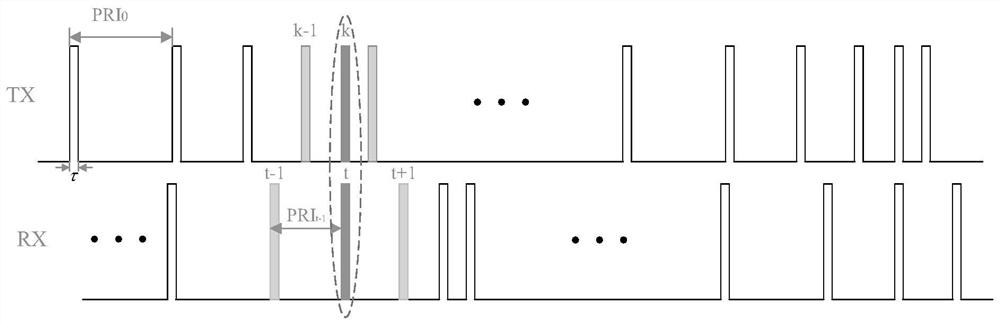
[0049] It is assumed that there are M different pulse repetition periods PRI in the transmission and reception timing m , PRI max and PRI min Corresponding to the maximum and minimum pulse repetition periods of the M PRIs, such as figure 2 shown; assuming that the PRI sequence varies linearly, satisfying
[0050] PRI m =PRI m-1 -Δ=PRI 0 -mΔ,m=0,...,M-1(1)
[0051] Among them, PRI 0 Represents the initial pulse repetition period, Δ represents the interval between two adjacent PRIs;
[0052] PRI is the pulse repetition period;
[0053] Assuming Δ>0, the value of the pulse repetition period of the PRI sequence is gradually reduced. The design of the sequence should not only ensure that the echoes of all targets in the observation area are not continuously lost, but also make the PRI as much as possible. min...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0056] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step 2, according to the result of step 1, the average pulse repetition period (zebra diagram) is considered to avoid pulse masking and the influence of sub-satellite echoes. According to the selection range of the average pulse repetition period (the PRF value range in the zebra diagram), the blind area range under the average pulse repetition period is calculated; the specific process is as follows:
[0057] The parameter design of the Staggered SAR system is similar to the parameter design of the traditional spaceborne SAR system. The difference is that the pulse repetition frequency is no longer a constant value, but changes continuously with the transmitted pulse sequence within a certain range. Selection needs to consider a certain range. Different PRF variation ranges and PRF variation rules affect the imaging performance index to a large extent, which is also the key to the des...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com