Catalytic conversion method and catalytic conversion device for producing low-carbon olefins
A catalytic conversion method and technology of low-carbon olefins, which is applied in the field of catalytic conversion devices and the production of low-carbon olefins, can solve the problems of low ethylene and propylene yields of light hydrocarbon raw materials, and limited precise control of the reaction zone, and achieve improved Effects of selectivity, increased yield, and high depth of conversion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
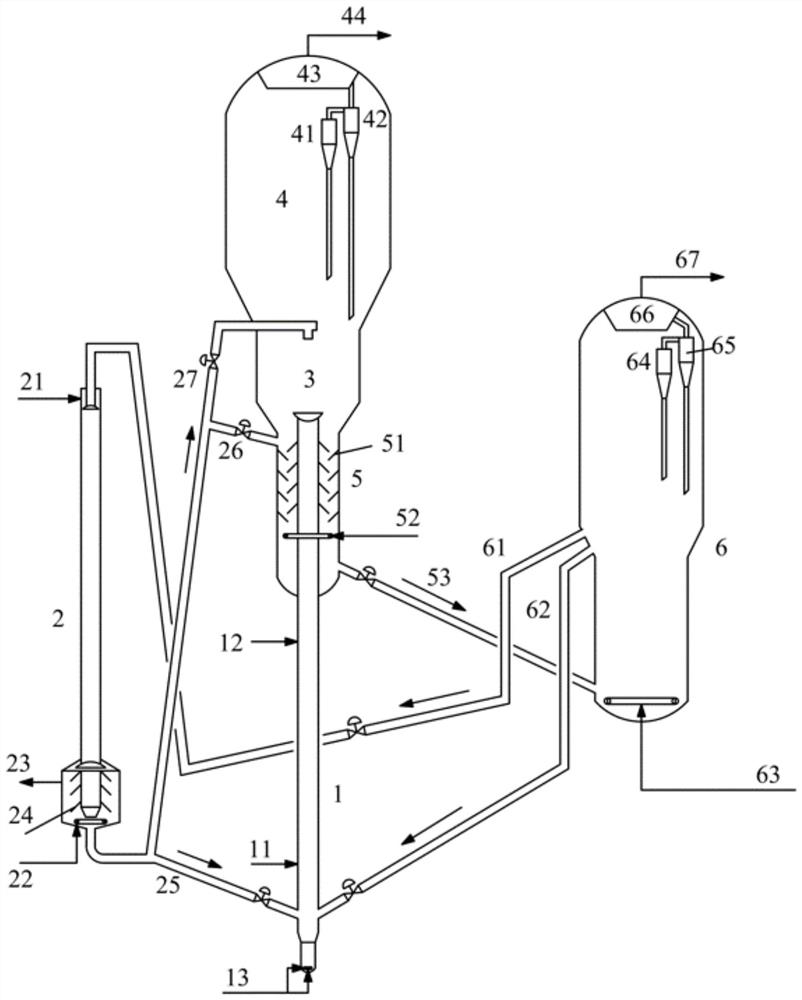
[0133] test in figure 1 It was carried out on the medium-scale test rig shown. The device includes three reactors, namely a riser reactor, a descending reactor and a fluidized bed reactor, wherein the riser reactor has an inner diameter of 16mm and a length of 3200mm, and the descending riser reactor has an inner diameter of 15mm. The length is 2500mm, the inner diameter of the fluidized bed reactor is 80mm, and the length is 500mm.
[0134] The heavy raw material is introduced into the bottom of the riser reactor, and reacts with the regenerated catalyst from the regenerator and the carbon-deposited catalyst in the down-flow reactor. The reacted oil mixture is introduced into the fluidized bed reactor to continue the reaction. The reacted oil The mixture is separated by a cyclone.
[0135] The light raw material is introduced into the top of the down-flow reactor, the regenerated catalyst CAT from the regenerator is contacted and reacted, and the resulting oil mixture is se...
Embodiment 2
[0139] According to the method of embodiment 1, the difference is that the catalyzer at the bottom of the down-flow reactor is not introduced into the bottom of the riser reactor and the stripper, but the catalyzer at the bottom of the down-flow reactor is introduced into the fluidized bed reactor and the stripper device. The weight ratio of the coke catalyst introduced into the fluidized bed reactor and the stripper is 0.5:1, and the weight ratio of light feedstock to heavy feedstock is 0.2:1. The reaction conditions and results are shown in Table 3.
Embodiment 3
[0141]According to the method of Example 1, the difference is that in addition to introducing the catalyst at the bottom of the down-flow reactor into the riser reactor and the stripper, the catalyst at the bottom of the down-flow reactor is also introduced into the fluidized bed reactor. The weight ratio of the coke catalyst introduced into the riser reactor, the fluidized bed reactor and the stripper is 0.3:0.2:1, and the weight ratio of the light feedstock to the heavy feedstock is 0.2:1. The reaction conditions and results are shown in Table 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com