Nucleotide compositions for inhibiting non-target regions in biological DNA samples and their applications
A target area and composition technology, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of not allowing doctors to make more drug decisions, false positives, etc., and achieve fast hybridization and specificity high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
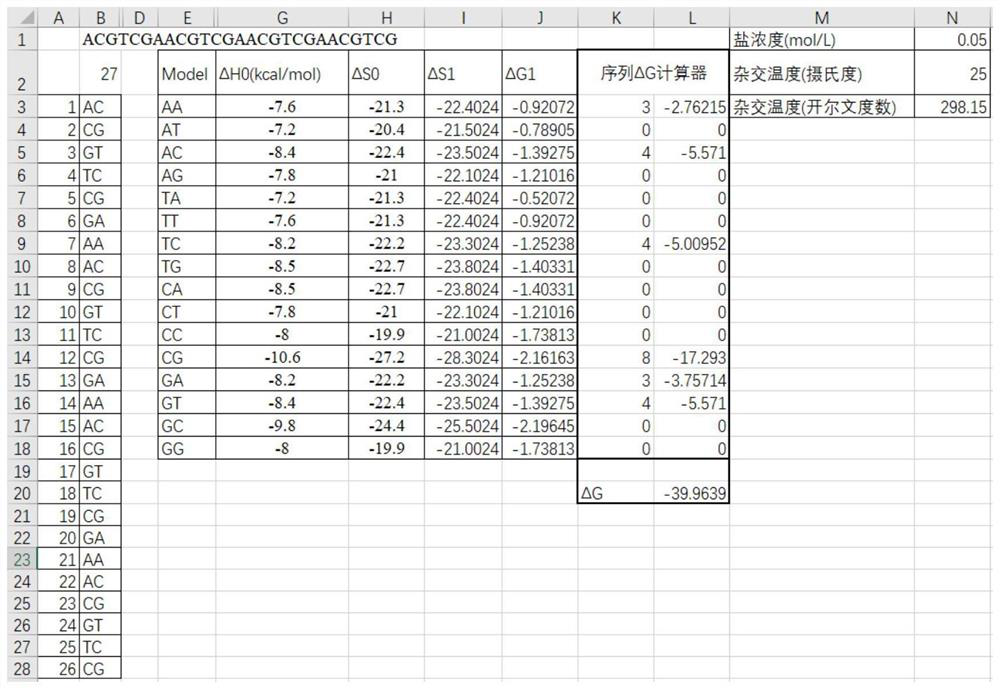
[0038] Example 1: Calculation of the Gibbs free energy of a nucleotide sequence
[0039] Although the calculation of Gibbs free energy is a public knowledge, in order to better support the content disclosed in the present invention, we will show the calculation process of Gibbs free energy here, as well as the implementation in excel, the present invention discloses The Gibbs free energies in the content of are all calculated by this calculation process.
[0040] 1. First of all, we chose the two-base estimation model, which is described in detail in the literature of the SantaLucia, J. team, such as "Thermodynamic parameters for expanded nearest-neighbor model for formation for formation" published in Biochemistry in 1998 of RNA duplexes with Watson-Crick pairs", in brief, involves the following formula:
[0041] a) ΔS1=ΔS0+0.368*log(Salinity);
[0042] b) ΔG1=ΔH0-Temp*ΔS1 / 1000;
[0043] 2. ΔH0 and ΔS0 are empirical constants obtained through research by SantaLucia, J. et ...
Embodiment 2
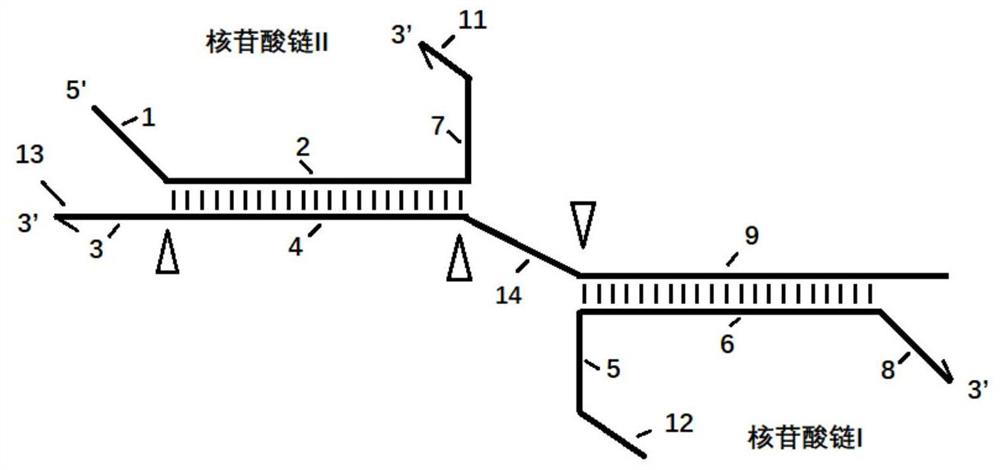
[0058] Example 2: Suppressing and eliminating PKD1 pseudogenes by using space-occupying methods to improve the detection of PKD1 true gene regions
[0059] 1. The PKD1 gene has 7 pseudogenes with a homology of about 95%. In order to better obtain the information of the true PKD1 gene, we designed a set of nucleosides for PKD1 exon 7, 17, 23, 28 and other positions Acid chain composition, as shown in the following table, wherein the nucleotide sequence I sequence is designed at the place where the PKD1 true and false genes have sequence differences, and biotin, nucleotide chain II and nucleosides are modified on the nucleotide chain I The ratio of acid chain I is 1:10; the nucleotide chain I completely matches the pseudogene, after hybridization, the biotin-labeled nucleotide chain is combined with avidin magnetic beads, and the pseudogene is also captured , and finally detect and verify the ratio of the true gene of PKD1 in the supernatant by common PCR method (which does not ...
Embodiment 3
[0083] Embodiment 3: Comparison of the inhibitory effect of different ratios of nucleotide chain I and nucleotide chain II on pseudogenes
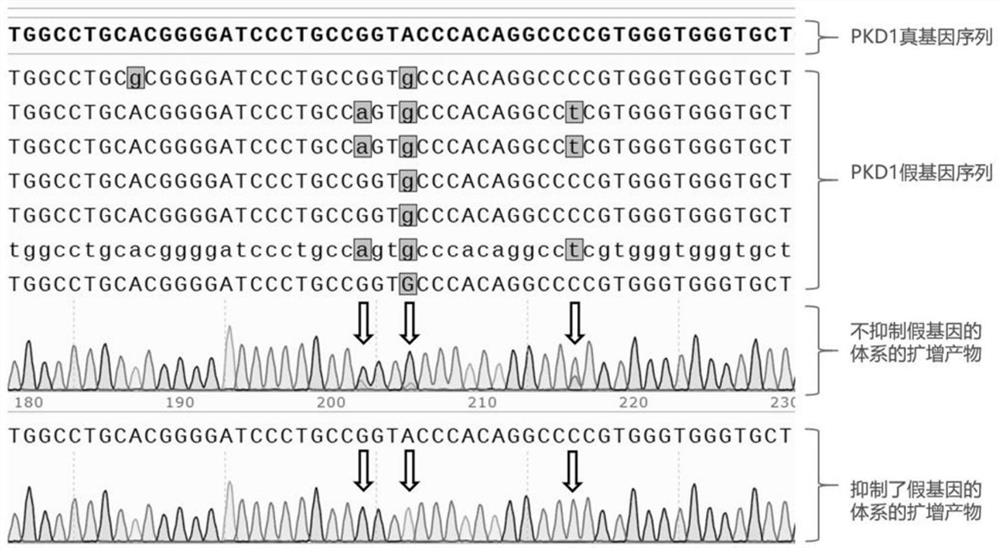
[0084] The specific process is the same as Example 2, the difference is that the ratios of nucleotide chain I and nucleotide chain II are different, and the results also show that the inhibitory effect on pseudogenes is different, such as Figure 7 As shown in the sanger results at the position of exon 11, the ratio of the number of molecules of nucleotide chain II: nucleotide chain I is: concentration condition a=1:10, concentration condition b=1:30.
[0085]
[0086] The analysis of Sanger sequencing results is as follows: Figure 7 As shown, the PCR product of the experimental group is marked as the amplification product of the system that suppresses the pseudogene, and the PCR product of the control group is marked as the amplification product of the system that does not suppress the pseudogene.
[0087] From the comparison of conc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com