Epidemic propagation control method for implementing isolation by considering individual infection states and individual attributes
A control method and epidemic technology, applied in the field of epidemic transmission, can solve problems such as waste of resources, neglect of activity and attraction, isolation and control of individuals without infection status, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
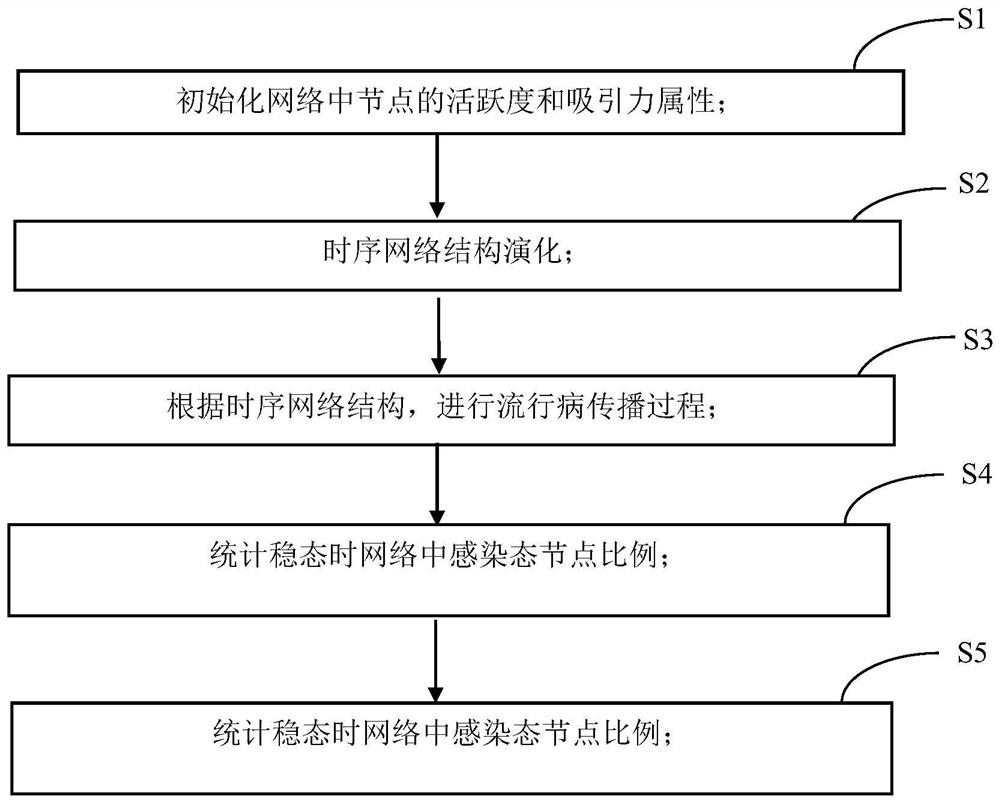
[0064] see figure 1 and figure 2 , a method for controlling the spread of an epidemic that considers individual infection status and individual attributes to implement isolation, the method is applied to a time series network, and the operation steps are as follows:
[0065] Step S1: Initialize the activity and attractive attributes of nodes in the network;
[0066] Step S2: Time series network structure evolution;
[0067] Step S3: Simulate the epidemic spreading process according to the time series network structure;
[0068] Step S4: Statistically calculate the proportion of infected nodes in the network at steady state;
[0069] Step S5: Under random isolation measures and isolation rate π, the critical infection rate threshold λ of the epidemic c .
[0070] This embodiment considers the individual infection status and individual attributes to implement the epidemic transmission control method of isolation, which provides a basis for judging whether ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
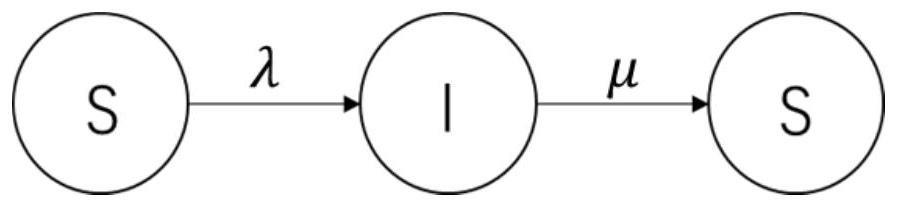
[0073] In this embodiment, the attractive activity-driven temporal network model is used to construct a temporal network, and the "susceptible (S)-infected (I)-susceptible (S)" propagation is used to simulate the epidemic propagation process, and random isolation is adopted. measure.
[0074] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of a method for controlling the spread of an epidemic that considers individual infection status and individual attributes to implement isolation provided by the embodiment of the present application. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that this embodiment mainly includes the following processes:
[0075] Step S1: Initialize the activity and attractive attributes of nodes in the network;
[0076] Step S2: Time series network structure evolution;
[0077] Step S3: Simulate the epidemic spreading process according to the time series netw...
Embodiment 3
[0112] See figure 1 , the processes of steps S1, S2, and S4 are the same as those in Embodiment 1, except that step S3.7 adopts "object isolation considering activity" and does not include step S5. details as follows:
[0113] Step S3.1: using the "SIS" propagation model to simulate the virus propagation process;
[0114] Step S3.2: Randomly select a certain proportion of nodes as the initial I-state seed nodes;
[0115] Step S3.3: The network evolves according to the rules of steps S2.1-S2.3 every time Δt;
[0116] Step S3.4: Node i updates its own epidemic status. When node i is in S state, each I-state neighbor j of node i infects node i with probability λ. When node i is in the I state, it returns to the S state with probability μ, and maintains the I state with probability 1-μ.
[0117] Step S3.5: After node i changes from S state to I state, the activity and attractiveness of node i will change according to active isolation measures and passive isolatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com