A general gait design and control method of a footed robot
A control method and robot technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, control/regulation system, non-electric variable control and other directions, can solve the problem of insufficient simulation, simplified Hopf oscillator output signal changes, poor stability of quadruped robots, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of accurate control, high control precision and simple control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] This embodiment provides a general gait design and control method for a footed robot. In the aspect of gait design, the present invention simplifies the gait design into the setting of gait parameters. A set of gait parameters corresponds to one gait type, and the A set of key locations within a gait cycle. Each gait cycle has 2 states: turning on the ground and swinging in the air, each leg is repeating the same gait cycle, but the starting position is different (with a phase difference). This method can quickly design a variety of gaits for the robot and smoothly switch between different synchronous states; in terms of control, the present invention provides a control method for different robot walking gait, walking speed, leg lift height, body height and other control variables. A set of universal foot robot foot trajectory calculation methods to adapt to various complex terrains.
[0070] The method described takes a hexapod robot as an example, and this embodiment...
Embodiment 2
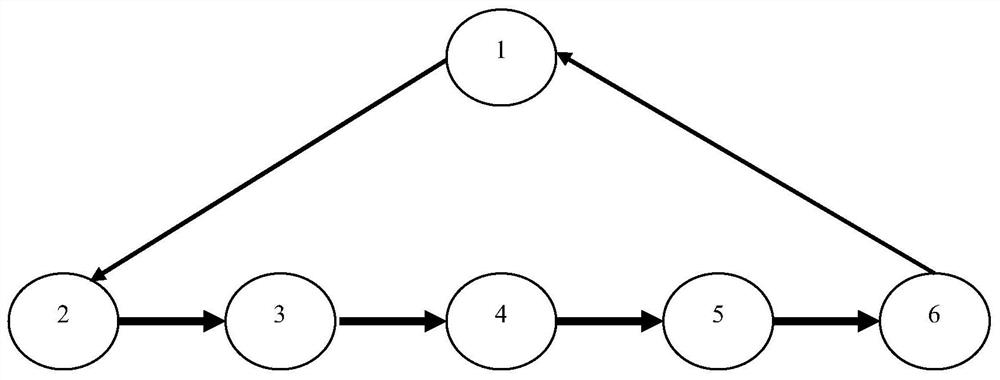
[0132] This embodiment provides a general gait design and control method for a footed robot. The method takes a hexapod robot as an example. This embodiment uses a triangle 12 gait for description. figure 2 shown, as follows:
[0133] In this embodiment, the following definitions are made:
[0134] StepsInGait=12 There are a total of 12 steps in a gait cycle;
[0135] NrLiftedPos=3 3 steps in a gait cycle are in the air;
[0136] TLDivFactor=8 moves on the ground 8 times in one gait cycle;
[0137] NomGaitSpeed=150 The step size of each step is 150 (unit: mm);
[0138] HalfLiftHeigth=True, the leg lift height of serial numbers 2 and 12 is half of serial number 1;
[0139] LRGaitLegNr=1 The starting sequence number of the left rear leg is 1;
[0140] RFGaitLegNr=3 The starting sequence number of the right front leg is 3;
[0141] LMGaitLegNr=5 The starting sequence number of the left middle leg is 5;
[0142] RRGaitLegNr=7 The starting sequence number of the right hind ...
Embodiment 3
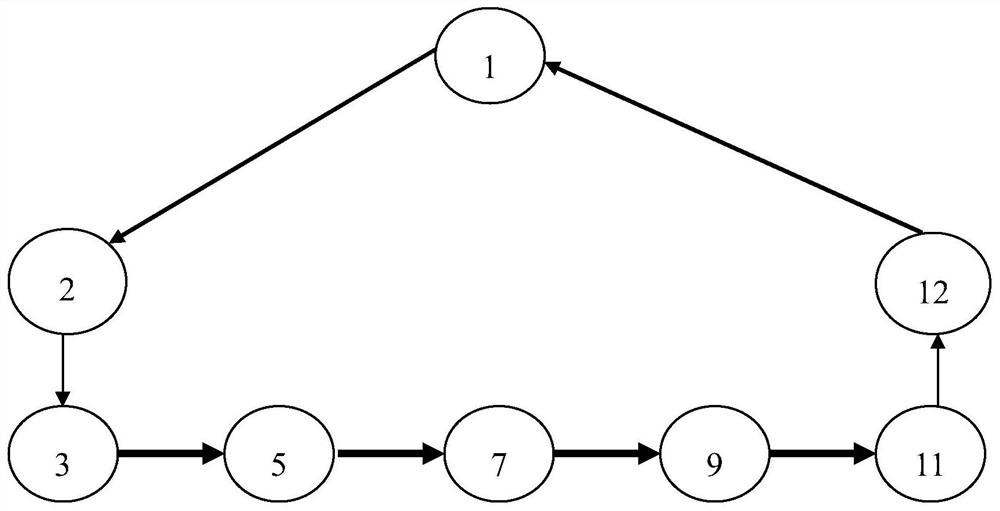
[0198] This embodiment provides a general gait design and control method for a footed robot. The method takes a hexapod robot as an example. This embodiment is described with a triangular 6 gait. image 3 shown, as follows:
[0199] In this embodiment, the following definitions are made:
[0200] StepsInGait=6 There are a total of 6 steps in a gait cycle;
[0201] NrLiftedPos=2 2 steps in a gait cycle are in the air;
[0202] TLDivFactor=3 moves on the ground 3 times in one gait cycle;
[0203] NomGaitSpeed=150 The step size of each step is 150 (unit: mm);
[0204] HalfLiftHeigth=FALSE No. 2 and 1 have the same height of the raised leg;
[0205] LRGaitLegNr=4 The starting sequence number of the left rear leg is 4;
[0206] RFGaitLegNr=1 The starting sequence number of the right front leg is 1;
[0207] LMGaitLegNr=1 The starting sequence number of the left middle leg is 1;
[0208] RRGaitLegNr=1 The starting sequence number of the right hind leg is 1;
[0209] LFGaitLegN...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com