Method for manufacturing nutritional compositions for plants and soils
A technology for composition and animal waste, which is applied in the preparation and application of fertilizer mixtures and organic fertilizers, and can solve the problems of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, increased cost, excessive foaming, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0142] Example 1. Method for producing fertilizer / nutritional composition from chicken manure
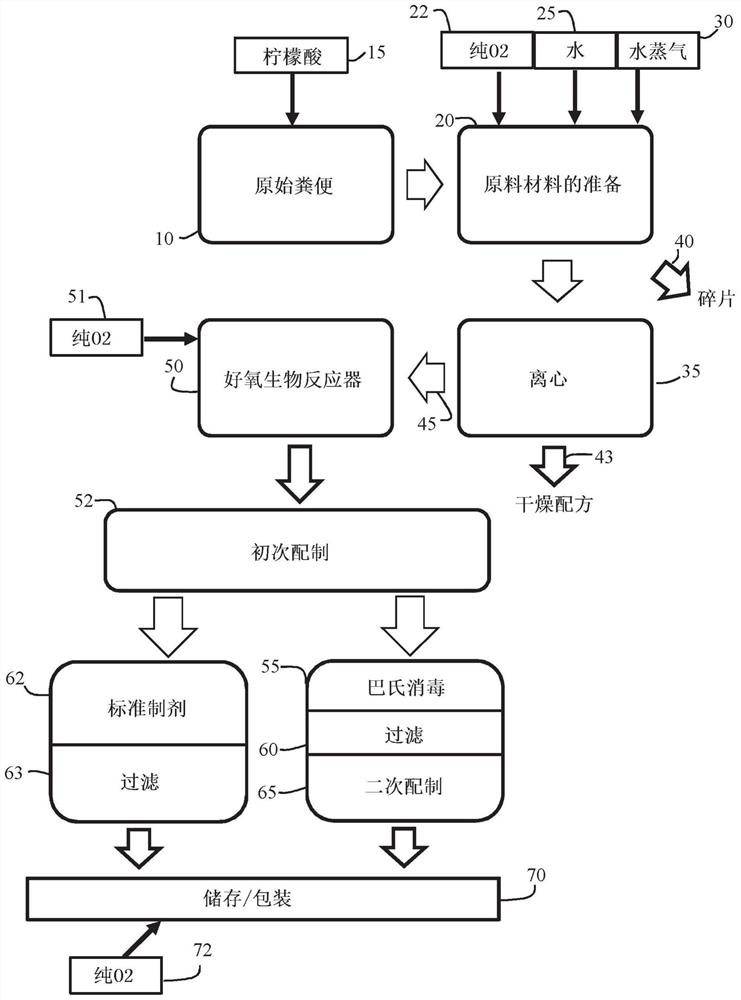
[0143] figure 1 Embodiments of the production methods described herein for the production of liquid and solid compositions from chicken manure are depicted in . figure 1 The production method depicted in produces a pathogen-free product that preserves the macro- and mesonutrients as well as micronutrients present in the manure of layer hens. In addition, the methods described herein remove potentially problematic phosphorus and hydrogen sulfide from the product.
[0144] Such as figure 1 As shown in , the process begins at 10 when raw chicken manure is transported directly from the farm to the site in a covered locker trailer. The trucks are unloaded into the mixing tank at said location and mixed with citric acid 15 and water to form a homogeneous slurry. Citric acid binds the natural organic ammonia in raw stool.
[0145]The next step in the method involves the preparation of...
Embodiment 2
[0167] Example 2. Bioreactor Kinetics During ATAB
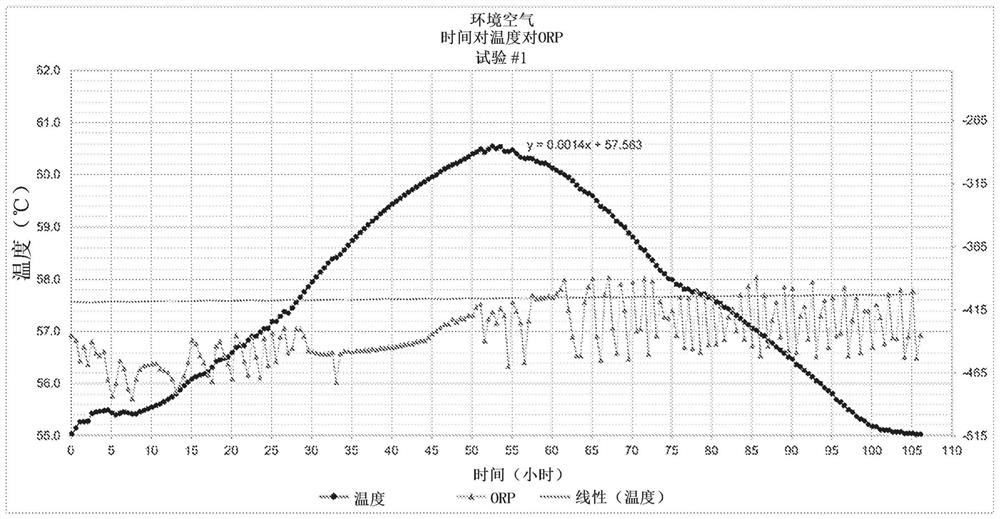
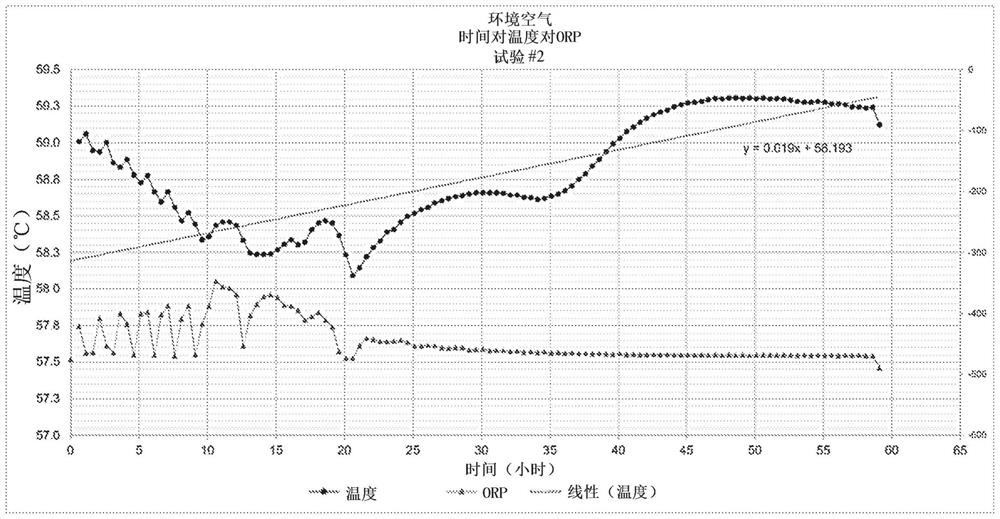
[0168] The rate of organic matter decomposition during ATAB is adversely affected by increased foaming in the bioreactor, which interferes with oxygen supply. Insufficient oxygen supply to the liquid stream during ATAB makes less oxygen available and reduces the efficiency of organic matter decomposition. Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) can be used to measure the efficiency of oxygen delivery resulting in increased oxidation of compounds in the liquid stream and decreased ORP value. Therefore, ORP can be used to measure the decomposition kinetics of organic matter in bioreactors.
[0169] To compare the ATAB kinetics of pure oxygen compared to atmospheric oxygen, a bioreactor delivered with pure oxygen was compared to, for example, ambient air. Five separate ATABs (see 3A-3E) for 80-90 hours were performed in a bioreactor equipped with 2 micron sintered stainless steel spargers injecting pure oxygen into the liquid stre...
Embodiment 3
[0174] Example 3. Bioreactor foam generation during ATAB
[0175] Foam levels generated during ATAB performed in bioreactors utilizing atmospheric oxygen delivery were compared to those generated in bioreactors using the pure or enriched oxygen delivery systems disclosed herein. The liquid fertilizer production method was performed on two different bioreactor oxygen delivery systems. In Process A, the production method was carried out as described in Example 1. Two bioreactors were used sequentially to promote the ATAB. Each bioreactor in Process A was equipped with 2 micron sintered stainless steel spargers that injected pure oxygen into the liquid stream at a rate of 1.0 CFM / 1,000 gallons. In Process B, each of the bioreactors was equipped with jet aeration to supply ambient air to the liquid stream. As shown in Table 8, delivery of pure oxygen significantly reduced foam levels in the bioreactor compared to ambient air delivery.
[0176] Table 8. Bioreactor Foam Levels
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com