Method for rapidly repairing damage of directly-buried cable
A cable and damage technology, which is applied in the field of rapid repair of direct buried cable damage, can solve the problems of damaged cable structure, slow repair timeliness, and high repair cost, and achieve the effects of low cost, originality, and electrical insulation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0080] The first embodiment of the present invention is directed to a method of rapid repairing straight buried cables, including:
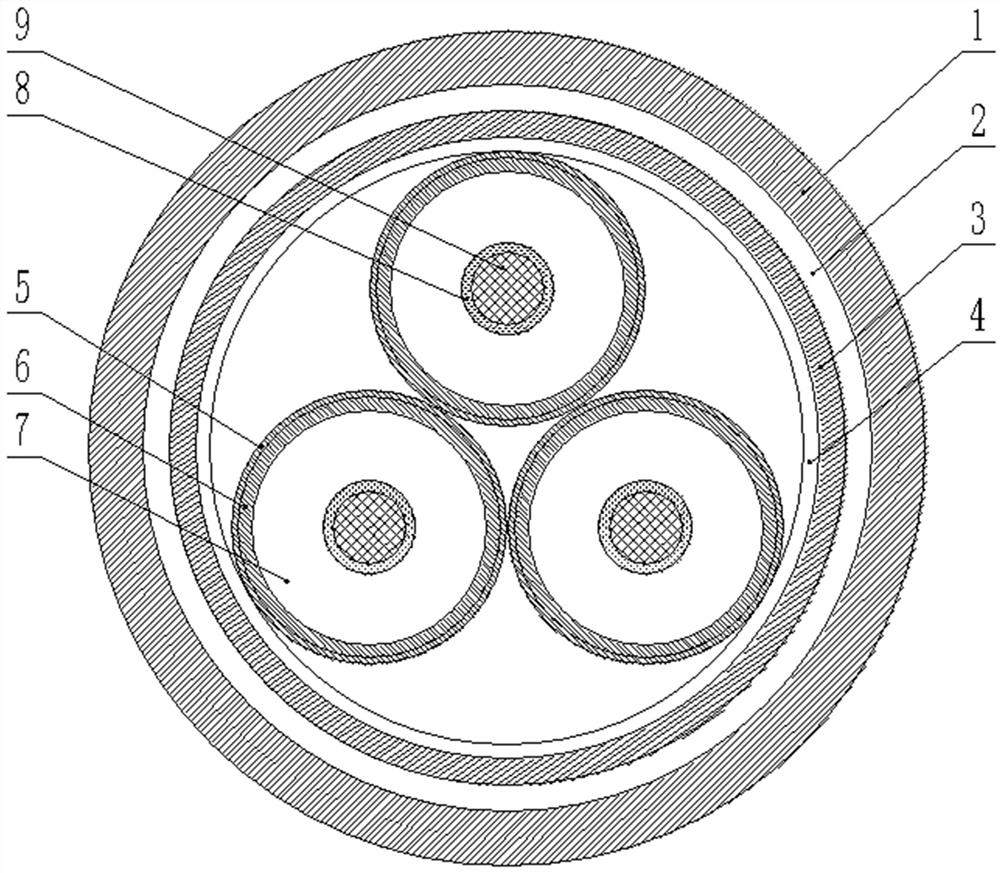
[0081] Find a fault point and excavate, determine the degree of damage to the cable, if it is damaged to the cable master insulation, then repair the original cable and does not cause the intermediate connector to repair damage; if only the outer surface of the cable outer sheath 1 is scratched, then Repair the scratches.
[0082] When the cable is only damaged by the outer sheath, there is no need to damage the original body structure of the cable, it is necessary to repair the outer sheath of the cable outer sheath to prevent water and moisture from entering the cable to cause the cable insulation.
[0083] When the cable is damaged to the main insulation, there is no need to cut the cable, simply repair the damaged phase insulation to prevent water and moisture from entering the cable to cause the cable insulation.
[0084] Compared with the origi...
no. 2 approach
[0086] If it is damaged to the cable master insulation, the damage is repaired under the premise of retaining the original cable and does not produce an intermediate joint, including:
[0087] S101. Find the fault point, center, excavate the trench, mount the bracket for supporting the cable in the trench, confirm that it is broken to the cable master insulation, carry out Next;
[0088] S102. Clean cable damage area and the damage area around the damaged area, remove sand and debris, wipe it with cleaning towel, stand dry;
[0089] S103. External sheath 1 surface graphite conductive coating is formed using a glass blade to scrape the damage area and the damage area.
[0090] The length of the damage area is: cover the damaged area;
[0091] The scraping length of the intact region around the damage area is: the left end of the damage area is the starting point, and the length of 400 mm is scraped to the left, and the right end of the damage area is the starting point, and the len...
no. 3 approach
[0126] In this embodiment, it is directed to a method of rapidly repairing a straight buried cable, and if only the outer surface of the cable outer sheath 1 is scratched, the scratches are repaired, including:
[0127] S201. Find a fault point and excavate, confirm that only the cable outer sheath 1 is damaged, and the next step;
[0128] S202. Cleaning the surface of the cable outer sheath 1;
[0129] S203. Judging the degree of damage of cable outer sheath 1, confirming that the insulating layer is not damaged, carrying the next step;
[0130] S204. Treatment of a good area around the damaged area and cleans the hair area;
[0131] S205. Clearing the graphite conductive coating around the damaged area and cleaned;
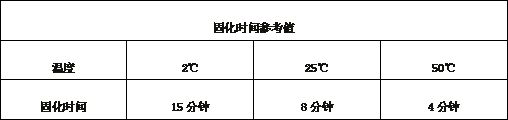
[0132] S206. Using high-pressure waterproof insulating composite tape with semi-winding method to uniformly winding the damage area and surrounding area, as a primary guard layer;
[0133] S207. Using a polytetrafluoride with a semi-winding method to uniformly wind ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com