Unsupervised clustering method and system for metagenome contigs
An unsupervised clustering and metagenomics technology, applied in the unsupervised clustering method and system field of metagenomic contigs, can solve problems affecting algorithm performance, limited effect, and large number of strains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] This embodiment provides a method for unsupervised clustering of metagenomic contigs, including steps:
[0078] S1. Assemble multiple reads into contigs by overlapping fragments;
[0079] S2. Calculate the frequency and abundance of the quadruplet oligonucleotides of the contigs using the eigenvectorization method to obtain the frequency and abundance of the quadruplet oligonucleotides of the contigs;
[0080] S3. Set the initial number of species K in the K-means algorithm 1 , and randomly select K 1 contigs as the initial cluster center;
[0081] S4. Calculate K according to the frequency and abundance of quadruple nucleotides obtained from contigs 1The probability of each contigs in the contigs to each cluster center, and assign each contigs to the cluster center with the highest probability among the calculated probabilities;
[0082] S5. Update the cluster center using the sample mean of each cluster;
[0083] S6. Repeat steps S4-S5 until the cluster center no...
Embodiment 2
[0126] This example provides an unsupervised clustering method for metagenomic contigs. The difference from Example 1 is that:
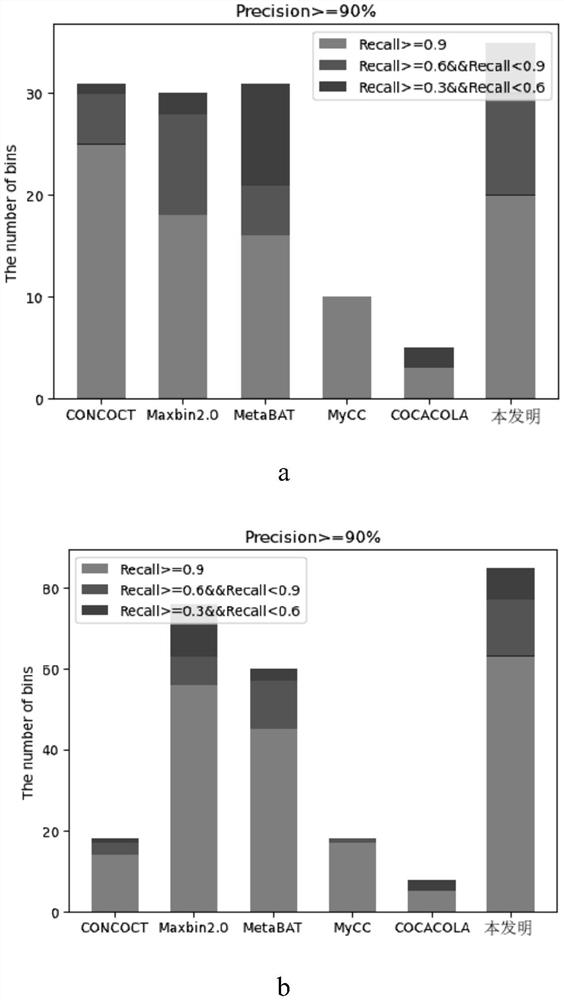
[0127] In this embodiment, the method of the present invention is tested on three data sets of different complexity, and compared with other state-of-the-art clustering tools CONCOCT, Maxbin2.0, MetaBAT, MyCC, and COCACOLA on the same data set.
[0128] The data adopts the simulation data set specially used for benchmarking in the CAMI paper, which is generated in order to have a unified evaluation standard for each clustering algorithm. It is divided into low-complexity datasets (40 genomes and 20 circular elements), medium-complexity datasets (132 genomes and 100 circular elements), and high-complexity datasets (596 genomes and 478 Circular Elements), these datasets are from newly sequenced approximately 700 microbial isolates and 600 circular element genomes that differ from the strain, species, genus, or sequence represented by the public genomes...
Embodiment 3
[0136] This embodiment provides an unsupervised clustering system for metagenomic contigs, including:
[0137] The assembly module is used to assemble multiple reads into contigs by overlapping fragments;
[0138] The first calculation module is used to calculate the frequency and abundance of the quadruple oligonucleotides of the contigs by using the eigenvectorization method to obtain the frequency and joint abundance of the quadruple nucleotides of the contigs;
[0139] Selection module, used to set the initial number of species K in the K-means algorithm 1 , and randomly select K 1 contigs as the initial cluster center;
[0140] The second calculation module is used to calculate K according to the obtained quadruple nucleotide frequency and abundance of contigs 1 The probability of each contig in the contigs to each cluster center, and assign each contig to the cluster center with the highest probability among the calculated probabilities;
[0141] An update module for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com