Certificateless threshold signcryption method under secret sharing mechanism
A secret sharing mechanism, certificateless technology, applied in the field of network information security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
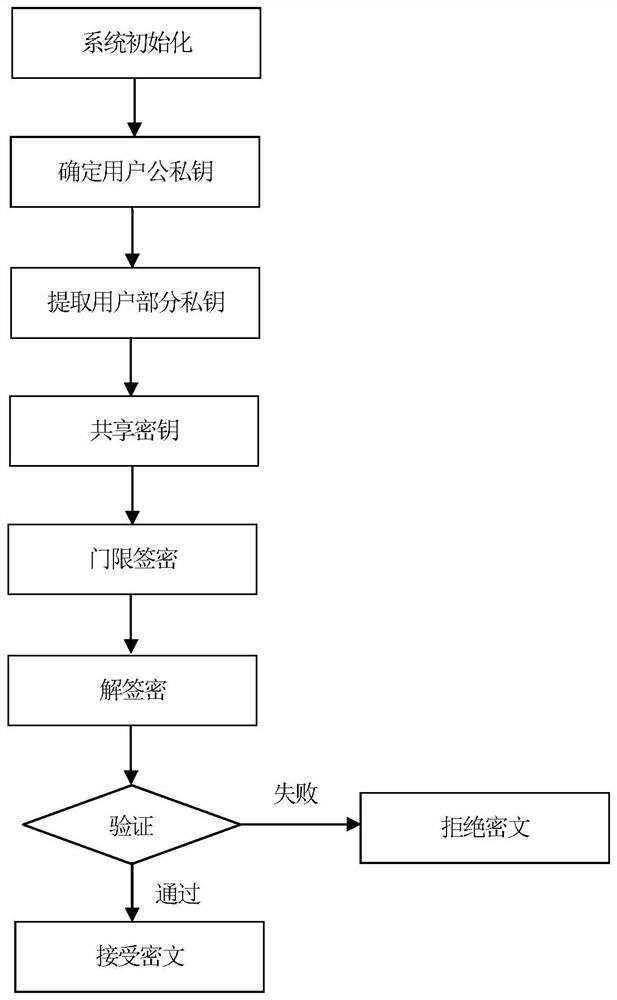
[0075] A large prime number q selected by the key generation center, q is 2 192 -2 64 -1 as an example, such as figure 1 As shown, the steps of the certificateless threshold signcryption method under the secret sharing system in this embodiment are as follows:
[0076] A. System initialization
[0077] (A1) The key generation center selects a large prime number q of k bits, and this embodiment adopts q as 2 192 -2 64 -1, k is a security parameter, a finite positive integer, set G 1 and G 2 are two q factorial cyclic groups, e is G 1 ×G 1 →G 2 is a bilinear map.
[0078] (A2) The key generation center selects three cryptographically secure hash functions H 1 、H 2 、H 3 :H 1 :{0,1} * ×G 1 ×G 1 →G 1 , H 2 :G 1 ×G 1 →{0,1} λ , H 3 :{0,1} λ ×G 1 3 ×G 2 → Z q * , where λ represents the message length, Z q * means {1,2,...,2 192 -2 64 -2}, {0,1} * Represents an identity of arbitrary length consisting of 0 and 1, {0,1} λ Represents a message of length ...
Embodiment 2
[0142] A large prime number q selected by the key generation center, q is 2 224 -2 96 +1 as an example, the steps of the non-certificate threshold signcryption method under the secret sharing mechanism of this embodiment are as follows:
[0143] A. System initialization
[0144] (A1) The key generation center selects a large prime number q of k bits, and this embodiment adopts q as 2 224 -2 96 +1, k is a security parameter, a finite positive integer, set G 1 and G 2 are two q factorial cyclic groups, e is G 1 ×G 1 →G 2 is a bilinear map.
[0145] (A2) The key generation center selects three cryptographically secure hash functions H 1 、H 2 、H 3 :H 1 :{0,1} * ×G 1 ×G 1 →G 1 , H 2 :G 1 ×G 1 →{0,1} λ , H 3 :{0,1} λ ×G 1 3 ×G 2 → Z q * , where λ represents the message length, Z q * means {1,2,...,2 224 -2 96}, {0,1} * Represents an identity of arbitrary length consisting of 0 and 1, {0,1} λ Represents a message of length λ consisting of 0s and 1s, H...
Embodiment 3
[0153] A large prime number q selected by the key generation center, q is 2 256 -2 224 +2 192 +2 96 +1 as an example, the steps of the non-certificate threshold signcryption method under the secret sharing mechanism of this embodiment are as follows:
[0154] A. System initialization
[0155] (A1) The key generation center selects a large prime number q of k bits, and this embodiment adopts q as 2 256 -2 224 +2 192 +2 96 +1, k is a security parameter, a finite positive integer, set G 1 and G 2 are two q factorial cyclic groups, e is G 1 ×G 1→G 2 is a bilinear map.
[0156] (A2) The key generation center selects three cryptographically secure hash functions H 1 、H 2 、H 3 :H 1 :{0,1} * ×G 1 ×G 1 →G 1 , H 2 :G 1 ×G 1 →{0,1} λ , H 3 :{0,1} λ ×G 1 3 ×G 2 → Z q * , where λ represents the message length, Z q * means {1,2,...,2 256 -2 224 +2 192 +2 96}, {0,1} * Represents an identity of arbitrary length consisting of 0 and 1, {0,1} λ Represents a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com