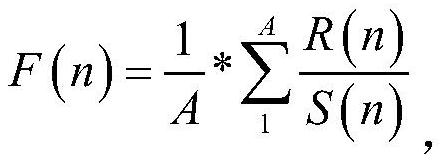Method for predicting remaining useful life of lithium ion battery based on long-correlation fractional order degradation model
A lithium-ion battery, effective life technology, applied in forecasting, data processing applications, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome forecasting steps, narrow application range, low forecasting accuracy, etc. The effect of a wide range and large economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0045] A method for predicting the remaining useful life of a lithium-ion battery based on a long-term correlation fractional-order degradation model provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
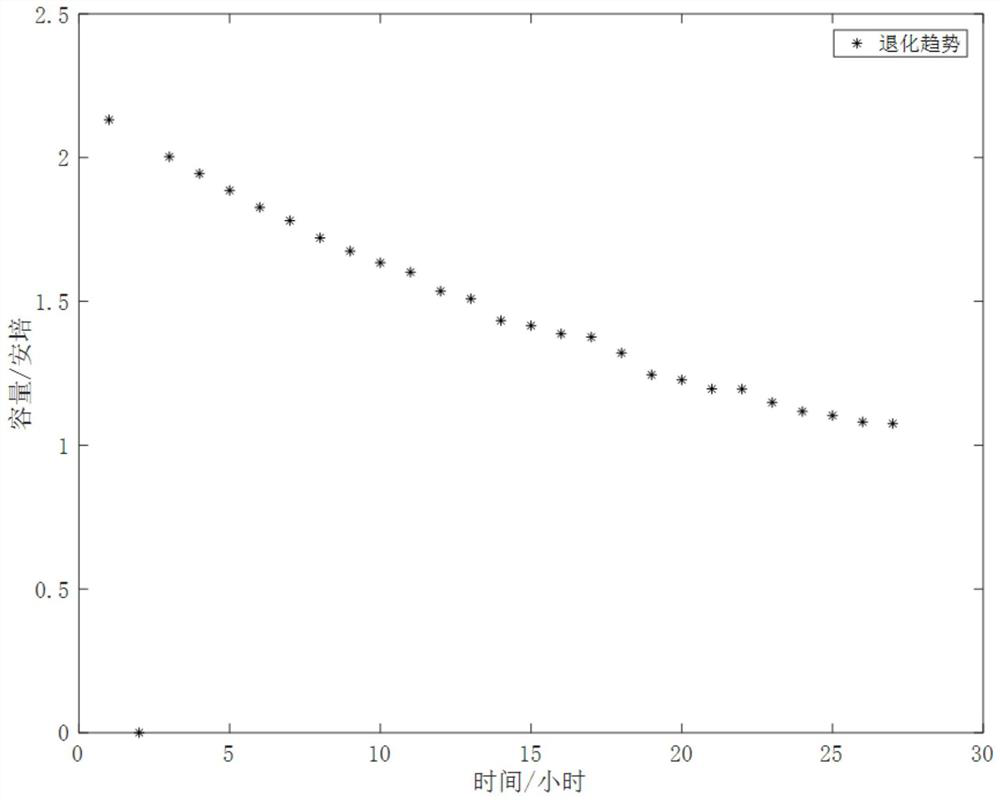
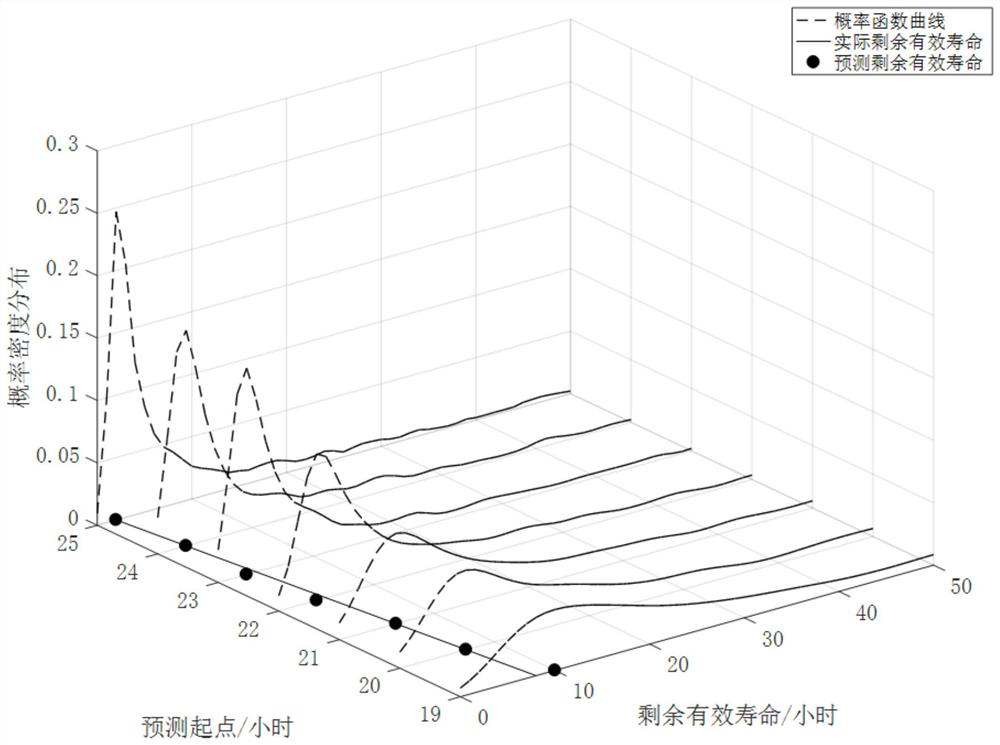
[0046] S1, obtain the historical degradation data of lithium-ion battery capacity (such as figure 1 shown) as the predicted input sequence {X t : t=1,2,...}: In this embodiment, the degradation data before the capacity degradation to 1.3A is selected as the prediction input sequence. In this embodiment, the degradation data of the lithium battery capacity used comes from NASA AI Ames database (NASA AmesPrognostics Data Repository) lithium battery open source data set;
[0047] S2. Using the rescaled range analysis method and the characteristic function method to calculate the estimated value of the Hurst exponent H and the characteristic index α of the predicted input sequence, the specific operations are as follows:
[0048] S21. Use the rescaled rang...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com