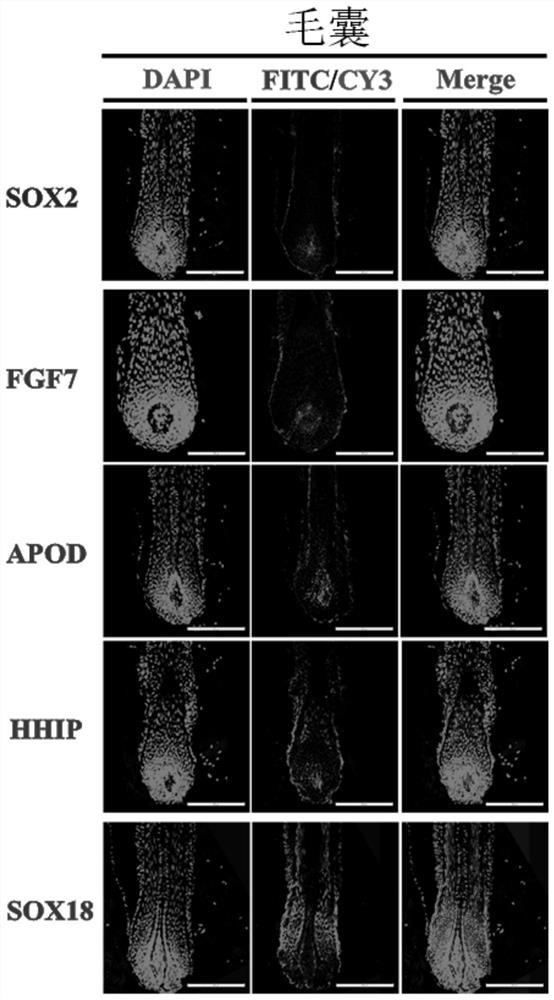
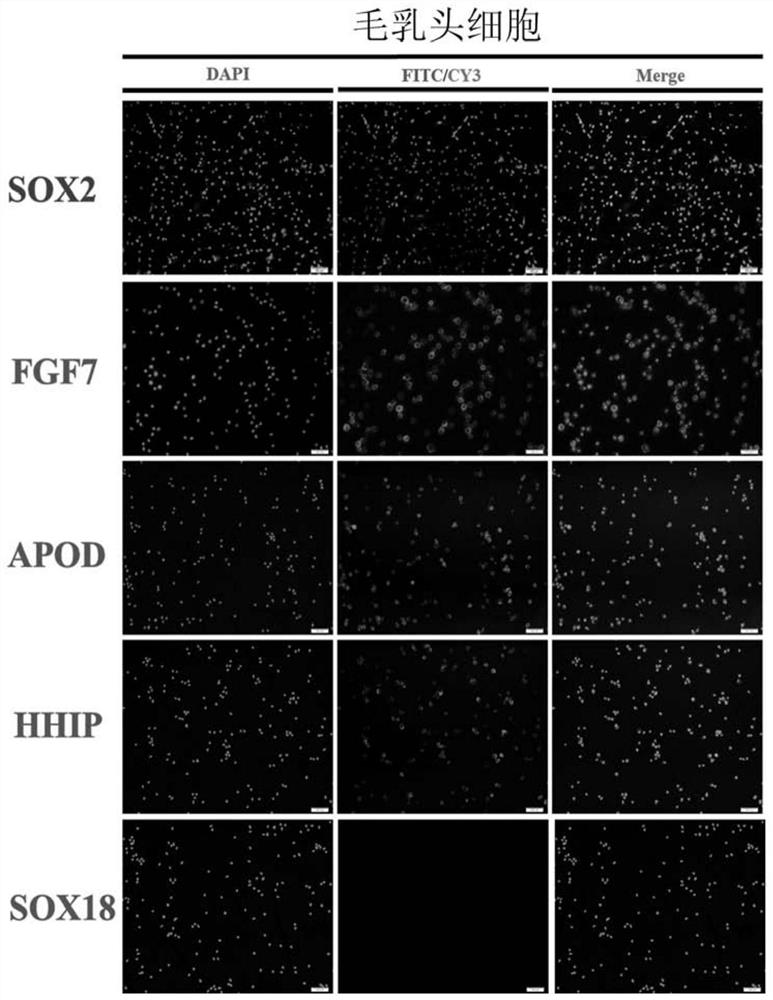
Separation and identification method of dermal papilla cells of cashmere goats
A technology of hair papilla cells and identification methods, which is applied in the field of identification and separation of cashmere hair papilla cells, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory identification results of DP cells, and achieve accurate identification results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0037]1. Isolation of cashmere goat DP cells: cut the dorsal skin tissue of the cashmere goat scapula, and repeatedly wash the skin tissue with PBS solution containing 1% (w / v) double antibodies (penicillin, streptomycin) to remove surface stains . Afterwards, they were placed in DMEM / F12 medium containing 1% (w / v) penicillin and streptomycin, and transported on ice to an ultra-clean working environment. After entering the ultra-clean workbench, use ophthalmic forceps to remove residual blood stains and impurities on the skin tissue, and brush the tissue sample with DMEM / F12 medium containing 1% penicillin and streptomycin. Subsequently, the skin tissue was cut into long strips along the growth direction of the hair follicle with a scalpel, with a thickness of about 2-3 mm, and the tissue was washed again with DMEM / F12 medium containing 1% (w / v) penicillin and streptomycin.
[0038] The skin tissue was transferred to 2 mg / mL collagenase solution and digested in a constant tem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com