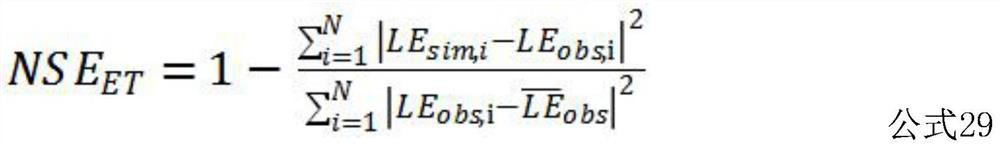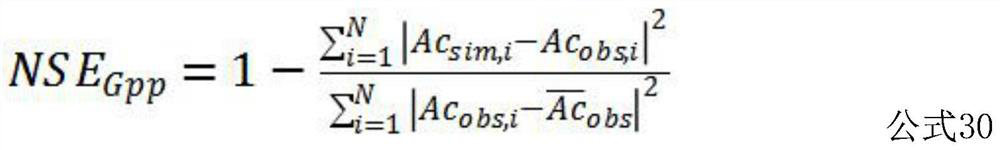Surface water, heat and carbon flux coupling estimation method based on remote sensing information
A surface water and carbon flux technology, applied in the field of remote sensing, can solve the problems of large differences in photosynthesis, without considering the influence of soil moisture, and without simultaneously estimating the sensible heat flux of the surface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0111] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
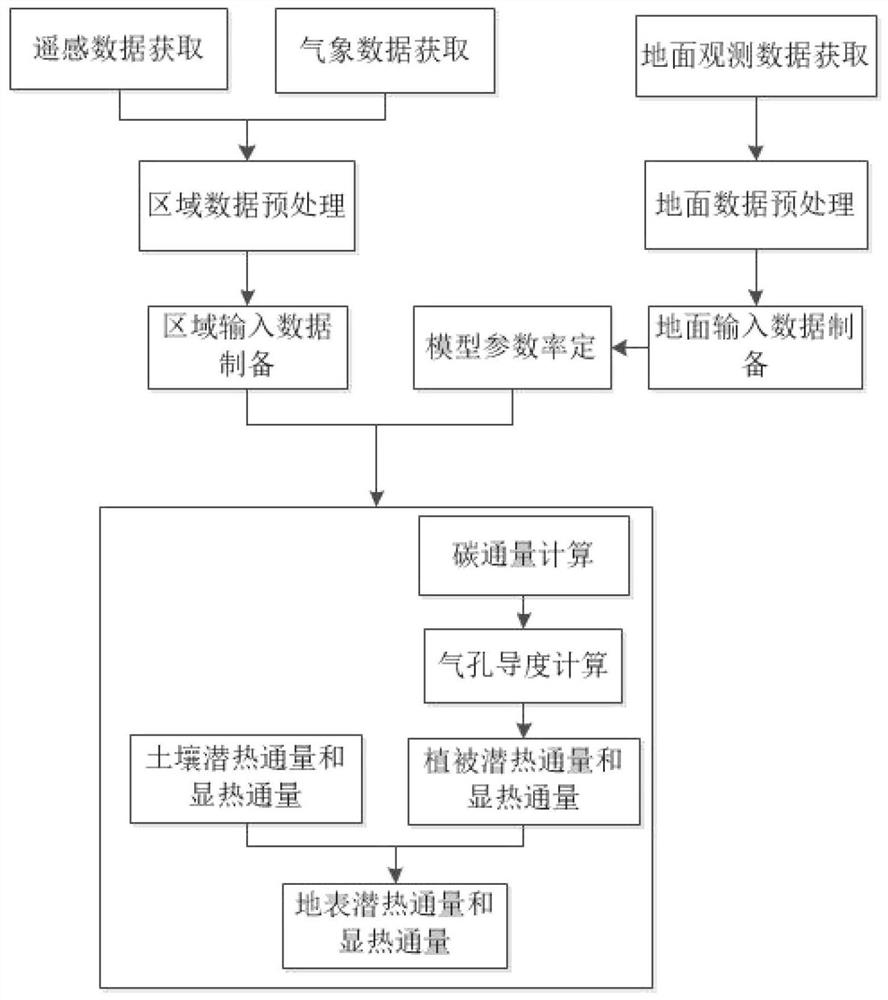
[0112] figure 1 A coupled estimation method of surface water, heat and carbon fluxes based on remote sensing information is shown. The steps of the method include:
[0113] Step S1, acquisition of ground observation data;
[0114] Obtain the daily average surface net radiation Rn, surface albedo σ, air temperature Ta, wind speed u of all surface flux observation stations in the study area m , air vapor pressure e a , Atmospheric CO 2 Concentration Ca, soil moisture SW; obtain the daily total photosynthetically active radiation PAR, latent heat flux LE and GPP; obtain the canopy height h of the day c , leaf diameter s, leaf area index LAI, stem area index SAI; determine the underlying surface type of the station according to the land cover / land use category of IGBP, saturated soil moisture SW s and withering coefficient SW min ; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com