Electric working machine
A working machine, electric technology, applied in the direction of electric vehicles, current collectors, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as time lag, impossible communication between electric working machines and external equipment, and reduced sense of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0058] [1-1. Overall structure]
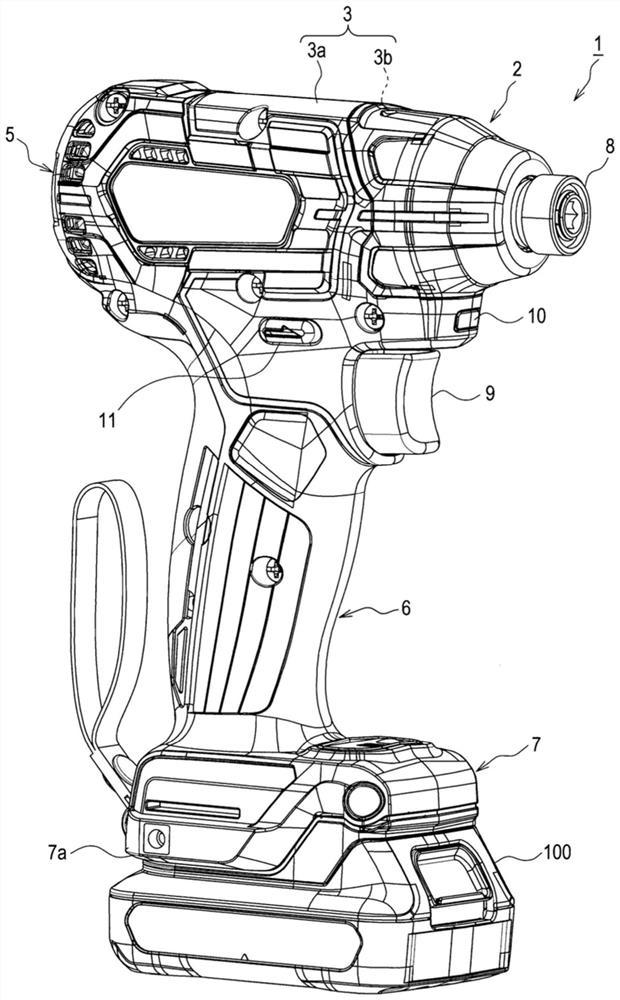
[0059] figure 1 The illustrated electric working machine 1 is configured as a cordless hammer drill, for example. The cordless hammer drill is driven by electric power supplied from the battery pack 100 described later. The cordless hammer drill is used, for example, to rotate fastening components such as screws and bolts. The cordless hammer drill is configured to apply an impact in the rotation direction according to the load when the fastening member is rotated, and thereby can generate a large torque in the rotation direction.
[0060] Such as figure 1 As shown, the electric working machine 1 of this embodiment includes a main body 2 and a battery pack 100. The battery pack 100 is configured to be detachable from the main body 2.
[0061] The main body 2 includes a housing 3. The housing 3 is provided with two split housings 3a, 3b divided into left and right, and is constructed by combining these split housings 3a, 3b. The housing 3 may be ...
no. 2 approach
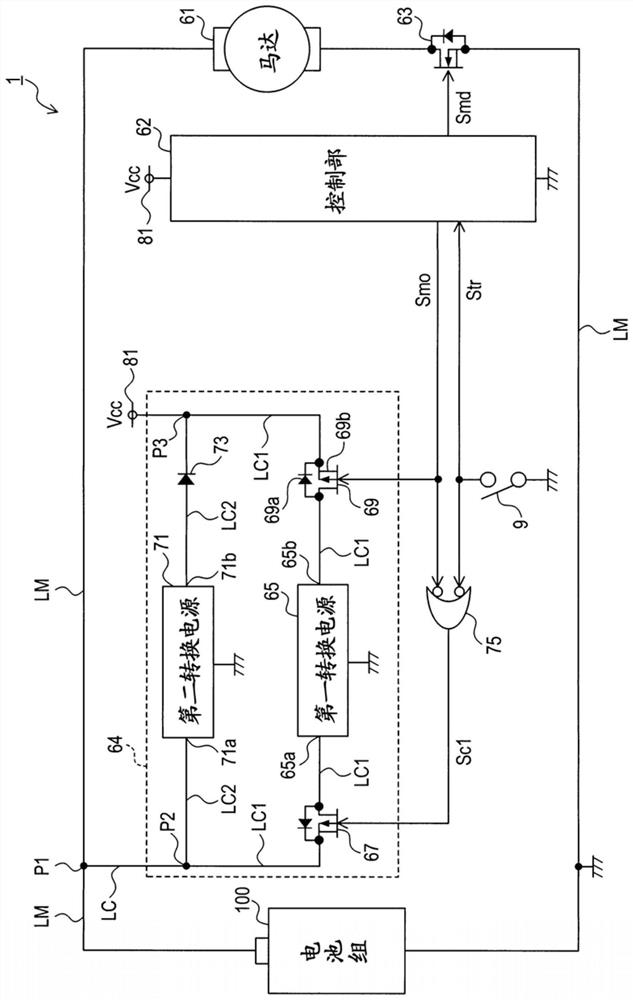
[0117] As a second embodiment, a second electric working machine 21 constructed by replacing a part of the constituent elements of the electric working machine 1 of the above-mentioned embodiment (hereinafter also referred to as the first embodiment) will be described.
[0118] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the second electric working machine 21 is configured by replacing the power supply 64 for the control unit, the motor 61, and the motor drive unit 63 in the electric working machine 1 with the power supply 91 for the second control unit, the brushless motor 97, and the motor driver, respectively. 99.
[0119] [2-1. Power supply for the second control unit]
[0120] The power supply 91 for the second control unit is configured to include a third conversion power supply 93 and a fourth conversion power supply 95 instead of the first conversion power supply 65 in the power supply 64 for the control unit.
[0121] The third conversion power source 93 includes a DC-DC converter that conve...
no. 3 approach
[0145] As a third embodiment, a third electric working machine 23 constructed by substituting some constituent elements in the second electric working machine 21 of the second embodiment will be described.
[0146] Such as Image 6 As shown, the third electric working machine 23 is configured to replace the power supply 91 for the second control unit in the second electric working machine 21 with the power supply 111 for the third control unit.
[0147] [3-1. Power supply for the third control unit]
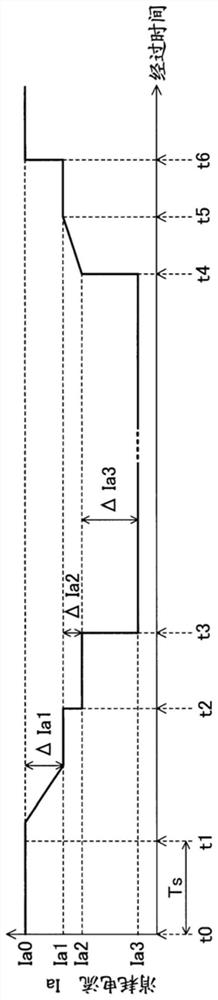
[0148] The third control unit uses the power supply 111 to voltage-convert the battery voltage VB from the battery pack 100 and outputs the voltage-converted constant voltage Vcc to the constant voltage supply line 81. The constant voltage Vcc is supplied to each part (control unit 62 and the like) of the third electric working machine 23 via the constant voltage supply line 81. In the third embodiment, the constant voltage Vcc is 5V. The power supplied from the third control unit pow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com