Fourier mode-locked laser device
A technology of mode-locked lasers and optical beam splitters, which is applied in the field of lasers and can solve problems such as poor laser coherence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
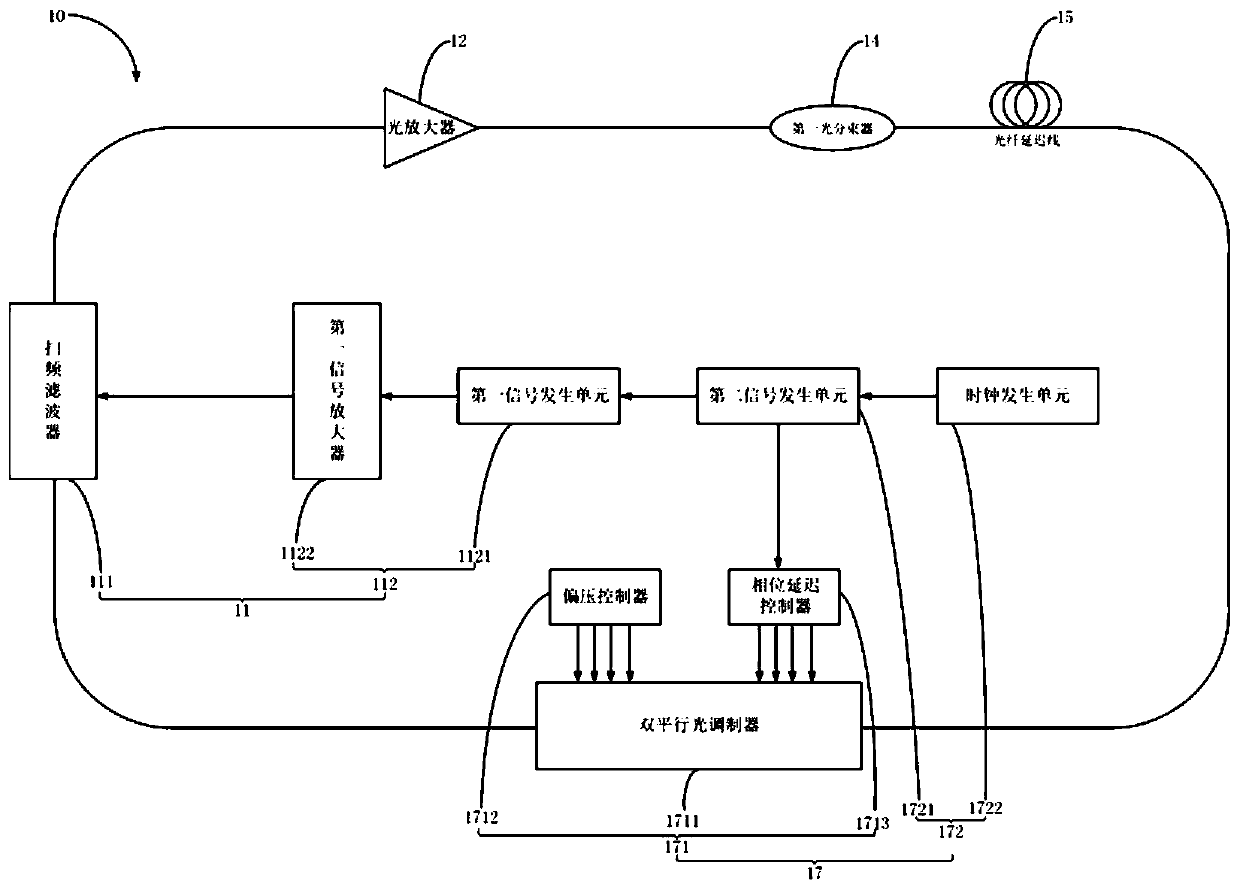
[0091] This embodiment designs a method of using a signal generator to generate RF signals to control the frequency shift of the carrier-suppressed single-sideband modulator, thereby compensating for the frequency shift of the Fourier mode-locked laser 10 due to scattering, nonlinearity, etc., and improving the instantaneous output of the laser. Linewidth (i.e. coherence length). The Fourier mode-locked laser 10 includes a filter module 11, a second optical isolator 18, an optical amplifier 12, a first optical isolator 13, a first optical beam splitter 14, a fiber delay line 15, and a polarization controller arranged in sequence along the circular optical path. 16 and light modulation module 17. The filter module 11 includes a frequency sweep filter 111 and a filter control unit 112, and the frequency sweep filter 111 is connected with the optical amplifier 12; the filter control unit 112 includes a first signal generation unit 1121 and a first signal amplifier 1122, and the f...
Embodiment 2
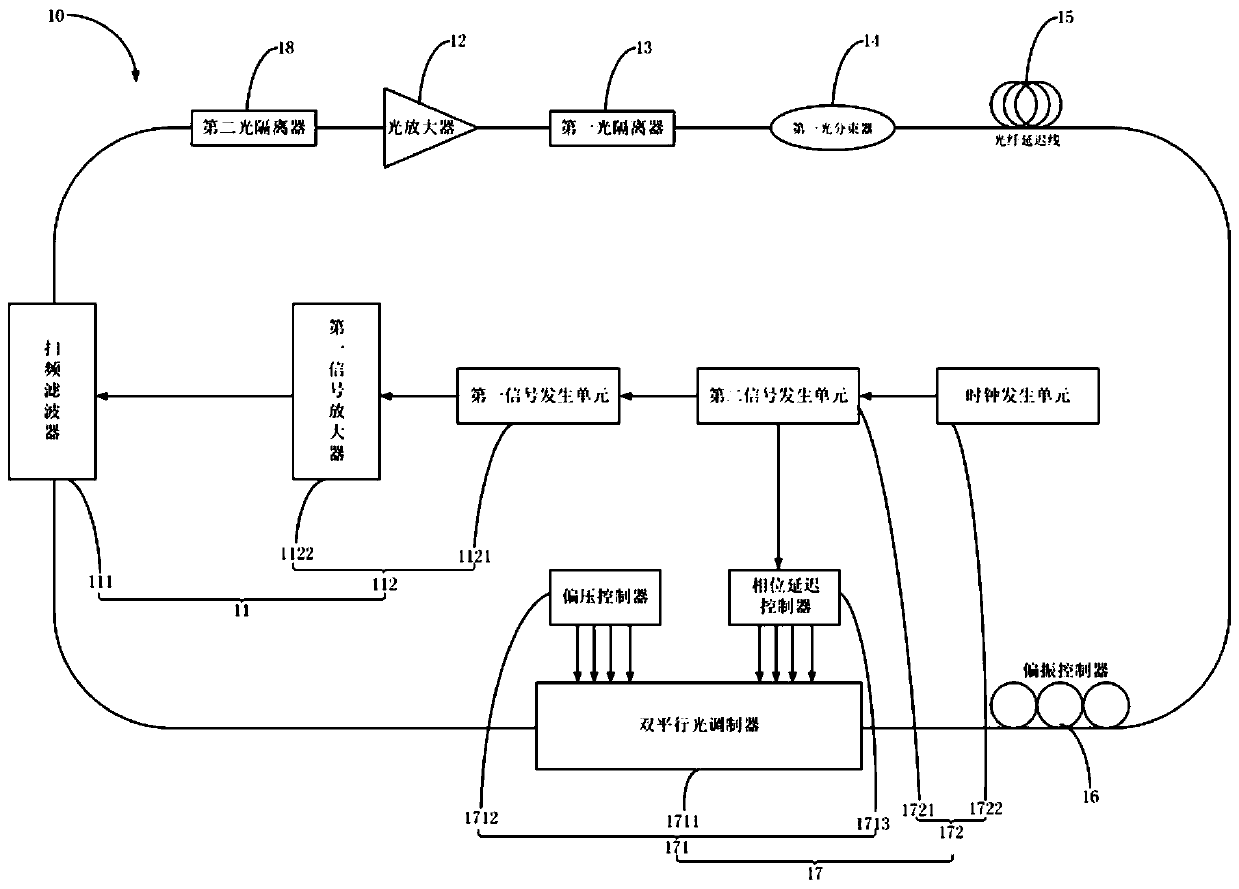
[0094] In this embodiment, a signal generator is used to generate an RF signal to control the frequency shift of the carrier-suppressed single-sideband modulator to compensate the frequency deviation of the discrete Fourier mode-locked laser, and improve the instantaneous linewidth (ie, coherence length) of the laser output. This embodiment is not limited to the continuous frequency-sweeping Fourier mode-locked laser, and is also applicable to the discrete Fourier mode-locked laser. The discrete Fourier mode-locked laser 10 based on frequency shift compensation includes a filter module 11, a second optical isolator 18, an optical amplifier 12, a first optical isolator 13, a first optical beam splitter 14, and an optical fiber arranged in sequence along the ring optical path. Delay line 15 , polarization controller 16 , optical modulation module 17 and multi-channel optical filter 19 . The filter module 11 includes a frequency sweep filter 111 and a filter control unit 112, and...
Embodiment 3
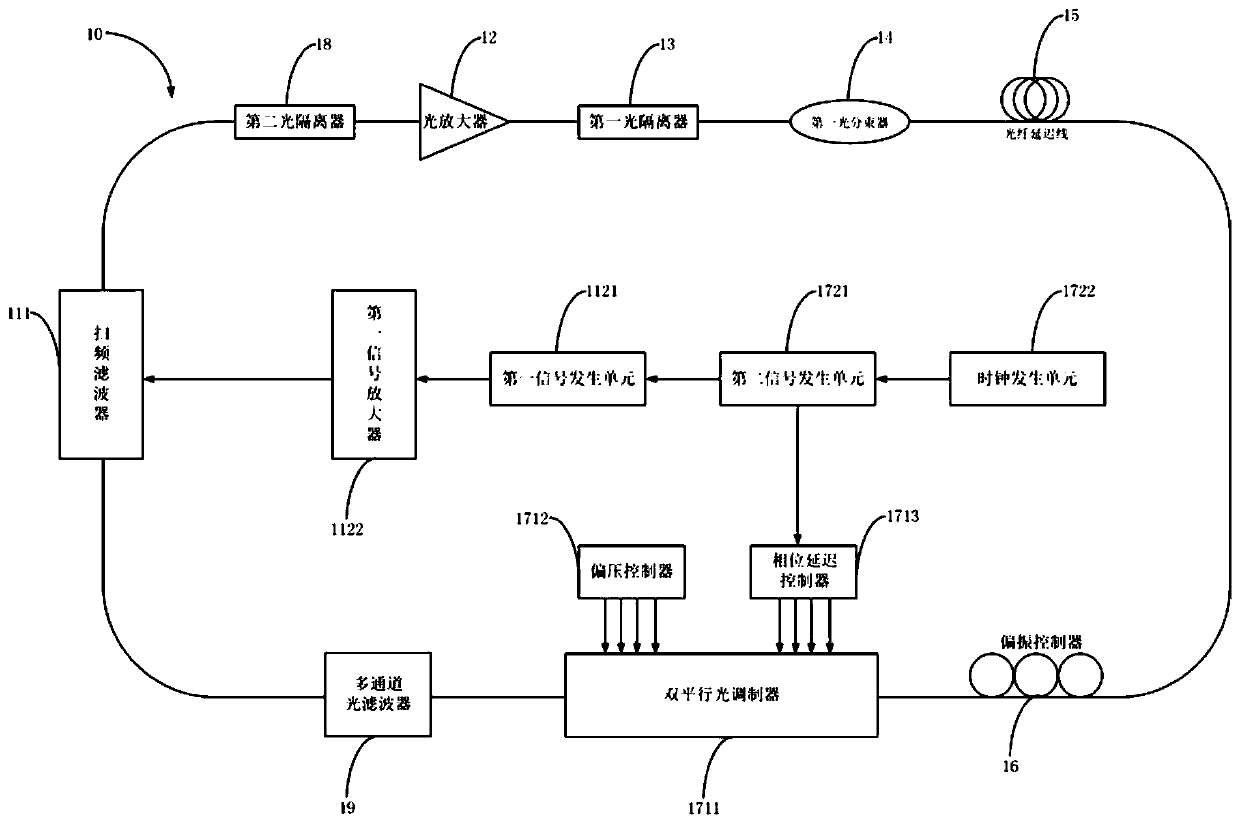
[0097] In this embodiment, a signal generator is used to generate an RF signal to control the frequency shift of the carrier-suppressed single-sideband modulator to compensate the frequency deviation of the discrete Fourier mode-locked laser, and improve the instantaneous linewidth (ie, coherence length) of the laser output. The discretization of the frequency-sweeping signal of the Fourier mode-locked laser 10 in the third embodiment is realized based on the multi-channel optical filter 19. This discretization can also be realized based on the time-domain modulation. The embodiment scheme is designed as image 3 shown.
[0098] The discrete Fourier mode-locked laser 10 based on frequency shift compensation includes a filter module 11, a second optical isolator 18, an optical amplifier 12, a first optical isolator 13, a first optical beam splitter 14, and an optical fiber arranged in sequence along the ring optical path. Delay line 15 , polarization controller 16 , light modul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com