Soft soil foundation embankment structure
A technology for soft soil foundations and embankments, which can be used in basic structure engineering, embankments, water conservancy projects, etc., and can solve problems such as overall instability of embankments, destruction of soil balance, and low cohesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
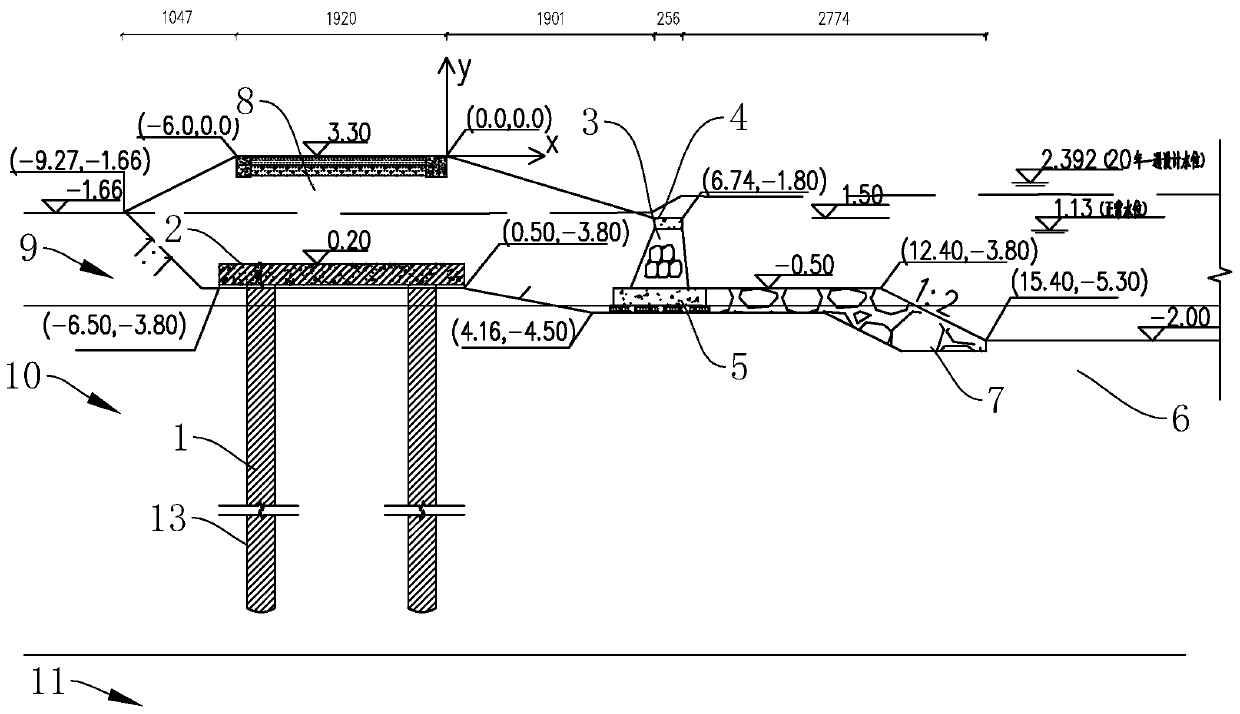
[0033] Embodiment one: if figure 1 As shown, it is a kind of soft ground embankment structure disclosed by the present invention, and it is arranged along the water bank, including pile foundation 1 arranged in the embankment soil layer, and the number of pile foundation 1 piles is one row or more rows, wherein In the present embodiment, the quantity of one pile of the pile foundation is two rows.
[0034] Further, the pile foundation 1 is Extruded piles or end-bearing piles, the pile length is 20m, and the upper end of the pile foundation 1 is poured integrally to form a foundation cap 2 with a thickness of C30600mm. The width of the foundation cap 2 is 2240mm, and the foundation cap 2 is embedded in the soil layer.
[0035] A grouting stone retaining wall 3 is arranged along the water bank, a C20 concrete topping 4 is arranged at the upper end of the retaining wall 3 , and a C25 concrete bottom plate 5 is arranged at the lower end of the retaining wall 3 . In addition, th...
Embodiment 2
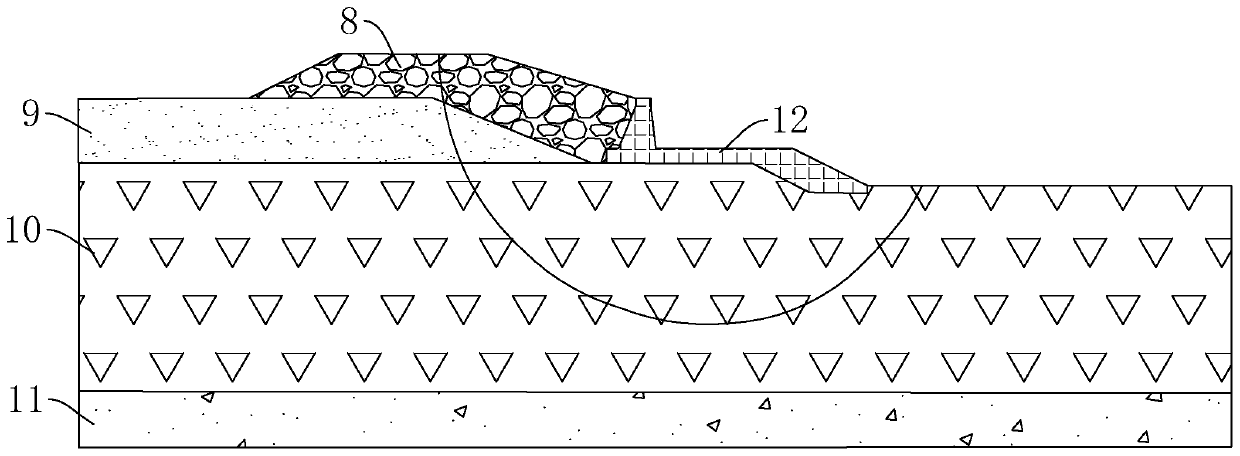
[0044] Embodiment two: if Figure 4 As shown, a soft soil foundation dike structure differs from the second embodiment in that a clay anti-seepage layer 14 is provided on the upper surface of the foundation cap 2 away from the water source. And, on the upper surface of the stone slag backfill layer 8, a embankment crest bearing layer 15 is also arranged, and the embankment crest bearing layer 15 can be a road layer for passing, while the clay anti-seepage layer 14 connects the embankment crest bearing plate and the foundation bearing up and down. station 2.
[0045]The gravel backfill layer 8 is used as the soil layer above the foundation cap 2 because the soil layer is relatively stable, so it is also difficult to deform when the gravel backfill layer 8 is subject to a larger load. But the porosity of the gravel backfill layer 8 is higher, and the water permeability is stronger, so when the water level overflows to the gravel backfill layer 8, water easily diffuses to the re...
Embodiment 3
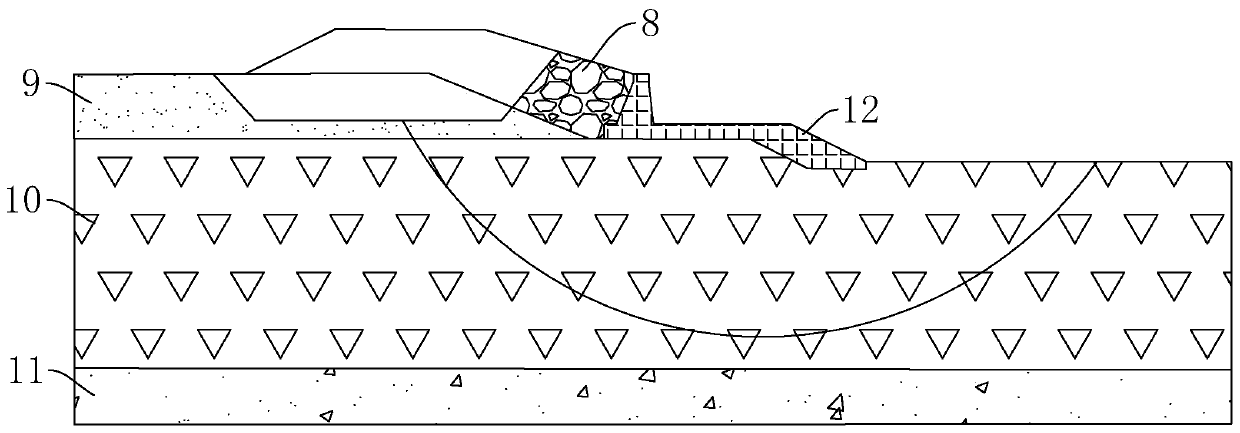
[0046] Embodiment three: as Figure 5 , 6 As shown, a soft soil foundation dike structure differs from the second embodiment in that a cement mixing pile 16 is provided in the silty clay anti-seepage layer 10 below the riprap foot guard 7 . The cement stirring piles 16 are cylindrical, and a plurality of cement stirring piles 16 are distributed in an array.
[0047] Depend on figure 2 , 3 It can be seen from the force analysis curve in the figure that the first embodiment solves the problem that the upper and lower soil layers of the foundation cap 2 are loaded, causing the soil to become unstable, which in turn leads to the overall sliding and destruction of the embankment. Although this problem is solved by setting the foundation cap 2 and the pile foundation 1 to unload the load above the foundation cap 2, thereby avoiding the direct stress of the weak soil layer below the foundation cap 2.
[0048] Such as Figure 6 It can be seen from the force analysis curve in Fig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com