Surgical instrument control method of a laparoscopic surgical robot
A surgical robot and surgical instrument technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems affecting surgical efficiency, less degrees of freedom, and attenuation of transmission power, and achieve the effect of improving surgical efficiency and reducing difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
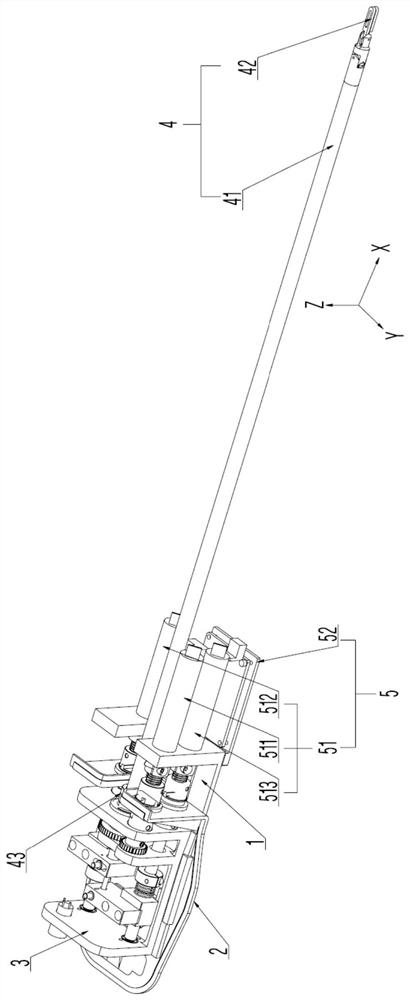
[0098] In a first embodiment of the invention, a surgical instrument 42 has a first degree of freedom (eg, an endoscope). Here, the first degree of freedom of the surgical instrument 42 means that the surgical instrument 42 can rotate around the axis of the instrument shaft 41 of the instrument connection mechanism 4 as the rotation axis (ie, along the X-axis direction). The first degree of freedom of the surgical instrument 42 can mimic the rotational motion of a human arm.
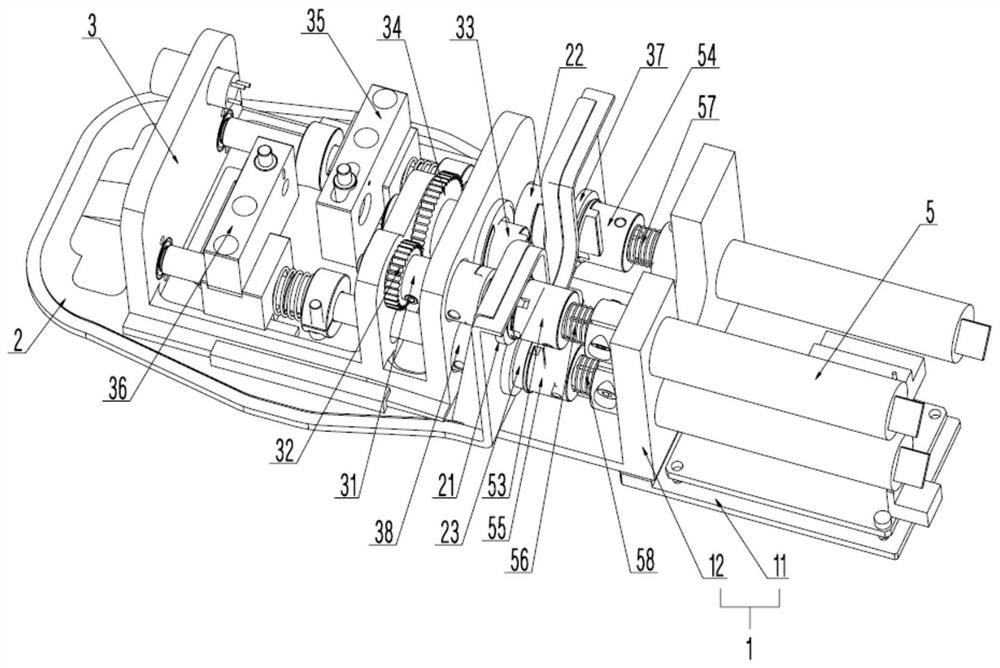
[0099] In this embodiment, the power source 51 of the driving mechanism 5 includes a first motor 511 , and the output shaft of the first motor 511 is disposed in the first hole 121 on the side wall of the fixing seat 12 of the driving seat 1 . In order to improve space utilization, the axial direction of the instrument shaft 41 , the axial direction of the first motor 511 and the length direction of the fixing seat 12 are the same.
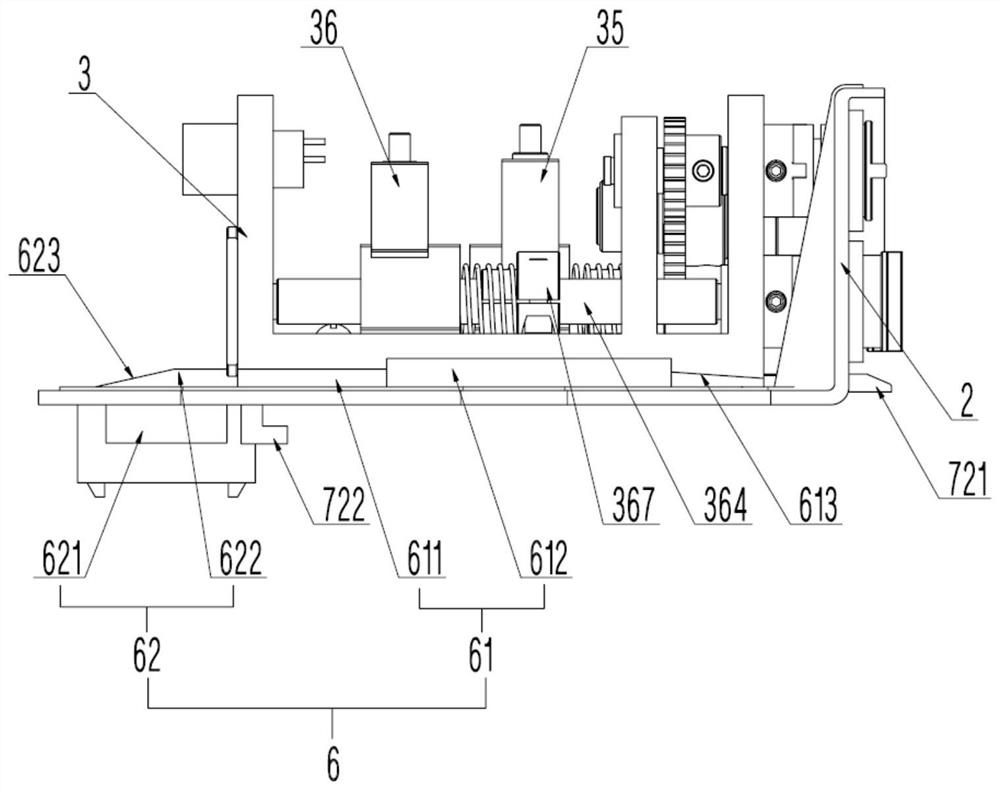
[0100] Specifically, the power transmission mode of the first motor 51...
Embodiment 2
[0124] In the second embodiment of the present invention, the surgical instrument 42 has a second degree of freedom (such as a scalpel that cuts only at designated locations). Here, the second degree of freedom of the surgical instrument 42 means that the surgical instrument 42 can be deflected around the Z-axis. The second degree of freedom of the surgical instrument 42 can imitate the deflection action of the human wrist joint.
[0125] In this embodiment, the power source 51 includes a second motor 512 , and the output shaft of the second motor 512 is disposed in the second hole 122 on the side wall of the fixing base 12 . In order to improve space utilization, the axial direction of the instrument shaft 41 , the axial direction of the second motor 512 and the length direction of the fixing seat 12 are the same.
[0126] In this embodiment, the power output by the second motor 512 is transmitted to the instrument rod 41 through the first lead screw 354 and the first seat 3...
Embodiment 3
[0155] In the third embodiment of the present invention, the surgical instrument 42 has a third degree of freedom (for example, surgical scissors that only cut at specified positions). Here, the third degree of freedom of the surgical instrument 42 means that the surgical instrument 42 can be opened and closed. The third degree of freedom of the surgical instrument 42 can imitate the closing and opening movements of human fingers.
[0156] In this embodiment, the power source 51 includes a third motor 513 , and the output shaft of the third motor 513 is disposed in the third hole 123 on the side wall of the fixing base 12 . In order to improve space utilization, the axial direction of the instrument shaft 41 , the axial direction of the third motor 513 and the length direction of the fixing seat 12 are the same.
[0157] In this embodiment, the power output by the third motor 513 is transmitted to the instrument rod 41 through the second lead screw 364 and the second seat 36 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com