Novel thrombus-taking stent and thrombus taking device comprising thrombus-taking stent
A new type of stent rod technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of easy thrombus falling off and insufficient radial support force of thrombus, and achieve the effect of improving flexibility and adherence, which is beneficial to surgical operation and judgment, and has good effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
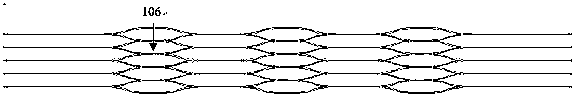
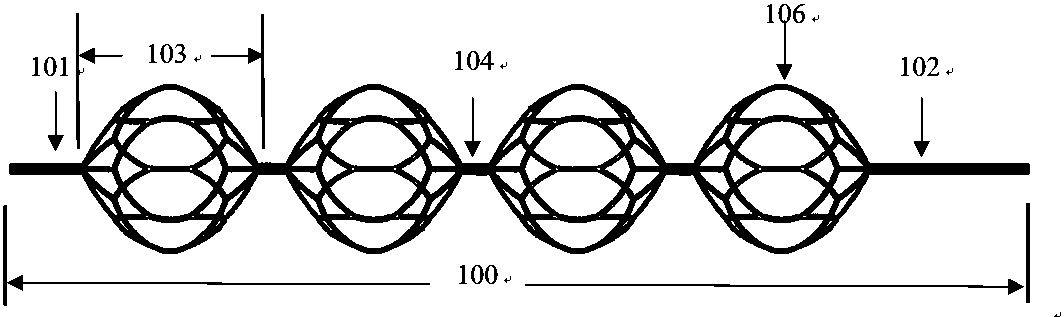
[0029] The invention provides a thrombectomy bracket, Figure 1 to Figure 3 An implementation example is given, including a self-expanding stent body 100 along its longitudinal axis and circumferential direction. The stent body 100 includes a distal region 101, a stent spherical unit 103, a stent unit node 104, a developing structure 105 and a push wire connected in sequence. 107 connected to the proximal region 102, the entire stent body 100 is an effective working section.
[0030] In this example, see image 3 , there are visualization structures 105 in the distal region 101 of the stent, the spherical unit nodes 104 and the proximal region 102 of the stent.
[0031] After the stent body 100 reaches the lesion site, the stent body 100 is pushed out from the microcatheter 200, and the stent rod 106 with the largest circumferential diameter and strong radial support force can quickly anchor the blood vessel wall and embed the thrombus, increasing the chance of thrombus captu...
Embodiment 2
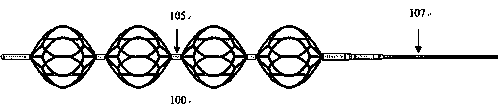
[0035] Figure 4 Embodiment 2 is shown, in which components identical or corresponding to those in Embodiment 1 are identified with reference numerals corresponding to Embodiment 1. For simplicity, only the differences between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 are described. The difference is that the imaging structure 105 is fixed on the distal end 101 of the stent, the spherical unit node 104 of the stent and the proximal end 102 of the stent in the first embodiment, and is fixed on the distal end 101 of the stent, the stent by winding. The rod 106, the stent spherical element node 104 and the wire on the proximal end 102 of the stent.
[0036] The thickness or diameter of the imaging structure is 0.02-0.15 mm, preferably 0.03-0.1 mm. This thickness setting can not only ensure that the diameter and length of the blood vessel and thrombus are clearly marked when removing the thrombus, but also save the cost of making the imaging structure to the greatest extent. Through the ray...
Embodiment 3
[0038]The present invention also provides a thrombus removal device, including the thrombus removal bracket described in any of the above embodiments, the push wire 107 is sheathed with a microcatheter 200 that can press the thrombus retrieval bracket into the interior, and the microcatheter 200 passes through the microcatheter The catheter connector is connected to the introduction sheath, and the stent body 100 is connected to the push wire 107 through physical winding, physical extrusion, medical adhesive, laser welding, polymer material fusion welding and the like. There are imaging structures distributed on the stent body 100 for real-time observation of whether the thrombus has fallen off during the capture and withdrawal process during thrombus removal, so as to guide the specific microscopic operation of thrombus removal and make thrombus removal more accurate. For the structure and working principle of the thrombectomy bracket, refer to the above-mentioned embodiments,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com